*************
C++
topic: 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
*************
Give the topic an inspection.
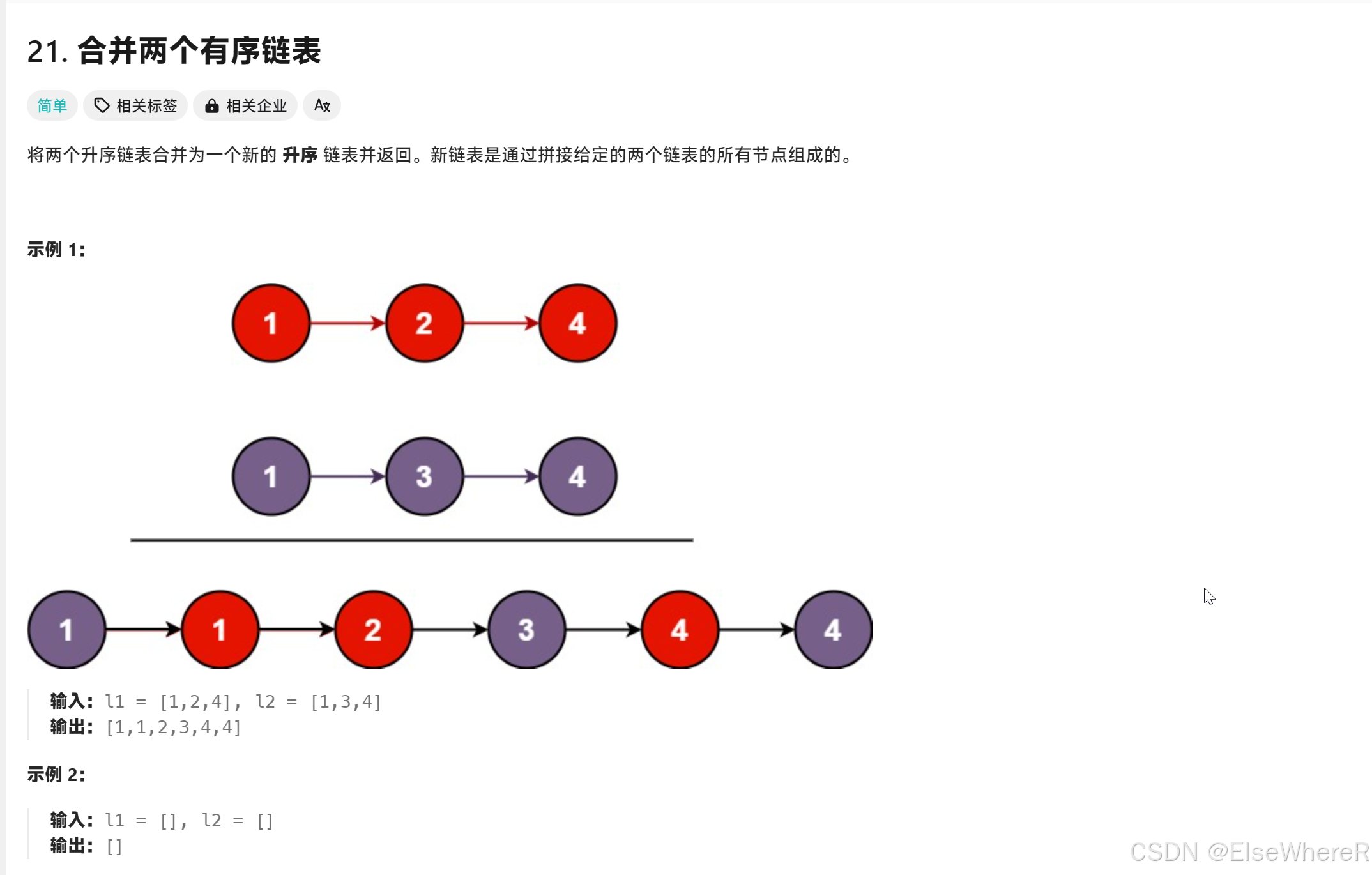 |
Linked list puzzles me for nearly a week. Do you have ever seen genius? Gine my primary school a glance that I have two mates, one boy and one girl. I love that girl of course because she is more beautiful at that time. You know in our 10 ~ 13 years, girls have a taller body. We were at the same class almost everyday. And we are trained to take part in Mathematical Olympiad. I remember that in my 4th grade, one exam, they got the top while I get nothing. The exam is really complex and they almost get the full mark.During my colluge, not in my school, but is one of my friend, he can use the concept while he first touched it. I am not one of them, I have to learn basic for many times and again and again. I accept that I have to learn many times and it doesnot borth me anymore. So just practise the basic.
