1.父子传参
在父组件里引入的子组件上进行传值
<child delete={this.ids} data={this.state.data} />
子组件中this.props.data引用data属性;this.props.delete(ids)引用delete方法并传参。
2.pubsub 发布订阅
在一个组件中发布
Pubsub.publish("username", value);
在另一个组件中订阅
Pubsub.subsribe("username", data)
3.通过redux或者react-redux
在大型项目中,react中的组件嵌套及跨级是非常频繁的,而react的数据本身是单向数据流,这样组件之间传递数据非常麻烦,Redux最主要是用作应用状态的管理,用于实现多级组件之前的数据共享.
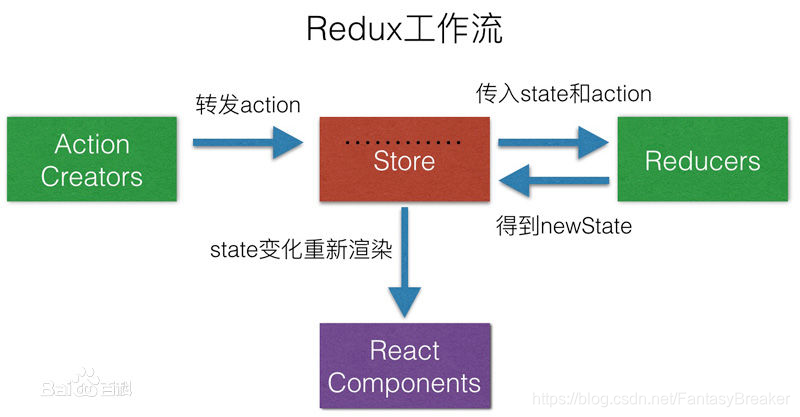
首先创建数据仓库store
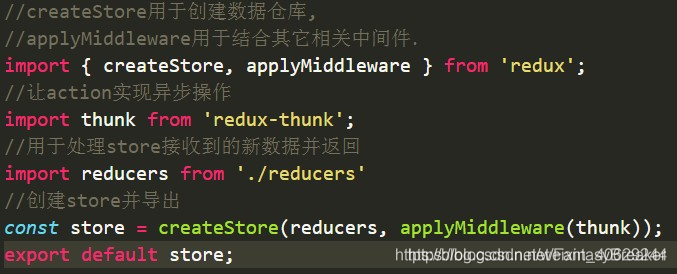
在项目入口文件index.js中传入store
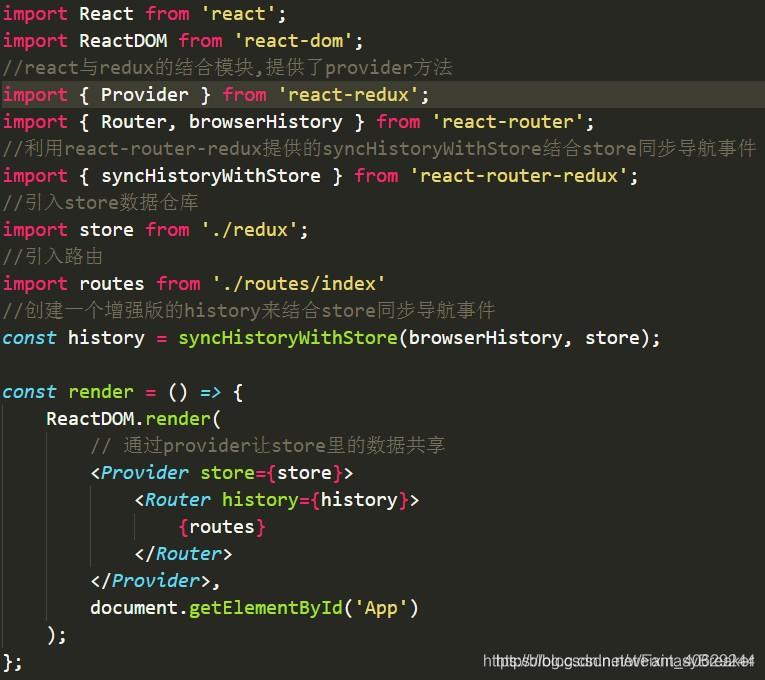
当组件需要修改store里的数据时必须要派发action,action有两个特定参数,一个为type,为action的名称,一个为payload,即需要传递的数据.
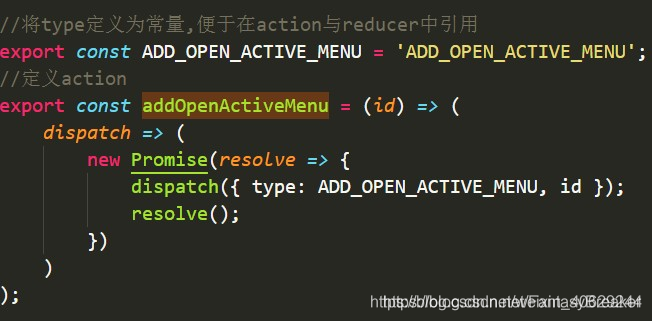
在需要修改数据的组件banDetail.js中引入action
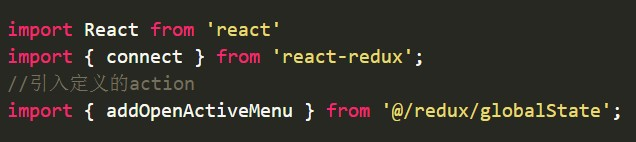
在需要修改数据的组件banDetail.js中通过connect让addOpenActiveMenu这个action方法与当前组件做链接

