
第一次:排序后索引号丢失,使用vector<pair<int,int>> vec保留索引好,解决这个问题;使用while(1)有死循环的风险,使用while (i<j) 来控制循环。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int i=0,j=nums.size()-1;
int sum;
while(1){
if(nums[j]>target)
j--;
else
break;
}
while(1){
sum=nums[i]+nums[j];
if(sum>target){
i++;
}else if(sum<target){
j--;
}else{
break;
}
}
vector<int> ans;
ans.push_back(i);
ans.push_back(j);
return ans;
}
};第二次:🔍 std::pair 默认排序规则:当你使用 std::sort 对 pair<int, int> 排序时,默认按 first 元素升序排序,如果 first 相同,则比较 second。
如果你需要自定义排序,比如按第二项排序,你可以写成:
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
return a.second < b.second;
});排序+双指针,但需要先保留索引,时间复杂度为O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<pair<int,int>> vec;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
vec.push_back({nums[i],i});
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
int i=0,j=nums.size()-1;
while(i<j){
int sum=vec[i].first+vec[j].first;
if(sum>target){
j--;
}else if(sum<target){
i++;
}else{
return {vec[i].second,vec[j].second};
}
}
return {};
}
};第三次:直接枚举,时间复杂度为O(n^2)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return {i, j};
}
}
}
return {};
}
};第四次:使用哈希表,每一次循环都可以在O(1)时间寻找到target-nums[i]
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int,int> mp;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){
int complement=target-nums[i];
if(mp.count(complement)){
return {mp[complement],i};
}
mp[nums[i]]=i;
}
return {};
}
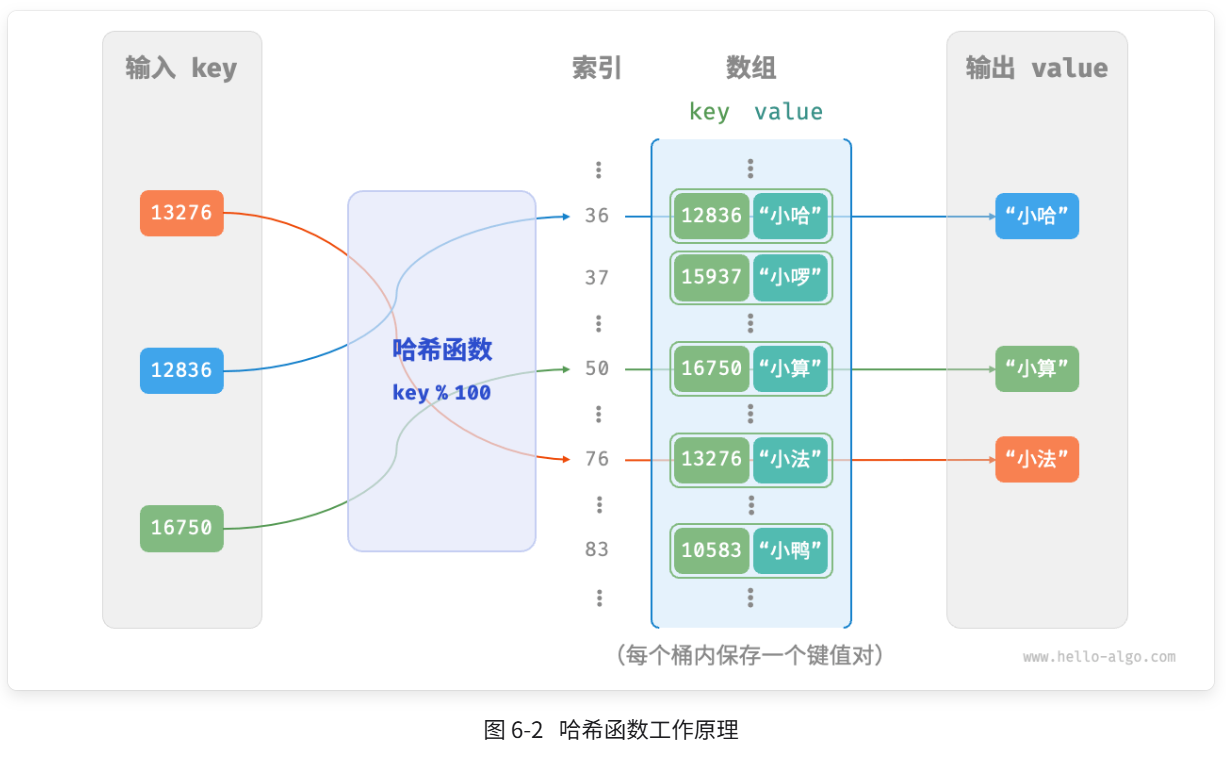
};这道题目的目的是为了让我们认识到哈希表的强大性能,那么为什么哈希表可以在O(1)时间实现搜索?
-
直接定位: 哈希表通过哈希函数将键
key映射成数组索引index = hash(key),避免了线性搜索或树的逐层查找。 -
数组访问是 O(1): 查找变成“访问数组下标”,这是最基本、最快的数据访问操作,时间复杂度是 O(1)。
-
冲突少时效率极高: 好的哈希函数使不同的键分布均匀,减少冲突;即使冲突,也只在小范围内查找。
📌 举例:
如果你要查找 key = 42:
-
哈希函数:
hash(42) = 7 -
你直接访问
table[7],一步就拿到值 —— 不需要排序、查找、比较!
