本文详细解析了Qwen3-VL视觉语言模型的源码实现,从图像预处理到模型输出的完整流程。重点分析了Qwen3VLProcessor处理图像数据、Qwen3VLModel融合文本与图像特征、以及Qwen3VLVision视觉编码器的实现。通过源码剖析,展示了模型如何将图像转为pixel_values,并与文本数据结合,最终通过语言模型生成输出,为理解多模态AI提供了实践指导。
前面不久 ,我写了一篇关于VLM的文章,不知道是不是内容不好还是标题的原因,导致大家好像不是很感兴趣,但是如果要知道Qwen3-VL的内部细节。如果基础不怎么牢固或者没有基础,那一篇还是需要看看的,了解视觉语言大模型(VLM),你需要知道哪些内容?,当然我也是认为大家看了这篇,才来看这边哈,这里也就不在重复一些知识了。不排除有些大佬可能有基础,跳过第一篇来看这个,也是可以。如果写的有不对的地方,也欢迎大家指正与批评。
视觉语言模型 (VLM) 是自回归 AI 模型,可将文本和图像处理为输入。在这一篇文章中我们也会详细的从源码来看Qwen3-VL模型怎么实现的。
写的很辛苦,动动小手,帮忙点赞、关注
Qwen3-VL源码解剖
首先我们来看下qwen3-vl源码有哪些文件
从上图可知,configuration_qwen3表示配置信息;modeling_qwen3表示整个多模态大模型的实现;processing_qwen3_vl表示图片处理;video_processing_qwen3_vl表示视频处理。老规矩,咱们还是从主类开始一步步分析,看看其背后的原理。
解剖之前,我们来看看Qwen3VLProcessor类,它是将我们输入的图片转为pixel的一个类。这个类是在processing_qwen3_vl中,从模型配置文件(preprocessor_config.json)可知,使用的视觉处理是Qwen2VLImageProcessorFast,也就是说,Qwen3-VL将图片转为pixel_value使用的是Qwen2-VL的处理器,具体代码如下:
def _preprocess(
self,
images: list["torch.Tensor"],
do_resize: bool,
size: SizeDict,
interpolation: Optional["F.InterpolationMode"],
do_rescale: bool,
rescale_factor: float,
do_normalize: bool,
image_mean: Optional[Union[float, list[float]]],
image_std: Optional[Union[float, list[float]]],
patch_size: int,
temporal_patch_size: int,
merge_size: int,
disable_grouping: Optional[bool],
return_tensors: Optional[Union[str, TensorType]],
**kwargs,
):
# Group images by size for batched resizing
grouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(images, disable_grouping=disable_grouping)
resized_images_grouped = {}
for shape, stacked_images in grouped_images.items():
height, width = stacked_images.shape[-2:]
if do_resize:
resized_height, resized_width = smart_resize(
height,
width,
factor=patch_size * merge_size,
min_pixels=size["shortest_edge"],
max_pixels=size["longest_edge"],
)
stacked_images = self.resize(
image=stacked_images,
size=SizeDict(height=resized_height, width=resized_width),
interpolation=interpolation,
)
resized_images_grouped[shape] = stacked_images
resized_images = reorder_images(resized_images_grouped, grouped_images_index)
# Group images by size for further processing
# Needed in case do_resize is False, or resize returns images with different sizes
grouped_images, grouped_images_index = group_images_by_shape(resized_images, disable_grouping=disable_grouping)
processed_images_grouped = {}
processed_grids = {}
for shape, stacked_images in grouped_images.items():
resized_height, resized_width = stacked_images.shape[-2:]
# Fused rescale and normalize
patches = self.rescale_and_normalize(
stacked_images, do_rescale, rescale_factor, do_normalize, image_mean, image_std
)
if patches.ndim == 4:
# add a temporal dimension if we have images
patches = patches.unsqueeze(1)
if patches.shape[1] % temporal_patch_size != 0:
repeats = patches[:, -1:].repeat(1, temporal_patch_size - 1, 1, 1, 1)
patches = torch.cat([patches, repeats], dim=1)
batch_size, grid_t, channel = patches.shape[:3]
grid_t = grid_t // temporal_patch_size
grid_h, grid_w = resized_height // patch_size, resized_width // patch_size
patches = patches.view(
batch_size,
grid_t,
temporal_patch_size,
channel,
grid_h // merge_size,
merge_size,
patch_size,
grid_w // merge_size,
merge_size,
patch_size,
)
