目录
AbstractStringBuilder append(String str)
String substring(int start, int end)
-
AbstractStringBuilder类简介
AbstractStringBuilder类由abstract修饰符修饰,说明此类是一个抽象类,不可被实例化,并且此类的声明用的是default默认修饰符修饰(类的定义没有任务修饰符,即为默认),代表此类只能被同一个包下的类访问,此类实现了CharSequence和Appendable两个接口,实现CharSequence接口代表此类将可以作为一个可读字符串序列,实现Appendable接口代表此类需实现内部的append方法用于追加字符序列。
abstract class AbstractStringBuilder implements Appendable, CharSequence{
}-
StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类
StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类都是AbstractStringBuilder的子类,两者差异不大,唯一的区别是StringBuilder在StringBuffer基础上对所有的方法都取消了synchronized关键词,所以StringBuilder不能在多线程中使用,但是效率更高,而StringBuffer支持多线程,不过效率较低。
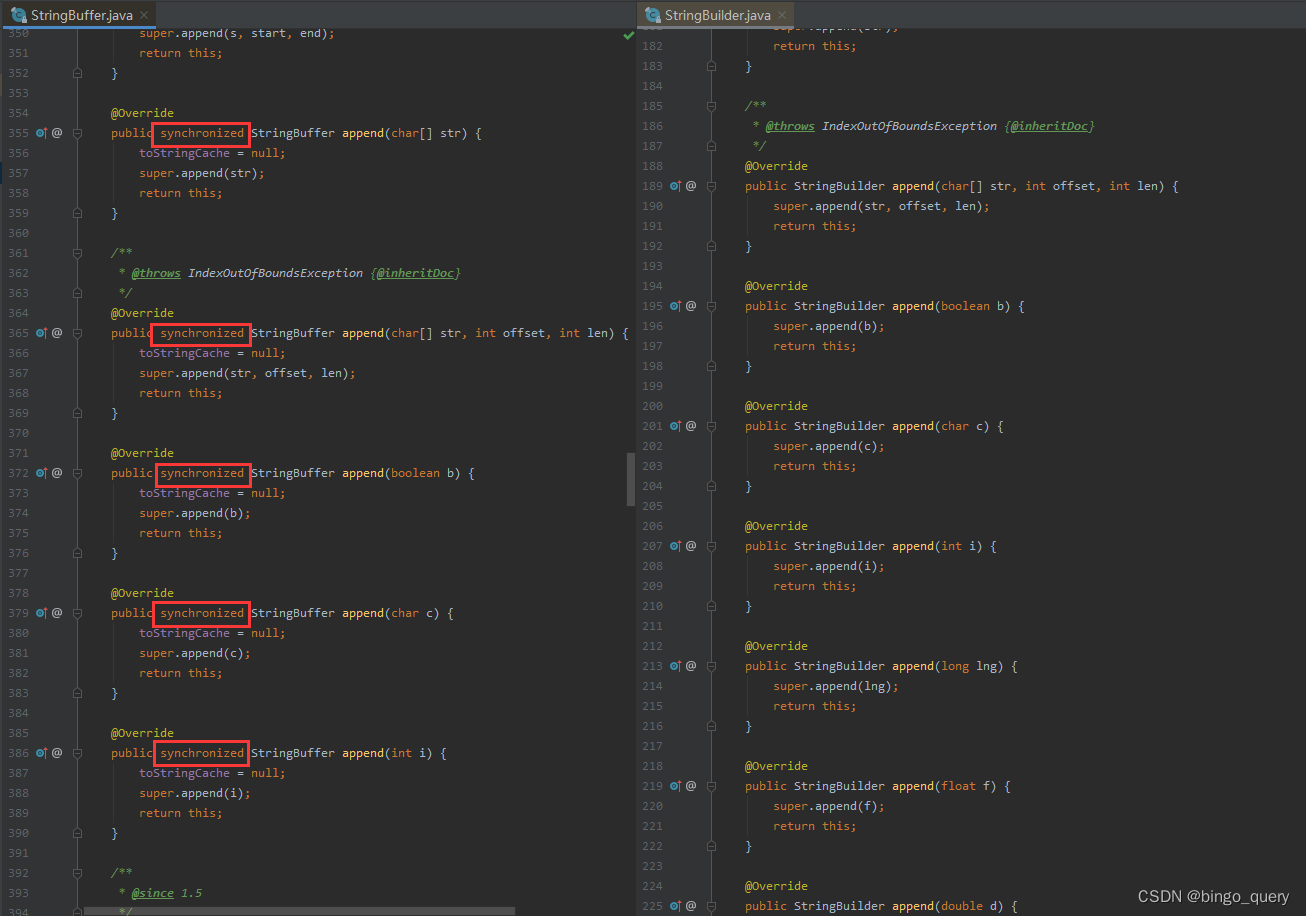
StringBuilder和StringBuffer基本上都是调用父类AbstractStringBuilder的实现,所以我们如果想了解StringBuilder和StringBuffer两个类,只需要学习AbstractStringBuilder类即可。
-
AbstractStringBuilder类基础属性
AbstractStringBuilder内部维护了一个value数组,用于储存当前对象所代表的字符序列,另外维护了一个count属性,用于统计当前对象使用到的字符序列长度,除了这两个变量之外,类里面还定义了一个属性作为value数组的最大容量,值为Integer.MAX_VALUE-8(减去8是因为不同的jvm平台在数组中保留了一些标题关键字,所以为了避免出现OOM异常,需要为这些关键词留出一些容量)。
/**
* The value is used for character storage.
*/
char[] value;
/**
* The count is the number of characters used.
*/
int count;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate (unless necessary).
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;AbstractStringBuilder类有两个构造方法,一个是无参构造,另一个是传入一个int类型的参数作为字符序列的初始容量,也就是value数组的初始容量。
/**
* This no-arg constructor is necessary for serialization of subclasses.
*/
AbstractStringBuilder() {
}
/**
* Creates an AbstractStringBuilder of the specified capacity.
*/
AbstractStringBuilder(int capacity) {
value = new char[capacity];
}-
AbstractStringBuilder类的常用方法
-
int length()
方法描述:返回当前对象代表的字符串序列长度。
public int length() {
return count;
}方法直接返回内部维护的count字段,其含义就是当前对象所代表的字符序列长度,注意此长度和内部的value数组长度不一样,value数组长度是指此对象的容量,而count是指有效数据数量。
-
char charAt(int index)
方法描述:方法指定索引位置的字符。
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return value[index];
}先判断传入的下标参数是否合法,然后直接返回数组的索引位置数据,注意这里判断也是用的count,也就是有效数据数量,而不是容量。
-
AbstractStringBuilder append(String str)
方法描述:将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
//第一步
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
//第二步
int len = str.length();
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//第三步