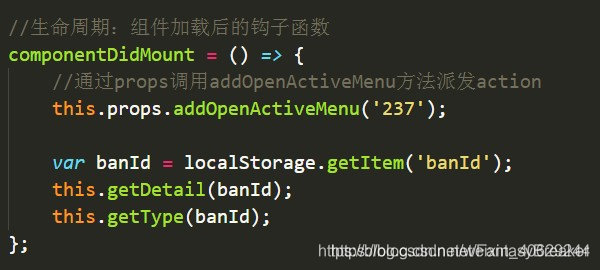
在banDetail.js调用方法
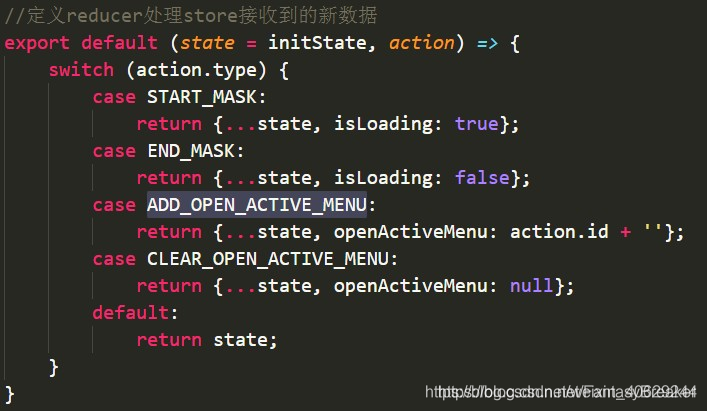
定义reducer,处理store接收到的新数据
4.上下文context传参
导入类型检测
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
定义导出的数据类型
static childContextTypes ={
color:PropTypes.string,//字符串颜色类型
setColor:PropTypes.func,//方法类型
}
获取需要传参的内容
getChildContext(){
return {
color:this.state.color,
setColor:v=>this.setState({color:v})
}
}
在子组件中定义上下文数据并使用数据和方法
static contextTypes = {
color:PropTypes.string,//字符串颜色类型
setColor:PropTypes.func,//方法类型
}
<Button style={{color:this.context.color}}
onClick={()=>this.context.setColor('gold')}>
</Button>
5.上下文provider方式
从react中引入

创建上下文
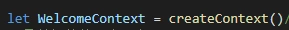
在父组件引入子组件的地方采用上下文.Provider 通过value=传递数据
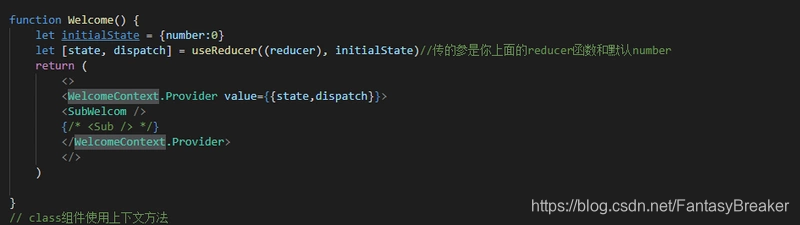
let {state, dispatch} = useContext(WelcomeContext);
6.eventEmitter监听事件传参
在实际使用中,实例化可以提出来单独作为引用文件:
import { EventEmitter } from 'fbemitter'
export default new EventEmitter()
在组件中使用
import emitter from './emitter'
this.eventEmitter = emitter.addListener("add", (x) => {
//回调函数
})
emitter.emit('add', value)
//组件将要销毁时取消事件监听
componentWillUnmount(){
this.eventEmitter.remove();
}
7.路由传参
params
<Route path='/path/:name' component={Path}/>
<link to="/path/2">xxx</Link>
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/path/" + name});
读取参数用:this.props.match.params.name
优势 : 刷新地址栏,参数依然存在
缺点: 只能传字符串,并且,如果传的值太多的话,url会变得长而丑陋。
query/state
<Route path='/query' component={Query}/>
<Link to={{ path : ' /query' , query/state : { name : 'sunny' }}}>
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/query",query/state: { name : 'sunny' }});
读取参数用: this.props.location.query.name/state
优势:传参优雅,传递参数可传对象;
缺点:刷新地址栏,参数丢失
search
<Route path='/web/departManange ' component={DepartManange}/>
<link to="web/departManange?tenantId=12121212">xxx</Link>
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/web/departManange?tenantId" + row.tenantId});
读取参数用: this.props.location.search
优缺点同params





 本文介绍了在React中实现组件间通信的多种方法,包括父子传参、pubsub发布订阅、使用Redux、上下文(context)传参、上下文Provider、eventEmitter事件监听以及通过路由params、query和state传递参数。详细阐述了每种方法的使用场景和优缺点,特别是在大型项目中处理多级组件数据共享的重要策略。
本文介绍了在React中实现组件间通信的多种方法,包括父子传参、pubsub发布订阅、使用Redux、上下文(context)传参、上下文Provider、eventEmitter事件监听以及通过路由params、query和state传递参数。详细阐述了每种方法的使用场景和优缺点,特别是在大型项目中处理多级组件数据共享的重要策略。
















 1690
1690

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








