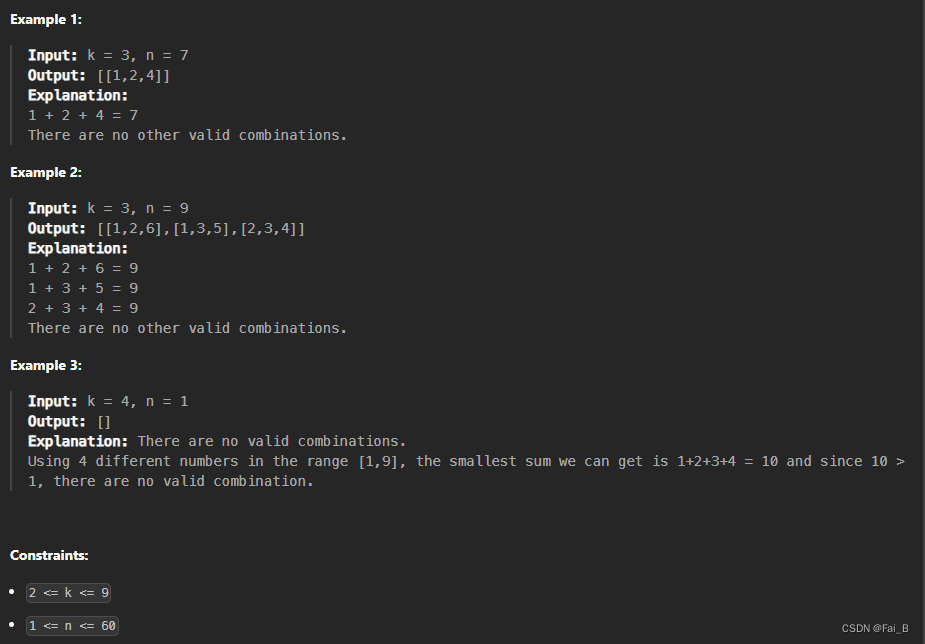
Find all valid combinations of k numbers that sum up to n such that the following conditions are true:
- Only numbers
1through9are used. - Each number is used at most once.
Return a list of all possible valid combinations. The list must not contain the same combination twice, and the combinations may be returned in any order.
my solution:
class Solution:
def combinationSum3(self, k: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result =[]
self.backtracking(k, n, [], result, 1)
return result
def backtracking(self, k, n, path, result, startindex):
if sum(path) == n and len(path) == k:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startindex, 10): # 超时 (startindex, 10 - (k-len(path)) + 1) ;因为sum 大于 target时候 没跳出循环,len会不断变大,for循环就是负数了
path.append(i)
self.backtracking(k, n, path, result, i+1)
path.pop()There is also a important pruning剪枝 place, when the number of individuals is not exceeded but the total number is exceeded, it returns directly
solution after pruning:
class Solution:
def combinationSum3(self, k: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result =[]
self.backtracking(k, n, [], result, 1)
return result
def backtracking(self, k, n, path, result, startindex):
if sum(path) > n: # for剪枝的要求
return
if sum(path) == n and len(path) == k:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startindex, 10 - (k-len(path)) + 1): #剪枝后
path.append(i)
self.backtracking(k, n, path, result, i+1)
path.pop()standard solution:
class Solution:
def combinationSum3(self, k: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
result = [] # 存放结果集
self.backtracking(n, k, 0, 1, [], result)
return result
def backtracking(self, targetSum, k, currentSum, startIndex, path, result):
if currentSum > targetSum: # 剪枝操作
return # 如果path的长度等于k但currentSum不等于targetSum,则直接返回
if len(path) == k:
if currentSum == targetSum:
result.append(path[:])
return
for i in range(startIndex, 9 - (k - len(path)) + 2): # 剪枝
currentSum += i # 处理
path.append(i) # 处理
self.backtracking(targetSum, k, currentSum, i + 1, path, result) # 注意i+1调整startIndex
currentSum -= i # 回溯
path.pop() # 回溯17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
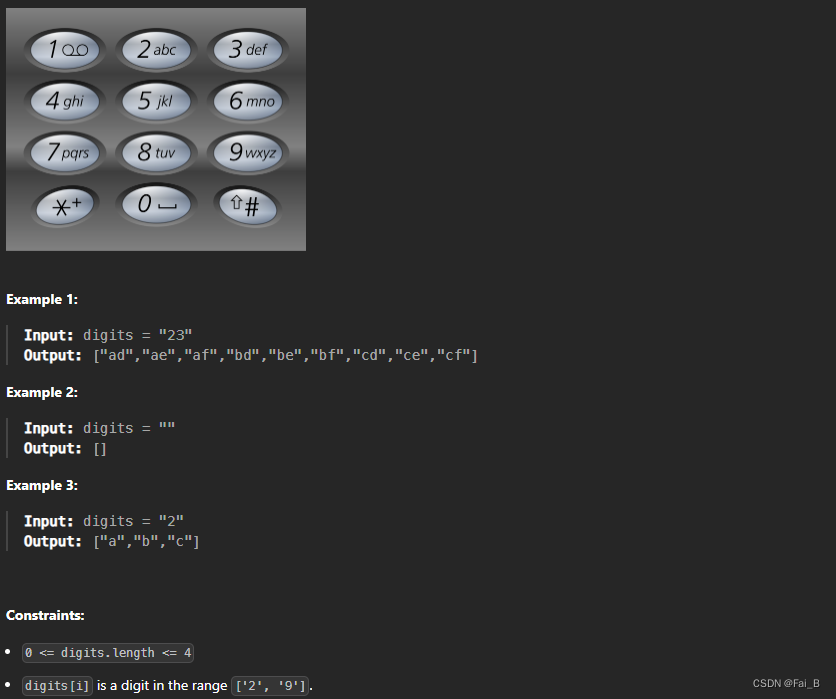
Given a string containing digits from 2-9 inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent. Return the answer in any order.
A mapping of digits to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.
def init : self. lettermap = [ ], self. result = [ ] , self.s =""
index: digits的index :Depth of the tree
backtracking:
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.s = ""
self.result = []
self.map =[
"", #0
"", #1
"abc",#2
"def",
"ghi",
"jkl",
"mno",
"pqrs",
"tuv",
"wxyz"
]
def backtracking(self, digits, index):
if len(self.s) == len(digits): # if index == len(digits)
self.result.append(self.s)
return # 这个return一定不能掉 ,下面的self.backtracking满足这个条件就直接执行 self.s = self.s[:-1]
digit = int(digits[index]) #Convert the number at the index to an integer
letters = self.map[digit] # Get the corresponding character set “abc”....
for letter in letters:
self.s += letter
self.backtracking(digits, index+1)
self.s = self.s[:-1] #Backtrack to remove the last added character
def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]:
if len(digits) == 0:
return self.result
self.backtracking(digits, 0)
return self.result



 文章描述了一个编程问题,要求找到所有由1到9的数字组成且和为n的有效组合,使用回溯算法(backtracking)实现,同时包含剪枝优化。另一个问题是将电话号码的数字转换为字母组合。
文章描述了一个编程问题,要求找到所有由1到9的数字组成且和为n的有效组合,使用回溯算法(backtracking)实现,同时包含剪枝优化。另一个问题是将电话号码的数字转换为字母组合。
















 217
217

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








