方法一:
知识点:学习使用if嵌套选择结构。
思路:定义字符,判断字符在ASCII码中的大小。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
char c;
int letters=0,space=0,number=0,others=0;
printf("please input some characters\n");
while((c=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(c>='a'&&c<='z'||c>='A'&&c<='Z')
letters=letters+1;
else if(c==' ')
{
space=space+1;
}
else if(c>='0'&&c<='9')
{
number=number+1;
}
else
{
others=others+1;
}
}
printf("all in all:char=%d space=%d number=%d others=%d\n",letters,space,number,others);
system("pause");
}
方法二:
知识点:使用函数调用计算
思路:定义一个数组,用子函数分别求出字母,数字,空格,其他的数字,具体看源码。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<string.h>
int zimu(char a[10])
{
int i,zimu=0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if ((a[i]>='a'&&a[i]<='z') || (a[i]>='A'&&a[i] <= 'Z'))
zimu++;
}
return (zimu);
}
int number(char a[10])
{
int i, number=0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (a[i]>='0'&&a[i] <= '9')
number++;
}
return (number);
}
int kongge(char a[10])
{
int i, kongge=0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (a[i] == ' ')
kongge++;
}
return(kongge);
}
int others(char a[10],int l)
{
int i, others=0;
for (i = 0; i < l; i++)
{
if ((a[i]>='a'&&a[i]<='z') || (a[i]>='A'&&a[i] <= 'Z') || (a[i]>='0'&&a[i] <= '9') || (a[i] == ' '))
continue;
else
{
others++;
}
}
return(others);
}
void main()
{
char a[10];
int e, b, c, d,l;
gets_s(a,10);
l=strlen(a);
e = zimu(a);
b = number(a);
c = kongge(a);
d = others(a,l);
printf("zimu:%d number:%d kongge:%d others:%d",e,b,c,d);
system("pause");
}
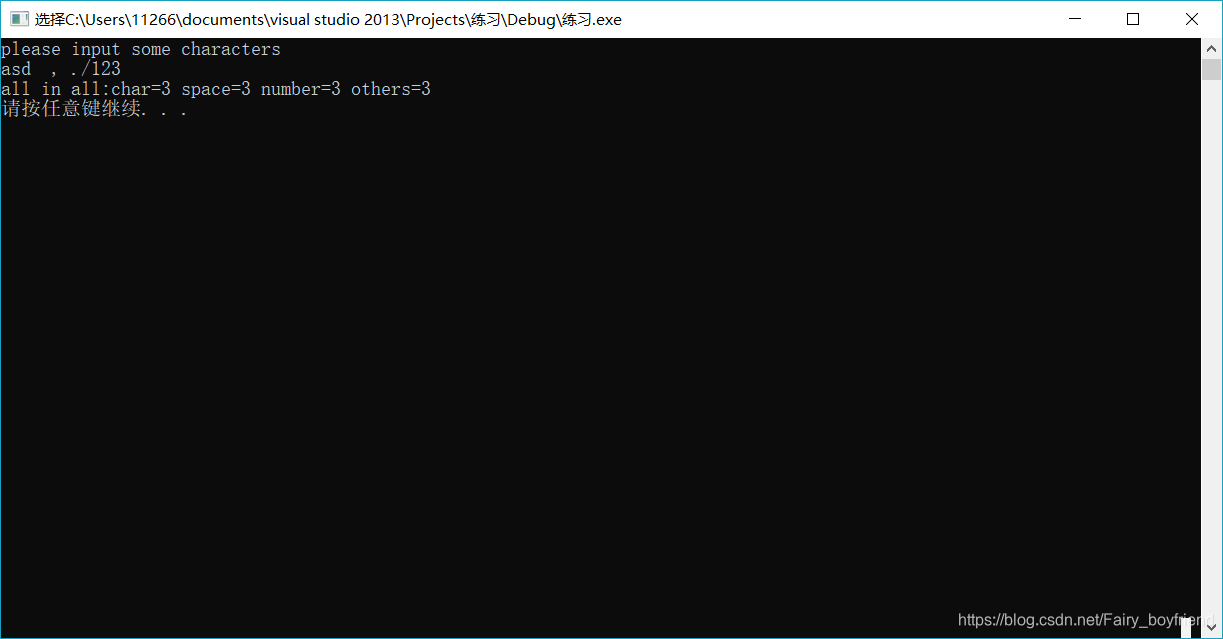
输出结果:




















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