str.getChars(0, len, value, count);
count += len;
return this;
}方法第一步先进行了null值判断,如果参数为null的话调用了appendNull方法,追加了一个null的字符串。所以如果我们在项目使用中想避免这种情况必须得自己提前进行非null判断。
private AbstractStringBuilder appendNull() {
int c = count;
ensureCapacityInternal(c + 4);
final char[] value = this.value;
value[c++] = 'n';
value[c++] = 'u';
value[c++] = 'l';
value[c++] = 'l';
count = c;
return this;
}方法第二步,如果不为null的话,调用了ensureCapacityIntenal方法,此方法的作用是为了避免给对象内部的value赋值的时候,出现数组越界的情况。
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) {
value = Arrays.copyOf(value,
newCapacity(minimumCapacity));
}
}如果追加后的有效数据量大于当前容量的话,就需要重新分配一个新的数组,并且初始化容量也调用了另一个单独的方法newCapacity去计算。
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int newCapacity = (value.length << 1) + 2;
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity <= 0 || MAX_ARRAY_SIZE - newCapacity < 0)
? hugeCapacity(minCapacity)
: newCapacity;
}newCapacity方法计算容量的方式就是当前字符数组的长度左移1(相当于x2),然后再加2,得到新的数组容量。
第三步,调用str.getChars方法复制字符串到目标数组,底层调用的是本地方法System.arraycopy()。
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin) {
if (srcBegin < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
}
if (srcEnd > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
}
if (srcBegin > srcEnd) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}-
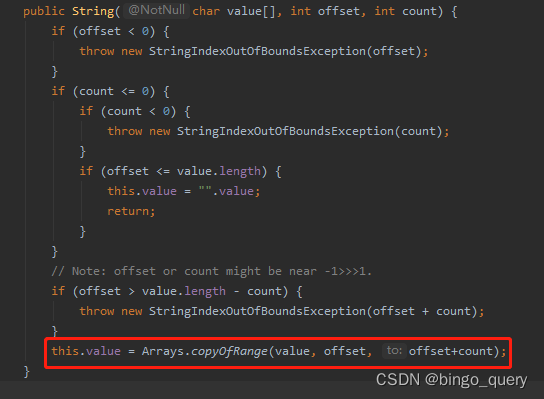
String substring(int start, int end)
方法描述:返回一个基于当前字符序列,从指定索引位置开始,到指定索引位置结束的一个子字符串。
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start < 0)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
return new String(value, start, end - start);
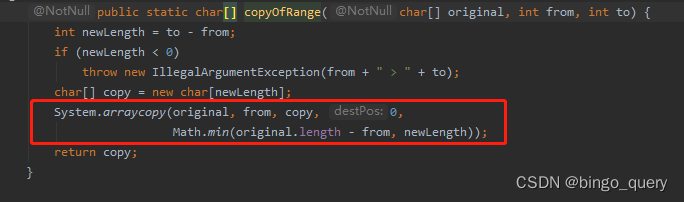
}内部实现是基于String类的构造器,然后追溯代码到最后发现还是依赖于本地方法System.arraycopy()。
结尾
作者是本着巩固学习和交流的目的编写,如果有问题或者不足之处请多多指导,感谢!
 Java中的AbstractStringBuilder:基础与应用
Java中的AbstractStringBuilder:基础与应用





 AbstractStringBuilder是一个抽象类,作为StringBuilder和StringBuffer的基础,实现CharSequence和Appendable接口。它维护了一个value数组和count属性,用于存储字符序列。类中有用于追加字符串、获取子字符串等的方法。StringBuilder和StringBuffer主要区别在于线程安全,StringBuilder适合单线程,效率高;StringBuffer适合多线程,但效率较低。
AbstractStringBuilder是一个抽象类,作为StringBuilder和StringBuffer的基础,实现CharSequence和Appendable接口。它维护了一个value数组和count属性,用于存储字符序列。类中有用于追加字符串、获取子字符串等的方法。StringBuilder和StringBuffer主要区别在于线程安全,StringBuilder适合单线程,效率高;StringBuffer适合多线程,但效率较低。
















 687
687

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