一个简单的哈希表实现
/* 键值对 */
struct Pair {
public:
int key;
string val;
Pair(int key, string val) {
this->key = key;
this->val = val;
}
};
/* 基于数组实现的哈希表 */
class ArrayHashMap {
private:
vector<Pair *> buckets;
public:
ArrayHashMap() {
// 初始化数组,包含 100 个桶
buckets = vector<Pair *>(100);
}
~ArrayHashMap() {
// 释放内存
for (const auto &bucket : buckets) {
delete bucket;
}
buckets.clear();
}
/* 哈希函数 */
int hashFunc(int key) {
int index = key % 100;
return index;
}
/* 查询操作 */
string get(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
Pair *pair = buckets[index];
if (pair == nullptr)
return "";
return pair->val;
}
/* 添加操作 */
void put(int key, string val) {
Pair *pair = new Pair(key, val);
int index = hashFunc(key);
buckets[index] = pair;
}
/* 删除操作 */
void remove(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
// 释放内存并置为 nullptr
delete buckets[index];
buckets[index] = nullptr;
}
/* 获取所有键值对 */
vector<Pair *> pairSet() {
vector<Pair *> pairSet;
for (Pair *pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
pairSet.push_back(pair);
}
}
return pairSet;
}
/* 获取所有键 */
vector<int> keySet() {
vector<int> keySet;
for (Pair *pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
keySet.push_back(pair->key);
}
}
return keySet;
}
/* 获取所有值 */
vector<string> valueSet() {
vector<string> valueSet;
for (Pair *pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
valueSet.push_back(pair->val);
}
}
return valueSet;
}
/* 打印哈希表 */
void print() {
for (Pair *kv : pairSet()) {
cout << kv->key << " -> " << kv->val << endl;
}
}
};但是上面哈希表的实现还有一些问题:
| 问题 | 说明 | 改进建议 |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ 没有处理冲突 | 若两个 key 哈希到同一个位置,会发生覆盖 | 使用链地址法(每个桶变为 vector 或链表) |
| ❌ 无动态扩容 | 当数据量大于桶数,会严重退化 | 检测负载因子并 rehash |
| ❌ 没有键比较 | 仅靠 hash(key) 定位,没有比较实际键值 | 插入、删除、查找时应比较 pair->key == key |
| ❌ 手动内存管理麻烦 | 使用原始指针,易出错 | 用 unique_ptr 或智能指针管理内存 |
下面是一个支持冲突处理(链地址法)+ 自动扩容(rehash)+ 负载因子管理的 C++ 哈希表类 ArrayHashMap 重构版本,完全自主实现核心功能:
✅ 功能特性
| 特性 | 实现方式 |
|---|---|
| 哈希冲突处理 | 链地址法(vector of vector) |
| 负载因子阈值 | 默认 0.75 |
| 自动扩容/rehash | 容量翻倍后重哈希 |
| 键值查找 | 支持同键覆盖 |
| 删除操作 | 支持安全删除 |
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class ArrayHashMap {
private:
struct Pair {
int key;
string val;
Pair(int k, string v) : key(k), val(v) {}
};
vector<vector<Pair>> buckets; // 哈希桶(链地址法)
int capacity; // 桶数量
int size; // 当前元素数量
const float loadFactorThreshold = 0.75;
/* 哈希函数 */
int hashFunc(int key) const {
return key % capacity;
}
/* 自动扩容 */
void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = capacity;
capacity *= 2;
vector<vector<Pair>> newBuckets(capacity);
for (const auto &bucket : buckets) {
for (const Pair &pair : bucket) {
int index = hashFunc(pair.key);
newBuckets[index].emplace_back(pair.key, pair.val);
}
}
buckets = move(newBuckets);
}
public:
ArrayHashMap(int initCap = 100) : capacity(initCap), size(0) {
buckets = vector<vector<Pair>>(capacity);
}
/* 插入或更新 */
void put(int key, const string &val) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
for (Pair &p : buckets[index]) {
if (p.key == key) {
p.val = val; // 若存在,更新
return;
}
}
buckets[index].emplace_back(key, val);
size++;
if ((float)size / capacity > loadFactorThreshold) {
rehash();
}
}
/* 查询 */
string get(int key) const {
int index = hashFunc(key);
for (const Pair &p : buckets[index]) {
if (p.key == key)
return p.val;
}
return "";
}
/* 删除 */
void remove(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
auto &bucket = buckets[index];
for (auto it = bucket.begin(); it != bucket.end(); ++it) {
if (it->key == key) {
bucket.erase(it);
size--;
return;
}
}
}
/* 所有键值对 */
vector<Pair> pairSet() const {
vector<Pair> result;
for (const auto &bucket : buckets) {
for (const Pair &p : bucket)
result.push_back(p);
}
return result;
}
/* 打印 */
void print() const {
for (const auto &bucket : buckets) {
for (const Pair &p : bucket) {
cout << p.key << " -> " << p.val << endl;
}
}
}
};
哈希表的学习,参考这里:第 6 章 哈希表 - Hello 算法





















 1532
1532

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