# Reorder dimensions to group grid and patch information for subsequent flattening.
# (batch, grid_t, grid_h, grid_w, merge_h, merge_w, channel, temp_patch_size, patch_h, patch_w)
patches = patches.permute(0, 1, 4, 7, 5, 8, 3, 2, 6, 9)
flatten_patches = patches.reshape(
batch_size,
grid_t * grid_h * grid_w,
channel * temporal_patch_size * patch_size * patch_size,
)
processed_images_grouped[shape] = flatten_patches
processed_grids[shape] = [[grid_t, grid_h, grid_w]] * batch_size
processed_images = reorder_images(processed_images_grouped, grouped_images_index)
processed_grids = reorder_images(processed_grids, grouped_images_index)
pixel_values = torch.cat(processed_images, dim=0)
image_grid_thw = torch.tensor(processed_grids)
return BatchFeature(
data={"pixel_values": pixel_values, "image_grid_thw": image_grid_thw}, tensor_type=return_tensors
)
从最后的return可以看到是返回了pixel_values,这个数据就是给到Qwen3-VL模型的一个输入值。
因为主类没有提及这一块,所以先提前给大家看到这个过程,避免在后面看到pixel_values不知道怎么来的,其实这个过程也类似将text文本数据转为input_ids的过程。
解剖Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration类
这个类是整个Qwen3-VL模型的入口类,废话不多说,整个类的主流程如下所示。

从上图可知:
第一步:输入是需要有pixel\_value和input\_ids;
第二步:将图像和文本的输出给到Qwen3-VL模型;
第三步:通过lm\_head(注意:lm\_head就是一个线性层,从代码可以查看)输出logist,并给到loss func 拿到loss输出;
第四步:给到Qwen3VLCausalLMOutputWithPast同统一格式输出。
可以对着上面的图和步骤看下面代码,你会非常清晰。
class Qwen3VLForConditionalGeneration(Qwen3VLPreTrainedModel, GenerationMixin):
_checkpoint_conversion_mapping = {}
_tied_weights_keys = ["lm_head.weight"]
# Reference: fix gemma3 grad acc #37208
accepts_loss_kwargs = False
config: Qwen3VLConfig
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.model = Qwen3VLModel(config)
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(config.text_config.hidden_size, config.text_config.vocab_size, bias=False)
self.post_init()
def get_input_embeddings(self):
return self.model.get_input_embeddings()
def set_input_embeddings(self, value):
self.model.set_input_embeddings(value)
def set_decoder(self, decoder):
self.model.set_decoder(decoder)
def get_decoder(self):
return self.model.get_decoder()
def get_video_features(
self, pixel_values_videos: torch.FloatTensor, video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None
):
return self.model.get_video_features(pixel_values_videos, video_grid_thw)
def get_image_features(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None):
return self.model.get_image_features(pixel_values, image_grid_thw)
# Make modules available through conditional class for BC
@property
def language_model(self):
return self.model.language_model
@property
def visual(self):
return self.model.visual
@can_return_tuple
@auto_docstring
def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
pixel_values_videos: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
logits_to_keep: Union[int, torch.Tensor] = 0,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> Union[tuple, Qwen3VLCausalLMOutputWithPast]:
r"""
labels (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
Labels for computing the masked language modeling loss. Indices should either be in `[0, ...,
config.vocab_size]` or -100 (see `input_ids` docstring). Tokens with indices set to `-100` are ignored
(masked), the loss is only computed for the tokens with labels in `[0, ..., config.vocab_size]`.
image_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_images, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each image in LLM.
video_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_videos, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each video in LLM.
Example:
TODO: Add example
"""
outputs = self.model(
input_ids=input_ids,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
pixel_values_videos=pixel_values_videos,
image_grid_thw=image_grid_thw,
video_grid_thw=video_grid_thw,
position_ids=position_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
cache_position=cache_position,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = outputs[0]
# Only compute necessary logits, and do not upcast them to float if we are not computing the loss
slice_indices = slice(-logits_to_keep, None) if isinstance(logits_to_keep, int) else logits_to_keep
logits = self.lm_head(hidden_states[:, slice_indices, :])
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss = self.loss_function(logits=logits, labels=labels, vocab_size=self.config.text_config.vocab_size)
return Qwen3VLCausalLMOutputWithPast(
loss=loss,
logits=logits,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
rope_deltas=outputs.rope_deltas,
)
接下来我们就来看看Qwen3VLModel,它是怎么处理pixel和input\_ids的。
解剖Qwen3VLModel类
这个类相对复杂点,我们也只针对主流程进行讲解,如果涉及到其他的处理,也会讲解,详细的可以看下面的图,便于理解。
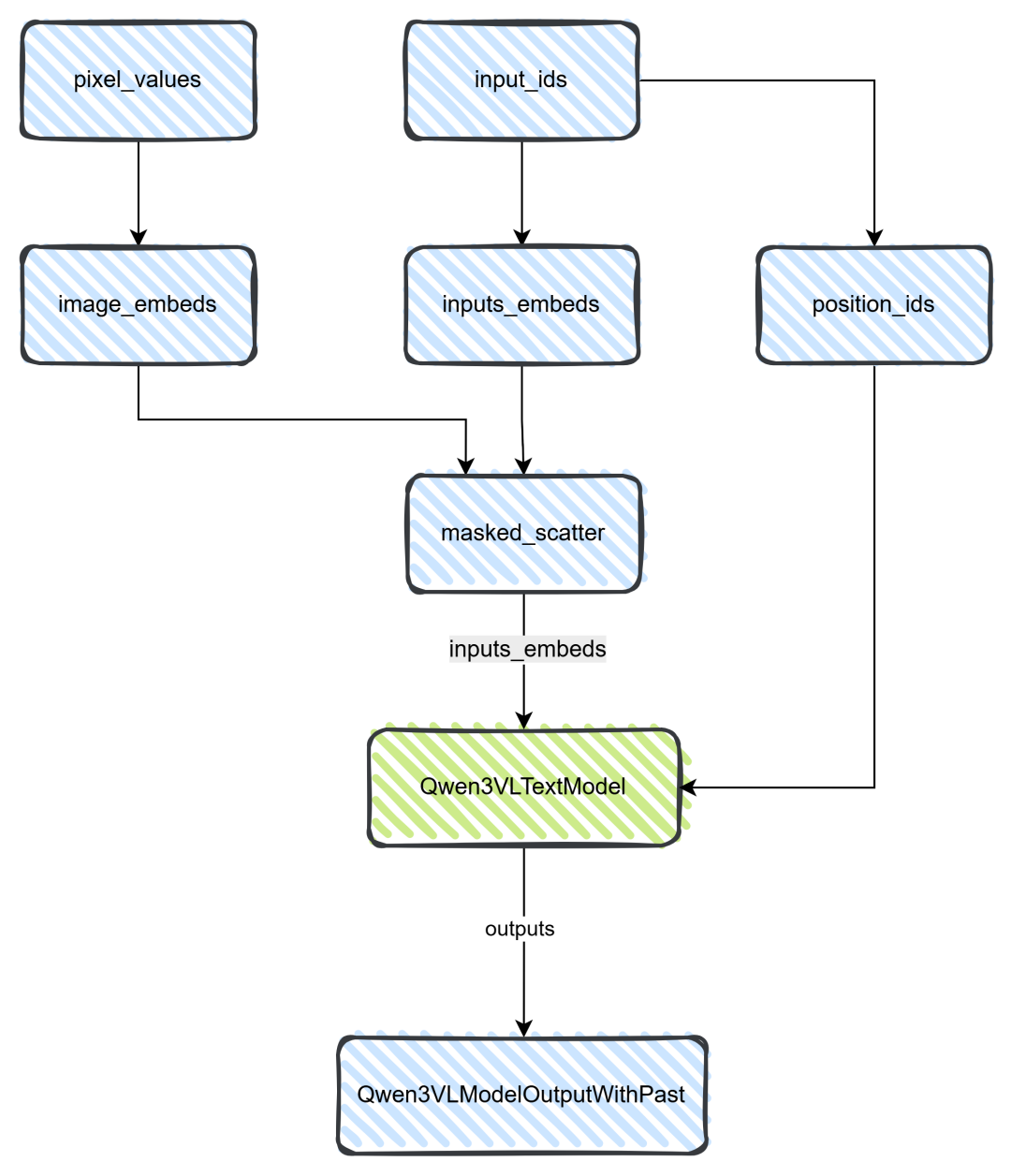
从上图可知:
第一步:piexl_value会通过get_image_features得到image_embeds;input_ids则通过get_input_embeddings得到inputs_embeds;
