本文主要目的是讲解tomcat中的pipeline机制
我们前面文章介绍过,tomcat中container有四种,分别是engine,host,context,wrapper,这4个。
container的实现类分别是StandardEngine,StandardHost,StandardContext,StandardWrapper。四个容器是包含关系,engine包含host,host包含context,context,包含wrapper,wappper代表最基础的一个servlet。
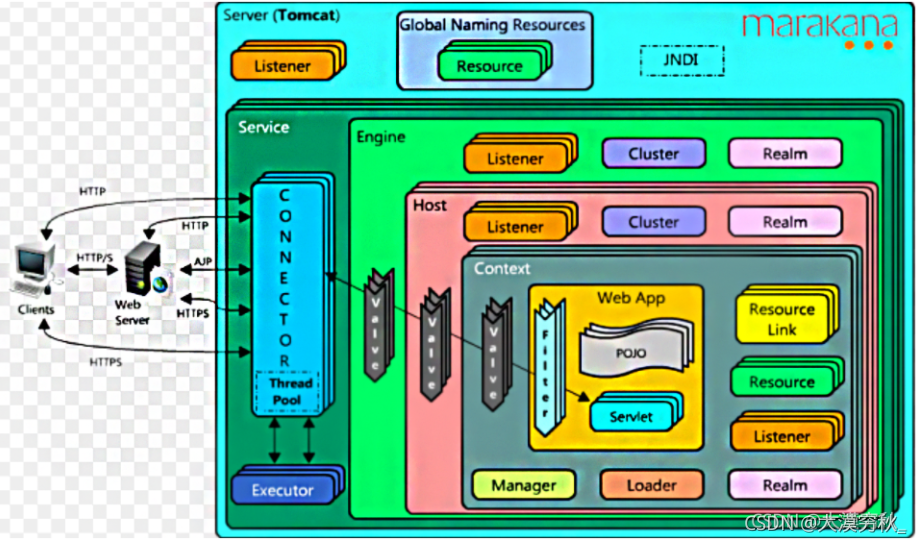
tomcat由Connector和Container两部分组成,而当网络请求过来的时候Connector先将请求包装为Request,然后将Request交由Container进行处理,最终返回给请求方。而Container处理的第一层就是Engine容器,但是在tomcat中Engine容器不会直接调用Host容器去处理请求,那么请求是怎么在4个容器中流转的,4个容器之间是怎么依次调用的,我们今天来讲解下。
当请求到达Engine容器的时候,Engine并非是直接调用对应的Host去处理相关的请求,而是调用了自己的一个组件去处理,这个组件就叫做pipeline组件,跟pipeline相关的还有个也是容器内部的组件,叫做valve组件。
在Catalina中,我们有4种容器,每个容器都有自己的Pipeline组件,每个Pipeline组件上至少会设定一个Valve(阀门),这个Valve我们称之为BaseValve(基础阀)。基础阀的作用是连接当前容器的下一个容器(通常是自己的自容器),可以说基础阀是两个容器之间的桥梁。
Pipeline定义对应的接口Pipeline,标准实现了StandardPipeline。Valve定义对应的接口Valve,抽象实现类ValveBase,4个容器对应基础阀门分别是StandardEngineValve,StandardHostValve,StandardContextValve,StandardWrapperValve。
catalina中pipeline,valve运行图如下
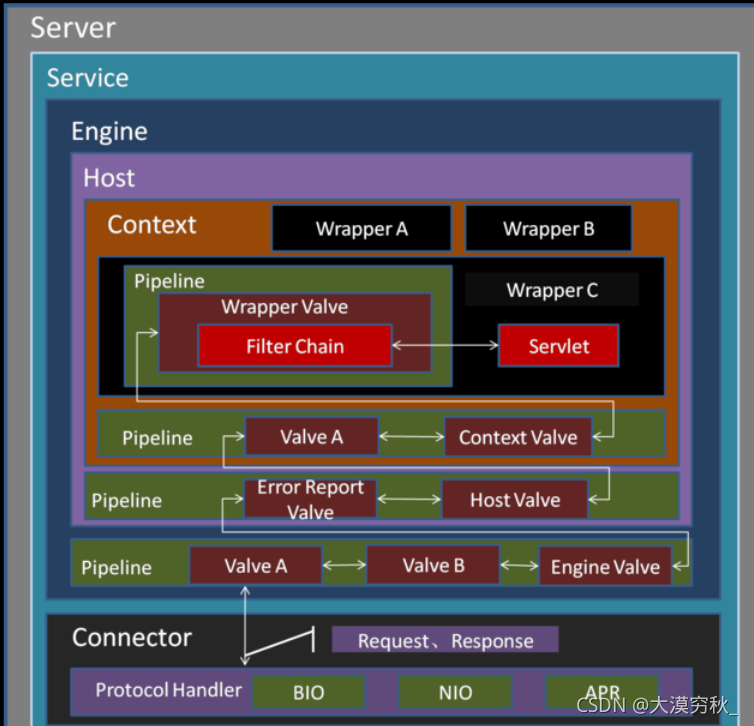
一个pipline上由多个valve,每个valve都可以做一些操作,无论是pipeline还是valve操作,都是request和response。再容器之间pipeline和valve则起到了桥梁的作用。
我们看下valve的接口
public interface Valve {
public String getInfo();
public Valve getNext();
public void setNext(Valve valve);
public void backgroundProcess();
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException;
public void event(Request request, Response response, CometEvent event) throws IOException,ServletException;
public boolean isAsyncSupported();
}
先看下valve接口的方法定义,方法不是很多,这里只介绍setNext(),getNext。在上面我们也看到了一个pipeline上面有很多valve。这些valve存放并非统一放在pipiline中,而是像链表,通过next指针相连。
pipeline
//pipeline 接口
public interface Pipeline {
public Valve getBasic();
public void setBasic(Valve valve);
public void addValve(Valve valve);
public Valve[] getValves();
public void removeValve(Valve valve);
public Valve getFirst();
public boolean isAsyncSupported();
public Container getContainer();
public void setContainer(Container container);
}
可以看出Pipeline中很多的方法都是操作Valve的,包括获取,设置,移除Valve,getFirst()返回的是Pipeline上的第一个Valve,而getBasic(),setBasic()则是获取/设置基础阀,我们都知道在Pipeline中,每个pipeline至少都有一个阀门,叫做基础阀,而getBasic(),setBasic()则是操作基础阀的。
- standardPipeline
public class StandardPipeline extends LifecycleBase implements Pipeline, Contained {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(StandardPipeline.class);
public StandardPipeline() {
this(null);
}
public StandardPipeline(Container container) {
super();
setContainer(container);
}
protected Valve basic = null;
protected Container container = null;
protected static final String info = "org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline/1.0";
//当前pipline的第一个阀门
protected Valve first = null;
//这里是生命周期的初始化方法
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).start();
current = current.getNext();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------- Pipeline Methods
//设置基础阀
@Override
public void setBasic(Valve valve) {
// Change components if necessary
Valve oldBasic = this.basic;
if (oldBasic == valve)
return;
// Stop the old component if necessary
//先停掉oldBasic,生命周期关掉
if (oldBasic != null) {
if (getState().isAvailable() && (oldBasic instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) oldBasic).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: stop", e);
}
}