还是会想到小学暑假的那个下午,当时仗着自己一点点数学上的天赋,进入奥数班学习,班上有个女孩子,黄黄的头发,高高的鼻梁,大大的眼睛。很奇怪的是,黄头发看起来营养不良,但是她却有着运动员一样的体态,饱满而紧实。数学上她几乎就是看一眼就会。做过数学的各位应该有种状态,一道题在你满前,看一眼就会的感觉很少在我身上发生过,特别是试卷的最后几题。那时候小学已经学了二元一次方程的我自诩天才,碾压那些还没学一元一次方程的同学们,我觉得我真的有天赋,我是个天才。有一次老师讲了求导,我当时听得都快睡着了,因为根本不会。后来放学的时候,我走在她旁边下楼梯,她突然回过头来,忽闪着大大的眼睛,问我“刚刚老师讲的加速度的求导公式是什么来着?”我看着阳光透过她的自然卷,将她的发丝点亮,我那清澈的没有被知识污染过的脑子什么也记不起来,现在回想起来,还是觉得那一刻我的笨拙。
Define the structure of linked list.
链表就像火车:
首先得有一个火车头Head,;
然后给第一节车厢装货,相当于存储数据;
其次将车厢与火车头相连,相当于指针指向下一个节点。
创建车厢 → 装货 → 连接到前一个车厢;
struct Node
{
int data; // 数据域,存储数据
Node* next; // 指针域,指向下一个节点
};
void creatLinked(void)
{
// 创建链表节点并连接
Node* head = new Node; // 创建头节点
head->data = 1; // 给头节点赋值
head->next = nullptr; // 初始化头节点的指针域为nullptr
Node* node2 = new Node;
node2->data = 2;
node2->next = nullptr;
head->next = node2; // 将头节点与第二个节点连接
Node* node3 = new Node;
node3->data = 3;
node3->next = nullptr;
node2->next = node3; // 将第二个节点与第三个节点连接
Node* node4 = new Node;
node4->data = 4;
node4->next = nullptr;
node3->next = node4; // 将第三个节点与第四个节点连接
Node* node5 = new Node;
node5->data = 5;
node5->next = nullptr;
node4->next = node5; // 将第四个节点与第五个节点连接
}But for better code, use constructor.
// 定义链表节点结构体,并包含构造函数
struct Node
{
int data; // 数据域
Node* next; // 指针域,指向下一个节点
// 构造函数,用于初始化节点
Node(int value) : data(value), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 函数:创建1→2→3→4→5的链表
Node* createList()
{
// 使用构造函数创建节点并连接
Node* head = new Node(1); //创建头节点并初始化为1
head->next = new Node(2); // 创建并连接第二个节点,初始化为2,[1]→[2]→NULL
head->next->next = new Node(3); // 创建并连接第三个节点,初始化为3,[1]→[2]→[3]→NULL
head->next->next->next = new Node(4); // 创建并连接第四个节点,初始化为4,[1]→[2]→[3]→[4]→NULL
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); // 创建并连接第五个节点,初始化为5,[1]→[2]→[3]→[4]→[5]→NULL
}构造函数的工作就是简化代码,new Node()的工作就是,创建一个新的节点,并且给节点赋值。head->next就是将这个节点与前一个节点连接起来。恍然大悟,链表就是这样工作的。
head->next = new Node(2); // 创建并连接第二个节点,初始化为2,[1]→[2]→NULL
火车头 -> 1车厢 = 1车厢装载货物2并且后面不在有车了nullptr |
add 0 in the very beginning
// 在链表头部插入新节点
void insertAtHead(Node* &head, int value)
{
Node* newNode = new Node(value); // 1. 创建新节点
newNode->next = head; // 2. 新节点指向原头节点
head = newNode; // 3. 更新头指针指向新节点
}use the function:
// 定义链表节点结构体,并包含构造函数
struct Node
{
int data; // 数据域
Node* next; // 指针域,指向下一个节点
// 构造函数,用于初始化节点
Node(int value) : data(value), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 在链表头部插入新节点
void insert0AtHead(Node* &head, int value)
{
Node* newNode = new Node(value); // 1. 创建新节点
newNode->next = head; // 2. 新节点指向原头节点
head = newNode; // 3. 更新头指针指向新节点
}
// 函数:创建1→2→3→4→5的链表
Node* createList()
{
// 使用构造函数创建节点并连接
Node* head = new Node(1); //创建头节点并初始化为1
head->next = new Node(2); // 创建并连接第二个节点,初始化为2,[1]→[2]→NULL
head->next->next = new Node(3); // 创建并连接第三个节点,初始化为3,[1]→[2]→[3]→NULL
head->next->next->next = new Node(4); // 创建并连接第四个节点,初始化为4,[1]→[2]→[3]→[4]→NULL