第二步:masked_scatter则将image_embeds嵌入到input_ids当中(<|im_start|>和 <|im_end|>),得到一个新的inputs_embeds;
第三步:inputs_embeds给到Qwen3VLTextModel(注意:这是一个大语言模型);
第四步:大语言模型的输出给到Qwen3VLModelOutputWithPast类,统一规则输出。
class Qwen3VLModel(Qwen3VLPreTrainedModel):
base_model_prefix = ""
_checkpoint_conversion_mapping = {}
# Reference: fix gemma3 grad acc #37208
accepts_loss_kwargs = False
config: Qwen3VLConfig
_no_split_modules = ["Qwen3VLTextDecoderLayer", "Qwen3VLVisionBlock"]
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.visual = Qwen3VLVisionModel._from_config(config.vision_config)
self.language_model = Qwen3VLTextModel._from_config(config.text_config)
self.rope_deltas = None # cache rope_deltas here
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def get_input_embeddings(self):
return self.language_model.get_input_embeddings()
def set_input_embeddings(self, value):
self.language_model.set_input_embeddings(value)
def set_decoder(self, decoder):
self.language_model = decoder
def get_decoder(self):
return self.language_model
def get_rope_index(
self,
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""Different from the original implementation, Qwen3VL use timestamps rather than absolute time position ids."""
# Since we use timestamps to seperate videos, like <t1> <vision_start> <frame1> <vision_end> <t2> <vision_start> <frame2> <vision_end>, the video_grid_thw should also be split
if video_grid_thw is not None:
video_grid_thw = torch.repeat_interleave(video_grid_thw, video_grid_thw[:, 0], dim=0)
video_grid_thw[:, 0] = 1
spatial_merge_size = self.config.vision_config.spatial_merge_size
image_token_id = self.config.image_token_id
video_token_id = self.config.video_token_id
vision_start_token_id = self.config.vision_start_token_id
mrope_position_deltas = []
if input_ids is not None and (image_grid_thw is not None or video_grid_thw is not None):
total_input_ids = input_ids
if attention_mask is None:
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(total_input_ids)
position_ids = torch.ones(
3,
input_ids.shape[0],
input_ids.shape[1],
dtype=input_ids.dtype,
device=input_ids.device,
)
image_index, video_index = 0, 0
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(total_input_ids.device)
for i, input_ids in enumerate(total_input_ids):
input_ids = input_ids[attention_mask[i] == 1]
image_nums, video_nums = 0, 0
vision_start_indices = torch.argwhere(input_ids == vision_start_token_id).squeeze(1)
vision_tokens = input_ids[vision_start_indices + 1]
image_nums = (vision_tokens == image_token_id).sum()
video_nums = (vision_tokens == video_token_id).sum()
input_tokens = input_ids.tolist()
llm_pos_ids_list: list = []
st = 0
remain_images, remain_videos = image_nums, video_nums
for _ in range(image_nums + video_nums):
if image_token_id in input_tokens and remain_images > 0:
ed_image = input_tokens.index(image_token_id, st)
else:
ed_image = len(input_tokens) + 1
if video_token_id in input_tokens and remain_videos > 0:
ed_video = input_tokens.index(video_token_id, st)
else:
ed_video = len(input_tokens) + 1
if ed_image < ed_video:
t, h, w = (
image_grid_thw[image_index][0],
image_grid_thw[image_index][1],
image_grid_thw[image_index][2],
)
image_index += 1
remain_images -= 1
ed = ed_image
else:
t, h, w = (
video_grid_thw[video_index][0],
video_grid_thw[video_index][1],
video_grid_thw[video_index][2],
)
video_index += 1
remain_videos -= 1
ed = ed_video
llm_grid_t, llm_grid_h, llm_grid_w = (
t.item(),
h.item() // spatial_merge_size,
w.item() // spatial_merge_size,
)
text_len = ed - st
st_idx = llm_pos_ids_list[-1].max() + 1 if len(llm_pos_ids_list) > 0 else 0
llm_pos_ids_list.append(torch.arange(text_len).view(1, -1).expand(3, -1) + st_idx)
# t_index is always 0 because llm_grid_t is always 1 (we use timestamps to encode the temporal information for videos)
t_index = torch.arange(llm_grid_t).view(-1, 1).expand(-1, llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w).flatten()
h_index = torch.arange(llm_grid_h).view(1, -1, 1).expand(llm_grid_t, -1, llm_grid_w).flatten()
w_index = torch.arange(llm_grid_w).view(1, 1, -1).expand(llm_grid_t, llm_grid_h, -1).flatten()
llm_pos_ids_list.append(torch.stack([t_index, h_index, w_index]) + text_len + st_idx)
st = ed + llm_grid_t * llm_grid_h * llm_grid_w
if st < len(input_tokens):
st_idx = llm_pos_ids_list[-1].max() + 1 if len(llm_pos_ids_list) > 0 else 0
text_len = len(input_tokens) - st
llm_pos_ids_list.append(torch.arange(text_len).view(1, -1).expand(3, -1) + st_idx)
llm_positions = torch.cat(llm_pos_ids_list, dim=1).reshape(3, -1)
position_ids[..., i, attention_mask[i] == 1] = llm_positions.to(position_ids.device)
mrope_position_deltas.append(llm_positions.max() + 1 - len(total_input_ids[i]))