if (oldBasic instanceof Contained) {
try {
((Contained) oldBasic).setContainer(null);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
}
}
}
//启动新的阈值
if (valve == null)
return;
if (valve instanceof Contained) {
((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container);
}
if (getState().isAvailable() && valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.setBasic: start", e);
return;
}
}
// Update the pipeline
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
//遍历阀门链表将新的阀门取代旧的阀门
//base节点添加到链表的最后,替换旧的阈值
if (current.getNext() == oldBasic) {
current.setNext(valve);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
this.basic = valve;
}
//添加阈值
@Override
public void addValve(Valve valve) {
// Validate that we can add this Valve
if (valve instanceof Contained)
((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container);
// Start the new component if necessary
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.addValve: start: ", e);
}
}
}
// Add this Valve to the set associated with this Pipeline
if (first == null) {
first = valve;
valve.setNext(basic);
} else {
//添加到basic节点的前一个位置
Valve current = first;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == basic) {
current.setNext(valve);
valve.setNext(basic);
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
}
container.fireContainerEvent(Container.ADD_VALVE_EVENT, valve);
}
//获取阀门
@Override
public Valve[] getValves() {
ArrayList<Valve> valveList = new ArrayList<Valve>();
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
valveList.add(current);
current = current.getNext();
}
return valveList.toArray(new Valve[0]);
}
//删除阀门,
@Override
public void removeValve(Valve valve) {
Valve current;
//删除的是第一个阀门,直接置空第一个节点
if(first == valve) {
first = first.getNext();
current = null;
} else {
current = first;
}
//遍历节点,删除节点的上一个节点,指向删除节点下一个节点
while (current != null) {
if (current.getNext() == valve) {
current.setNext(valve.getNext());
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
//检查,如果第一个节点是基节点,置空
if (first == basic) first = null;
if (valve instanceof Contained)
((Contained) valve).setContainer(null);
if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) {
// Stop this valve if necessary
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.removeValve: stop: ", e);
}
}
try {
((Lifecycle) valve).destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("StandardPipeline.removeValve: destroy: ", e);
}
}
container.fireContainerEvent(Container.REMOVE_VALVE_EVENT, valve);
}
//如果第一个节点不空位,返回基节点
@Override
public Valve getFirst() {
if (first != null) {
return first;
}
return basic;
}
}





 本文深入探讨了Tomcat的Pipeline和Valve机制。Pipeline作为容器间的通信桥梁,每个容器拥有自己的Pipeline,其中包含至少一个基础Valve。Valve是处理请求的组件,它们形成一个链式结构,每个Valve可以执行特定操作。Pipeline通过next指针链接Valve,请求从Engine开始,逐级通过Host、Context到Wrapper进行处理。StandardPipeline是Pipeline的实现,包含了添加、移除和管理Valve的方法。通过对Valve接口和Pipeline的了解,我们可以更好地理解Tomcat的内部工作流程。
本文深入探讨了Tomcat的Pipeline和Valve机制。Pipeline作为容器间的通信桥梁,每个容器拥有自己的Pipeline,其中包含至少一个基础Valve。Valve是处理请求的组件,它们形成一个链式结构,每个Valve可以执行特定操作。Pipeline通过next指针链接Valve,请求从Engine开始,逐级通过Host、Context到Wrapper进行处理。StandardPipeline是Pipeline的实现,包含了添加、移除和管理Valve的方法。通过对Valve接口和Pipeline的了解,我们可以更好地理解Tomcat的内部工作流程。
















 4157
4157

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