head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); // 创建并连接第五个节点,初始化为5,[1]→[2]→[3]→[4]→[5]→NULL
insert0AtHead(head, 0); // 0→1→2→3→4→5→nullptr
}
delete the selected node.
// 删除指定值的节点
void deleteNode(Node* &head, int value)
{
// 处理空链表情况
if (head == nullptr) return;
// 如果要删除的是头节点
if (head->data == value)
{
Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
delete temp;
return;
}
// 查找要删除的节点
Node* current = head;
while (current->next != nullptr && current->next->data != value)
{
current = current->next;
}
// 找到节点后删除
if (current->next != nullptr)
{
Node* temp = current->next;
current->next = current->next->next; // 直接指向下下个节点
delete temp;
}
}back to the topic.
1、create a new list to store the result
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 上述备注中已经规定了构造函数,直接使用 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode dummy(0); // 创建一个新的链表
ListNode *tail = &dummy; // tail -> dummy
}
};2、compare the value of list1 and list2
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 上述备注中已经规定了构造函数,直接使用 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode dummy(0); // 创建一个新的链表
ListNode *tail = &dummy; // tail -> dummy
// 比较list1和list2的大小
while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr)
{
if (list1->value <= list2->value)
{
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
// tail要到新链表的末尾,尾巴一直在后面
tail = tail->next;
}
}
};3、deal with the left list'
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 上述备注中已经规定了构造函数,直接使用 ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode dummy(0); // 创建一个新的链表
ListNode *tail = &dummy; // tail -> dummy
// 比较list1和list2的大小
while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr)
{
if (list1->val <= list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
// tail要到新链表的末尾,尾巴一直在后面
tail = tail->next;
}
// 处理剩下的链表,如果其中一个已经全用完了
tail->next = (list1 != nullptr) ? list1 : list2;
return dummy.next;
}
};of course the code runs well. let's see an example
合并 [1,3] 和 [2,4]:
初始状态:
dummy(0) -> nullptr
tail -> dummy
list1 -> 1 -> 3 -> nullptr
list2 -> 2 -> 4 -> nullptr
- 第一次循环(
1 <= 2):tail->next = list1→dummy(0) -> 1 -> 3 -> nullptrtail = tail->next→tail现在指向1list1 = list1->next→list1现在指向3
- 第二次循环(
2 <= 3):tail->next = list2→dummy(0) -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> nullptrtail = tail->next→tail现在指向2list2 = list2->next→list2现在指向4
- 第三次循环(
3 <= 4):tail->next = list1→dummy(0) -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> nullptrtail = tail->next→tail现在指向3list1 = list1->next→list1现在为nullptr
- 退出循环后:
list1为空,list2还剩4,所以tail->next = list2:dummy(0) -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> nullptr
完结撒花。





















 2642
2642

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