mrope_position_deltas = torch.tensor(mrope_position_deltas, device=input_ids.device).unsqueeze(1)
return position_ids, mrope_position_deltas
else:
if attention_mask is not None:
position_ids = attention_mask.long().cumsum(-1) - 1
position_ids.masked_fill_(attention_mask == 0, 1)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand(3, -1, -1).to(attention_mask.device)
max_position_ids = position_ids.max(0, keepdim=False)[0].max(-1, keepdim=True)[0]
mrope_position_deltas = max_position_ids + 1 - attention_mask.shape[-1]
else:
position_ids = (
torch.arange(input_ids.shape[1], device=input_ids.device)
.view(1, 1, -1)
.expand(3, input_ids.shape[0], -1)
)
mrope_position_deltas = torch.zeros(
[input_ids.shape[0], 1],
device=input_ids.device,
dtype=input_ids.dtype,
)
return position_ids, mrope_position_deltas
def get_video_features(
self, pixel_values_videos: torch.FloatTensor, video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None
):
"""
Encodes videos into continuous embeddings that can be forwarded to the language model. The deepstack visual features are also returned.
Args:
pixel_values_videos (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)`):
The tensors corresponding to the input videos.
video_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_videos, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each video in LLM.
"""
# Same implementation as for images
return self.get_image_features(pixel_values_videos, video_grid_thw)
def get_image_features(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None):
"""
Encodes images into continuous embeddings that can be forwarded to the language model. The deepstack visual features are also returned.
Args:
pixel_values (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size)`):
The tensors corresponding to the input images.
image_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_images, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each image in LLM.
"""
pixel_values = pixel_values.type(self.visual.dtype)
image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds = self.visual(pixel_values, grid_thw=image_grid_thw)
split_sizes = (image_grid_thw.prod(-1) // self.visual.spatial_merge_size**2).tolist()
image_embeds = torch.split(image_embeds, split_sizes)
return image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds
def get_placeholder_mask(
self,
input_ids: torch.LongTensor,
inputs_embeds: torch.FloatTensor,
image_features: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
video_features: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
):
"""
Obtains multimodal placeholder mask from `input_ids` or `inputs_embeds`, and checks that the placeholder token count is
equal to the length of multimodal features. If the lengths are different, an error is raised.
"""
if input_ids is None:
special_image_mask = inputs_embeds == self.get_input_embeddings()(
torch.tensor(self.config.image_token_id, dtype=torch.long, device=inputs_embeds.device)
)
special_image_mask = special_image_mask.all(-1)
special_video_mask = inputs_embeds == self.get_input_embeddings()(
torch.tensor(self.config.video_token_id, dtype=torch.long, device=inputs_embeds.device)
)
special_video_mask = special_video_mask.all(-1)
else:
special_image_mask = input_ids == self.config.image_token_id
special_video_mask = input_ids == self.config.video_token_id
n_image_tokens = special_image_mask.sum()
special_image_mask = special_image_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(inputs_embeds).to(inputs_embeds.device)
if image_features is not None and inputs_embeds[special_image_mask].numel() != image_features.numel():
raise ValueError(
f"Image features and image tokens do not match: tokens: {n_image_tokens}, features {image_features.shape[0]}"
)
n_video_tokens = special_video_mask.sum()
special_video_mask = special_video_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(inputs_embeds).to(inputs_embeds.device)
if video_features is not None and inputs_embeds[special_video_mask].numel() != video_features.numel():
raise ValueError(
f"Videos features and video tokens do not match: tokens: {n_video_tokens}, features {video_features.shape[0]}"
)
return special_image_mask, special_video_mask
@auto_docstring
@can_return_tuple
def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
pixel_values: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
pixel_values_videos: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> Union[tuple, Qwen3VLModelOutputWithPast]:
r"""
image_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_images, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each image in LLM.
video_grid_thw (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(num_videos, 3)`, *optional*):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each video in LLM.
