- 环境搭建
a.安装anaconda
首先去官网下载,我也不清楚网速怎么样,我是直接去清华大学开源软件镜像下载的,链接如下
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
找到anaconda 在archive中找到并下载最新版的适合自己系统的安装包
接着就是进行安装,安装完成后右键管理员身份运行如图快捷方式
输入conda upgrade --all
然后会显示并且会有更新的提示,此时输入y即可
b.解释器
就用的官方的cpython
- python初体验
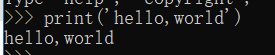
这里相对简单一点
- python基础讲解
-
变量的命名规则:
1.变量名只能是字母(a-z、A-Z)、数字(0-9)或下划线( _ )的任意组合
2.变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
3.变量名大小写敏感(temp与TEMP不是同一个变量)
4.关键字不能声明为变量名(Python交互模式下查询关键字) -
Python注释:
Python中的注释有单行注释和多行注释:
Python中
单行注释以 # 开头单行注释
多行用三个单引号 或 三个双引号 包括要注释的内容 -
python中“:”的作用
对于Python而言代码缩进是一种语法,Python没有像其他语言一样采用{}或者begin…end分隔代码块,而是采用代码缩进和冒号来区分代码之间的层次。缩进的空白数量是可变的,但是所有代码块语句必须包含相同的缩进空白数量,这个必须严格执行。参照此博主文章
- Python dir()函数
dir() 函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时,返回参数的属性、方法列表。如果参数包含方法__dir__(),该方法将被调用。如果参数不包含__dir__(),该方法将最大限度地收集参数信息。
语法:dir([object])
object – 对象、变量、类型。
如果对 dir() 的用法不是很清楚,可以使用 help() 来查看帮助:
>>> help(dir)
Help on built-in function dir in module builtins:
dir(...)
dir([object]) -> list of strings
If called without an argument, return the names in the current scope.
