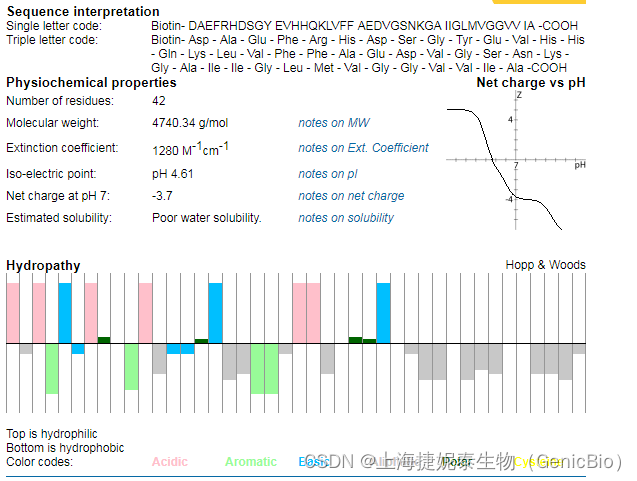
单字母序列:Biotin-DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVVIA
三字母序列:Biotin-Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Glu-Val-His-His-Gln-Lys-Leu-Val-Phe-Phe-Ala-Glu-Asp-Val-Gly-Ser-Asn-Lys-Gly-Ala-Ile-Ile-Gly-Leu-Met-Val-Gly-Gly-Val-Val-Ile-Ala
CAS No.:102577-21-9
分子量:4740.4
In Alzheimer's disease (AD) Aβ accumulates because of imbalance between the production of Aβ and its removal from the brain. There is increasing evidence that in most sporadic forms of AD, the accumulation of Aβ is partly, if not in some cases solely, because of defects in its removal—mediated through a combination of diffusion along perivascular extracellular matrix, transport across vessel walls into the blood stream and enzymatic degradation.
在阿尔茨海默病(AD)中,Aβ的积累是由于Aβ的产生和从大脑中清除之间的不平衡。越来越多的证据表明,在大多数散发形式的AD中,Aβ的积累在一定程度上(如果不是在某些情况下)是由于其去除过程中的缺陷——通过沿着血管周围细胞外基质的扩散、穿过血管壁进入血流和酶降解的组合介导。
Alzheimer's Disease (AD), the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by progressive cognitive decline, synaptic loss, the formation of extracellular β-amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal cell death. Despite the massive neuronal loss in the ‘late stage’ of disease, dendritic spine loss represents the best pathological correlate to the cognitive impairment in AD patients. The ‘amyloid hypothesis’ of AD recognizes the Aβ peptide as the principal player in the pathological process. Many lines of evidence point out to the neurotoxicity of Aβ, highlighting the correlation between soluble Aβ oligomer accumulation, rather than insoluble Aβ fibrils and disease progression. Pathological increase of Aβ in AD brains, resulting from an imbalance between its production, aggregation and clearance, might target mitochondrial function promoting a progressive synaptic impairment. The knowledge of the exact mechanisms by which Aβ peptide impairs neuronal function will help us to design new pharmacological tools for preventing AD neurodegeneration.
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是最常见的与年龄相关的神经退行性疾病,其特征是进行性认知能力下降、突触丧失、细胞外β-淀粉样蛋白斑块和细胞内神经原纤维缠结的形成以及神经元细胞死亡。尽管在疾病的“晚期”有大量神经元丢失,但树突棘丢失是AD患者认知障碍的最佳病理相关性。AD的“淀粉样蛋白假说”认为Aβ肽是病理过程中的主要参与者。许多证据表明Aβ具有神经毒性,突出了可溶性Aβ低聚物积累而非不溶性Aβ原纤维与疾病进展之间的相关性。AD大脑中Aβ的病理性增加,由于其产生、聚集和清除之间的不平衡,可能靶向线粒体功能,促进进行性突触损伤。了解Aβ肽损害神经元功能的确切机制将有助于我们设计新的预防AD神经退行性变的药理学工具。
Biotin-beta amyloid 1-42 序列分析:
引用文献:
1, SYMPOSIUM: Clearance of Aβ from the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease: Aβ-Degrading Enzymes in Alzheimer's Disease
作者:James Scott Miners, Shabnam Baig, Jennifer Palmer, Laura E. Palmer, Patrick G. Kehoe, Seth Love
期刊:Brain Pathology, Volume18, Issue2. April 2008.Pages 240-252
2, Aβ Toxicity in Alzheimer's Disease
作者:Virve Cavallucci,Marcello D’Amelio1 & Francesco Cecconi1
期刊:Molecular Neurobiology Aims。Volume 45, pages 366–378, (2012)
3, High-Level Neuronal Expression of Aβ1–42 in Wild-Type Human Amyloid Protein Precursor Transgenic Mice: Synaptotoxicity without Plaque Formation
作者:Lennart Mucke, Eliezer Masliah, Gui-Qiu Yu, Margaret Mallory, Edward M. Rockenstein, Kelly Johnson-Wood and Lisa McConlogue;
期刊:Journal of Neuroscience 1 June 2000, 20 (11) 4050-4058

产品链接:http://www.genicbio.cn/detail.html?article_id=81
上海捷妮泰生物科技有限公司(GenicBio Limited)
微 信: 199 1653 7972
Q Q: 1704635669
邮 箱: service@genicbio.cn
网 址: www.genicbio.cn




















 372
372

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