"""
if (input_ids is None) ^ (inputs_embeds is not None):
raise ValueError("You must specify exactly one of input_ids or inputs_embeds")
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.get_input_embeddings()(input_ids)
image_mask = None
video_mask = None
if pixel_values is not None:
image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds = self.get_image_features(pixel_values, image_grid_thw)
image_embeds = torch.cat(image_embeds, dim=0).to(inputs_embeds.device, inputs_embeds.dtype)
image_mask, _ = self.get_placeholder_mask(
input_ids, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, image_features=image_embeds
)
inputs_embeds = inputs_embeds.masked_scatter(image_mask, image_embeds)
if pixel_values_videos is not None:
video_embeds, deepstack_video_embeds = self.get_video_features(pixel_values_videos, video_grid_thw)
video_embeds = torch.cat(video_embeds, dim=0).to(inputs_embeds.device, inputs_embeds.dtype)
_, video_mask = self.get_placeholder_mask(
input_ids, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, video_features=video_embeds
)
inputs_embeds = inputs_embeds.masked_scatter(video_mask, video_embeds)
visual_pos_masks = None
deepstack_visual_embeds = None
if image_mask is not None and video_mask is not None:
# aggregate visual_pos_masks and deepstack_visual_embeds
image_mask = image_mask[..., 0]
video_mask = video_mask[..., 0]
visual_pos_masks = image_mask | video_mask
deepstack_visual_embeds = []
image_mask_joint = image_mask[visual_pos_masks]
video_mask_joint = video_mask[visual_pos_masks]
for img_embed, vid_embed in zip(deepstack_image_embeds, deepstack_video_embeds):
embed_joint = img_embed.new_zeros(visual_pos_masks.sum(), img_embed.shape[-1]).to(img_embed.device)
embed_joint[image_mask_joint, :] = img_embed
embed_joint[video_mask_joint, :] = vid_embed
deepstack_visual_embeds.append(embed_joint)
elif image_mask is not None:
image_mask = image_mask[..., 0]
visual_pos_masks = image_mask
deepstack_visual_embeds = deepstack_image_embeds
elif video_mask is not None:
video_mask = video_mask[..., 0]
visual_pos_masks = video_mask
deepstack_visual_embeds = deepstack_video_embeds
if position_ids is None:
attention_mask_tensor = (
attention_mask if not isinstance(attention_mask, dict) else attention_mask["full_attention"]
)
if attention_mask_tensor is not None and attention_mask_tensor.ndim == 4:
attention_mask_tensor = torch.diagonal(attention_mask_tensor[:, 0], dim1=1, dim2=2)
# Only apply conversion for floating point tensors (inverted masks)
if attention_mask_tensor.dtype.is_floating_point:
attention_mask_tensor = attention_mask_tensor / torch.finfo(attention_mask_tensor.dtype).min
attention_mask_tensor = (1.0 - attention_mask_tensor).int()
# Calculate RoPE index once per generation in the pre-fill stage only.
# When compiling, we can't check tensor values thus we check only input length
# It is safe to assume that `length!=1` means we're in pre-fill because compiled
# models currently cannot do asssisted decoding
prefill_compiled_stage = is_torchdynamo_compiling() and (
(input_ids is not None and input_ids.shape[1] != 1)
or (inputs_embeds is not None and inputs_embeds.shape[1] != 1)
)
prefill_noncompiled_stage = not is_torchdynamo_compiling() and (
(cache_position is not None and cache_position[0] == 0)
or (past_key_values is None or past_key_values.get_seq_length() == 0)
)
if (prefill_compiled_stage or prefill_noncompiled_stage) or self.rope_deltas is None:
position_ids, rope_deltas = self.get_rope_index(
input_ids,