Else, return an alphabetized list of names comprising (some of) the attributes
of the given object, and of attributes reachable from it.
If the object supplies a method named __dir__, it will be used; otherwise
the default dir() logic is used and returns:
for a module object: the module's attributes.
for a class object: its attributes, and recursively the attributes
of its bases.
for any other object: its attributes, its class's attributes, and
recursively the attributes of its class's base classes.
(END)
使用 dir()可以查看指定模块中定义的名称,它返回的是一个已排序的字符串列表:
如:
>>> s = 'Hello'
>>> l = [1, 2, 3]
>>> abs = math.fabs
>>> dir()
['__builtins__', '__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'l', 'math', 's']
- help()函数
函数很多常用的python函数或模块,经常需要查看帮助,很不方便。
在python的交互命令行下使用help()或在python文件中调用help()函数可以很方便的查看帮助。
一 查看所有的关键字:help(“keywords”
二 其他
查看python所有的modules:help(“modules”)
单看python所有的modules中包含指定字符串的modules: help(“modules yourstr”)
查看python中常见的topics: help(“topics”)
查看python标准库中的module:import os.path + help(“os.path”)
查看python内置的类型:help(“list”)
查看python类型的成员方法:help(“str.find”)
查看python内置函数:help(“open”)
- import的使用
1.导入包名
import os
2.从包中导入函数
from math import pow
3.导入包并赋予别名
import math as m
4.从包中导入常量并赋予别名
from math import pi as p
5.导入包中所有内容
from math import * - pep8介绍
PEP8是一个编程规范,内容是一些关于如何让你的程序更具可读性的建议。
- python数值基本知识:
对于Python,它的整型并不像C的整型还分short ,int ,long 。Python里面只有一种整型,整型拥有准确的精度,或者说整型拥有无限精度。不管你用多少位数进行加减,都能得到一个正确的结果。
在Python中,浮点型本质是实现C语言中的double类型,即用本机双精度(64 bit)表示,有效位数为16位(不是小数点后16位)。
•int(符号整数):通常被称为是整数或整数,没有小数点的正或负整数。
•long(长整数):或渴望,无限大小的整数,这样写整数和一个大写或小写的L。
•float(浮点实际值):彩车,代表实数,小数除以整数部分和小数部分的书面。花车也可能是在科学记数法与E或指示的10次方é(2.5e2= 2.5×102=250)。
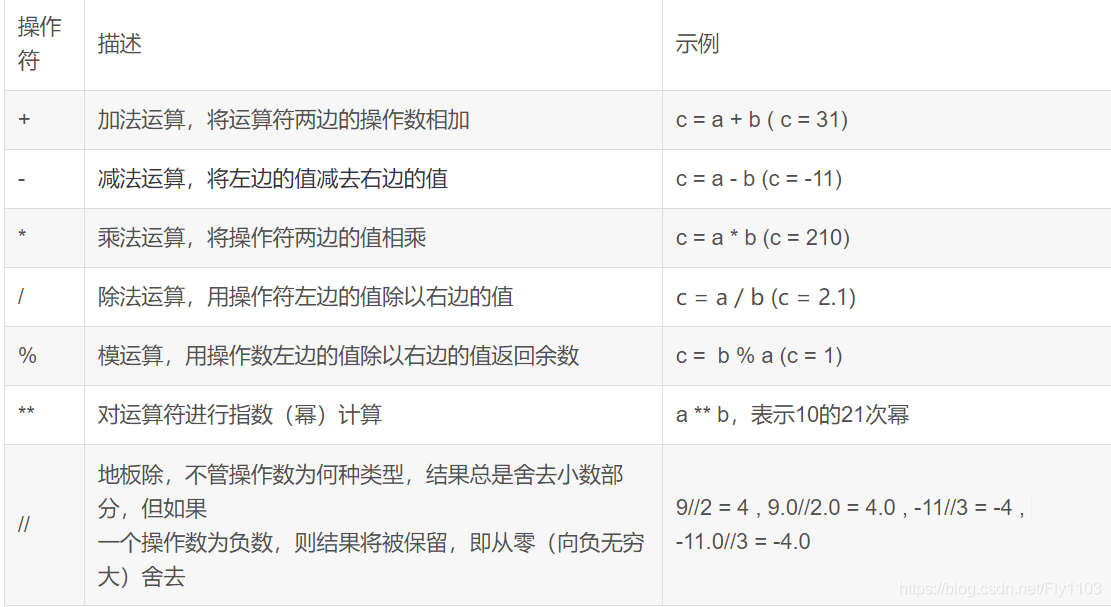
算术运算符
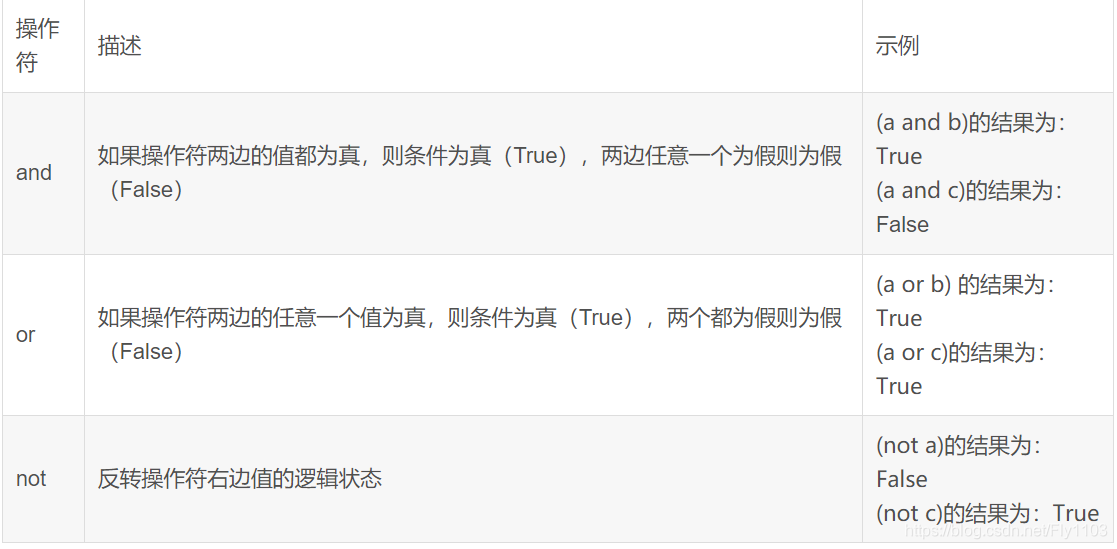
逻辑运算
成员运算符
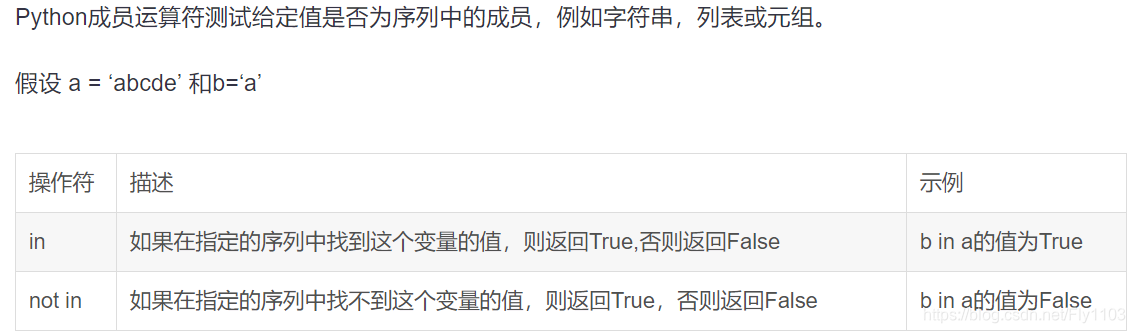
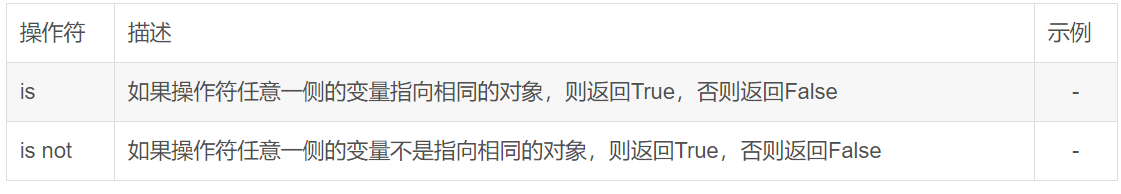
身份运算符
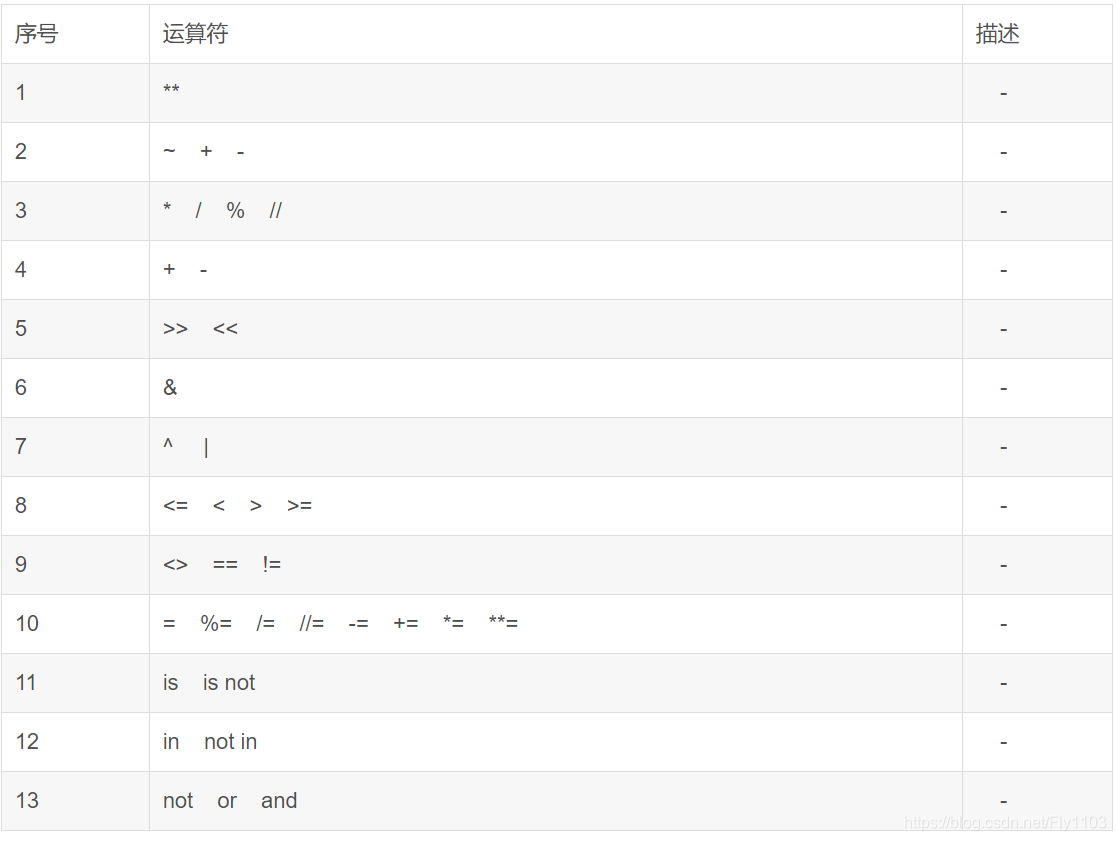
运算符优先




 本文详细介绍Python环境的搭建过程,包括Anaconda的安装及更新,并介绍了Python的基础知识,如变量命名规则、注释方法、数据类型等。此外,还涉及了一些常用函数如dir()、help()的使用方法及PEP8编程规范。
本文详细介绍Python环境的搭建过程,包括Anaconda的安装及更新,并介绍了Python的基础知识,如变量命名规则、注释方法、数据类型等。此外,还涉及了一些常用函数如dir()、help()的使用方法及PEP8编程规范。
















 3911
3911

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