image_grid_thw,
video_grid_thw,
attention_mask=attention_mask_tensor,
)
self.rope_deltas = rope_deltas
# then use the prev pre-calculated rope-deltas to get the correct position ids
else:
batch_size, seq_length, _ = inputs_embeds.shape
delta = (
(cache_position[0] + self.rope_deltas).to(inputs_embeds.device)
if cache_position is not None
else 0
)
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, device=inputs_embeds.device)
position_ids = position_ids.view(1, -1).expand(batch_size, -1)
if cache_position is not None: # otherwise `deltas` is an int `0`
delta = delta.repeat_interleave(batch_size // delta.shape[0], dim=0)
position_ids = position_ids.add(delta)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand(3, -1, -1)
outputs = self.language_model(
input_ids=None,
position_ids=position_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
cache_position=cache_position,
visual_pos_masks=visual_pos_masks,
deepstack_visual_embeds=deepstack_visual_embeds,
**kwargs,
)
return Qwen3VLModelOutputWithPast(
last_hidden_state=outputs.last_hidden_state,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
rope_deltas=self.rope_deltas,
)
从第三步可知,至此图片和文本数据已经嵌入在一起,给到大语言模型的输入当中,后面的流程就是按大语言模型的流程走了,没有其他的特殊情况了。如果你也看到这里了,也不清楚后续的流程,可以看看我写的这篇文章:扒开大模型外衣:手搓一个Qwen3。
解剖Qwen3VLVisionModel视觉编码器
以为结束了?哈哈,还没,咱们再讲解下Qwen3-VL重要的一环视觉编码器。Qwen3-VL的视觉编码器没有使用clip或者siglip这种现有的编码器,而是自己重写了一个编码器。
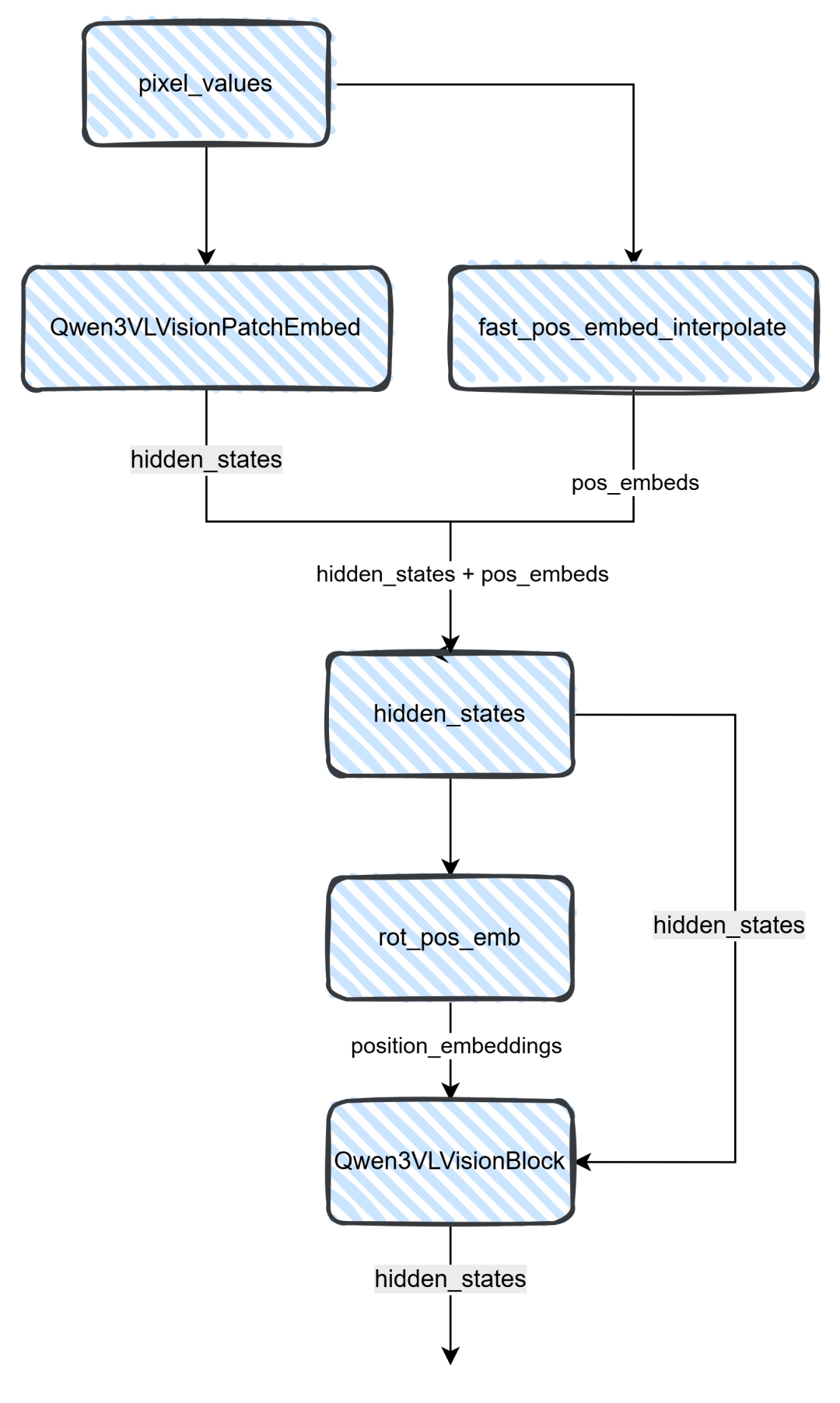
从上图可知,pixel通过Qwen3VLVisionPatchEmbed将图片转为hidden_states,而Qwen3VLVisionPatchEmbed则通过一个3维卷积来实现,然后将图片hidden_states信息(注意:图片patch为16)和位置编码结合,整合之后给到Qwen3VLVisionBlock模块,这个模块是一个Attention模块,它具有27层,具体的实现可以看下图。
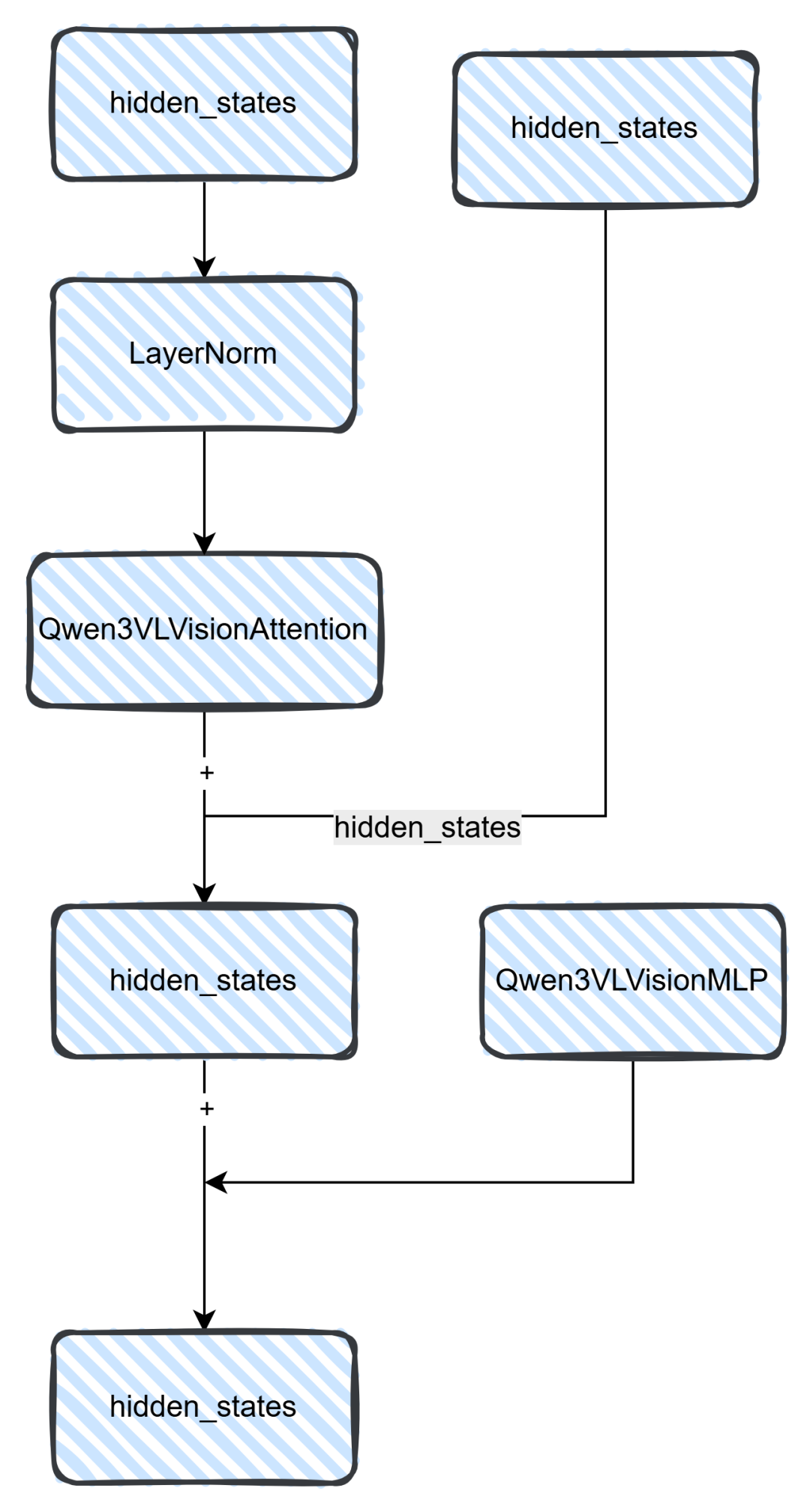
上图就是Block模块的具体内容,最后通过hidden_states和MLP层相加拿到最后的hidden_states。其代码实现可以看下面,Attention里面这里就不做过多的解析,无非就是QKV的计算,这里之前的文章有介绍,详细可以看这篇图解Qwen3 MoE模型源码或者一文读懂大模型使用的旋转位置编码(ROPE)。
lass Qwen3VLVisionModel(Qwen3VLPreTrainedModel):
config: Qwen3VLVisionConfig
_no_split_modules = ["Qwen3VLVisionBlock"]
def __init__(self, config, *inputs, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(config, *inputs, **kwargs)
self.spatial_merge_size = config.spatial_merge_size
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
self.spatial_merge_unit = self.spatial_merge_size * self.spatial_merge_size
self.patch_embed = Qwen3VLVisionPatchEmbed(
config=config,
)
self.pos_embed = nn.Embedding(config.num_position_embeddings, config.hidden_size)
self.num_grid_per_side = int(config.num_position_embeddings**0.5)
head_dim = config.hidden_size // config.num_heads
self.rotary_pos_emb = Qwen3VLVisionRotaryEmbedding(head_dim // 2)
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([Qwen3VLVisionBlock(config) for _ in range(config.depth)])
self.merger = Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger(
config=config,
use_postshuffle_norm=False,
)
self.deepstack_visual_indexes = config.deepstack_visual_indexes
self.deepstack_merger_list = nn.ModuleList(
[
Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger(
config=config,
use_postshuffle_norm=True,
)
for _ in range(len(config.deepstack_visual_indexes))
]
)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
def rot_pos_emb(self, grid_thw: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
merge_size = self.spatial_merge_size
max_hw = int(grid_thw[:, 1:].max().item())
freq_table = self.rotary_pos_emb(max_hw) # (max_hw, dim // 2)
device = freq_table.device
total_tokens = int(torch.prod(grid_thw, dim=1).sum().item())
pos_ids = torch.empty((total_tokens, 2), dtype=torch.long, device=device)
offset = 0
for num_frames, height, width in grid_thw:
merged_h, merged_w = height // merge_size, width // merge_size
block_rows = torch.arange(merged_h, device=device) # block row indices
block_cols = torch.arange(merged_w, device=device) # block col indices
intra_row = torch.arange(merge_size, device=device) # intra-block row offsets
intra_col = torch.arange(merge_size, device=device) # intra-block col offsets
# Compute full-resolution positions
row_idx = block_rows[:, None, None, None] * merge_size + intra_row[None, None, :, None]
col_idx = block_cols[None, :, None, None] * merge_size + intra_col[None, None, None, :]
row_idx = row_idx.expand(merged_h, merged_w, merge_size, merge_size).reshape(-1)
col_idx = col_idx.expand(merged_h, merged_w, merge_size, merge_size).reshape(-1)
coords = torch.stack((row_idx, col_idx), dim=-1)
if num_frames > 1:
coords = coords.repeat(num_frames, 1)
num_tokens = coords.shape[0]
pos_ids[offset : offset + num_tokens] = coords
offset += num_tokens
embeddings = freq_table[pos_ids] # lookup rotary embeddings
embeddings = embeddings.flatten(1)
return embeddings
def fast_pos_embed_interpolate(self, grid_thw):
grid_ts, grid_hs, grid_ws = grid_thw[:, 0], grid_thw[:, 1], grid_thw[:, 2]
idx_list = [[] for _ in range(4)]
weight_list = [[] for _ in range(4)]
for t, h, w in zip(grid_ts, grid_hs, grid_ws):
h_idxs = torch.linspace(0, self.num_grid_per_side - 1, h)
w_idxs = torch.linspace(0, self.num_grid_per_side - 1, w)
h_idxs_floor = h_idxs.int()
w_idxs_floor = w_idxs.int()
h_idxs_ceil = (h_idxs.int() + 1).clip(max=self.num_grid_per_side - 1)
w_idxs_ceil = (w_idxs.int() + 1).clip(max=self.num_grid_per_side - 1)
dh = h_idxs - h_idxs_floor
dw = w_idxs - w_idxs_floor
base_h = h_idxs_floor * self.num_grid_per_side
base_h_ceil = h_idxs_ceil * self.num_grid_per_side
indices = [
(base_h[None].T + w_idxs_floor[None]).flatten(),
(base_h[None].T + w_idxs_ceil[None]).flatten(),
(base_h_ceil[None].T + w_idxs_floor[None]).flatten(),
(base_h_ceil[None].T + w_idxs_ceil[None]).flatten(),
]
weights = [
((1 - dh)[None].T * (1 - dw)[None]).flatten(),
((1 - dh)[None].T * dw[None]).flatten(),
(dh[None].T * (1 - dw)[None]).flatten(),
(dh[None].T * dw[None]).flatten(),
]
for i in range(4):
idx_list[i].extend(indices[i].tolist())
weight_list[i].extend(weights[i].tolist())
idx_tensor = torch.tensor(idx_list, dtype=torch.long, device=self.pos_embed.weight.device)
weight_tensor = torch.tensor(
weight_list, dtype=self.pos_embed.weight.dtype, device=self.pos_embed.weight.device
)
pos_embeds = self.pos_embed(idx_tensor) * weight_tensor[:, :, None]
patch_pos_embeds = pos_embeds[0] + pos_embeds[1] + pos_embeds[2] + pos_embeds[3]
patch_pos_embeds = patch_pos_embeds.split([h * w for h, w in zip(grid_hs, grid_ws)])
patch_pos_embeds_permute = []
merge_size = self.config.spatial_merge_size
for pos_embed, t, h, w in zip(patch_pos_embeds, grid_ts, grid_hs, grid_ws):
pos_embed = pos_embed.repeat(t, 1)
pos_embed = (
pos_embed.view(t, h // merge_size, merge_size, w // merge_size, merge_size, -1)
.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5)
.flatten(0, 4)
)
patch_pos_embeds_permute.append(pos_embed)
patch_pos_embeds = torch.cat(patch_pos_embeds_permute)
return patch_pos_embeds
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, grid_thw: torch.Tensor, **kwargs) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Args:
hidden_states (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(seq_len, hidden_size)`):
The final hidden states of the model.
grid_thw (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(num_images_or_videos, 3)`):
The temporal, height and width of feature shape of each image in LLM.
Returns:
`torch.Tensor`: hidden_states.
"""
hidden_states = self.patch_embed(hidden_states)
pos_embeds = self.fast_pos_embed_interpolate(grid_thw)
hidden_states = hidden_states + pos_embeds
rotary_pos_emb = self.rot_pos_emb(grid_thw)
seq_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(seq_len, -1)
rotary_pos_emb = rotary_pos_emb.reshape(seq_len, -1)
emb = torch.cat((rotary_pos_emb, rotary_pos_emb), dim=-1)
position_embeddings = (emb.cos(), emb.sin())
cu_seqlens = torch.repeat_interleave(grid_thw[:, 1] * grid_thw[:, 2], grid_thw[:, 0]).cumsum(
dim=0,
# Select dtype based on the following factors:
# - FA2 requires that cu_seqlens_q must have dtype int32
# - torch.onnx.export requires that cu_seqlens_q must have same dtype as grid_thw
# See https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/34852 for more information
dtype=grid_thw.dtype if torch.jit.is_tracing() else torch.int32,
)
cu_seqlens = F.pad(cu_seqlens, (1, 0), value=0)
deepstack_feature_lists = []
for layer_num, blk in enumerate(self.blocks):
hidden_states = blk(
hidden_states,
cu_seqlens=cu_seqlens,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
if layer_num in self.deepstack_visual_indexes:
deepstack_feature = self.deepstack_merger_list[self.deepstack_visual_indexes.index(layer_num)](
hidden_states
)
deepstack_feature_lists.append(deepstack_feature)
hidden_states = self.merger(hidden_states)
return hidden_states, deepstack_feature_lists
从以上的描述,我相信大家对Qwen3-VL模型结构有一定了解了,如果还有不懂得欢迎大家留言一起讨论。
如何学习AI大模型 ?
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。【保证100%免费】🆓
优快云粉丝独家福利
这份完整版的 AI 大模型学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以扫描下方二维码&点击下方优快云官方认证链接免费领取 【保证100%免费】

读者福利: 👉👉优快云大礼包:《最新AI大模型学习资源包》免费分享 👈👈
对于0基础小白入门:
如果你是零基础小白,想快速入门大模型是可以考虑的。
一方面是学习时间相对较短,学习内容更全面更集中。
二方面是可以根据这些资料规划好学习计划和方向。
👉1.大模型入门学习思维导图👈
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
对于从来没有接触过AI大模型的同学,我们帮你准备了详细的学习成长路线图&学习规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习路线,大家跟着这个大的方向学习准没问题。(全套教程文末领取哈)

👉2.AGI大模型配套视频👈
很多朋友都不喜欢晦涩的文字,我也为大家准备了视频教程,每个章节都是当前板块的精华浓缩。


👉3.大模型实际应用报告合集👈
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。(全套教程文末领取哈)

👉4.大模型实战项目&项目源码👈
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起做,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战项目来学习。(全套教程文末领取哈)

👉5.大模型经典学习电子书👈
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点。这些大型预训练模型,如GPT-3、BERT、XLNet等,以其强大的语言理解和生成能力,正在改变我们对人工智能的认识。 那以下这些PDF籍就是非常不错的学习资源。(全套教程文末领取哈)

👉6.大模型面试题&答案👈
截至目前大模型已经超过200个,在大模型纵横的时代,不仅大模型技术越来越卷,就连大模型相关的岗位和面试也开始越来越卷了。为了让大家更容易上车大模型算法赛道,我总结了大模型常考的面试题。(全套教程文末领取哈)

为什么分享这些资料?
只要你是真心想学AI大模型,我这份资料就可以无偿分享给你学习,我国在这方面的相关人才比较紧缺,大模型行业确实也需要更多的有志之士加入进来,我也真心希望帮助大家学好这门技术,如果日后有什么学习上的问题,欢迎找我交流,有技术上面的问题,我是很愿意去帮助大家的!
这些资料真的有用吗?
这份资料由我和鲁为民博士共同整理,鲁为民博士先后获得了北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位,在包括IEEE Transactions等学术期刊和诸多国际会议上发表了超过50篇学术论文、取得了多项美国和中国发明专利,同时还斩获了吴文俊人工智能科学技术奖。目前我正在和鲁博士共同进行人工智能的研究。
资料内容涵盖了从入门到进阶的各类视频教程和实战项目,无论你是小白还是有些技术基础的,这份资料都绝对能帮助你提升薪资待遇,转行大模型岗位。


优快云粉丝独家福利
这份完整版的 AI 大模型学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以扫描下方二维码&点击下方优快云官方认证链接免费领取 【保证100%免费】

读者福利: 👉👉优快云大礼包:《最新AI大模型学习资源包》免费分享 👈👈
 Qwen3-VL源码解析与多模态AI入门
Qwen3-VL源码解析与多模态AI入门





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








