题目链接
题目描述
One important factor to identify acute stroke (急性脑卒中) is the volume of the stroke core. Given the results of image analysis in which the core regions are identified in each MRI slice, your job is to calculate the volume of the stroke core.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 positive integers: M, N, L and T, where M and N are the sizes of each slice (i.e. pixels of a slice are in an M×N matrix, and the maximum resolution is 1286 by 128); L (≤60) is the number of slices of a brain; and T is the integer threshold (i.e. if the volume of a connected core is less than T, then that core must not be counted).
Then L slices are given. Each slice is represented by an M×N matrix of 0's and 1's, where 1 represents a pixel of stroke, and 0 means normal. Since the thickness of a slice is a constant, we only have to count the number of 1's to obtain the volume. However, there might be several separated core regions in a brain, and only those with their volumes no less than T are counted. Two pixels are connected and hence belong to the same region if they share a common side, as shown by Figure 1 where all the 6 red pixels are connected to the blue one.

Figure 1
Output Specification:
For each case, output in a line the total volume of the stroke core.
Sample Input:
3 4 5 2
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 0 1 1
0 0 1 1
1 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0
1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0结尾无空行
Sample Output:
26结尾无空行
题目大意
三维bfs,找上下左右前后为1的个数大于T的数
解题思路
不信邪,就dfs,dfs不能向上一层遍历,,否则就会段错误,而且上面只要出现的都已经被遍历过了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool g[70][1330][130];
int sum;
int cnt=2;
int m,n,l,t;
void dfs(int i,int j,int k){
if(g[i][j][k]==false||i>l||j>m||k>n||i<1||j<1||k<1) return ;
sum++;
g[i][j][k]=false;
//dfs(i-1,j,k);
dfs(i+1,j,k);
dfs(i,j+1,k);
dfs(i,j-1,k);
dfs(i,j,k+1);
dfs(i,j,k-1);
}
int main(){
cin>>m>>n>>l>>t;
//memset(g,1,sizeof(g));
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
scanf("%d",&g[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
int num=0;
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){
if(g[i][j][k]){
sum=0;
dfs(i,j,k);
if(sum>=t) num+=sum;
}
}
}
}
cout<<num;
}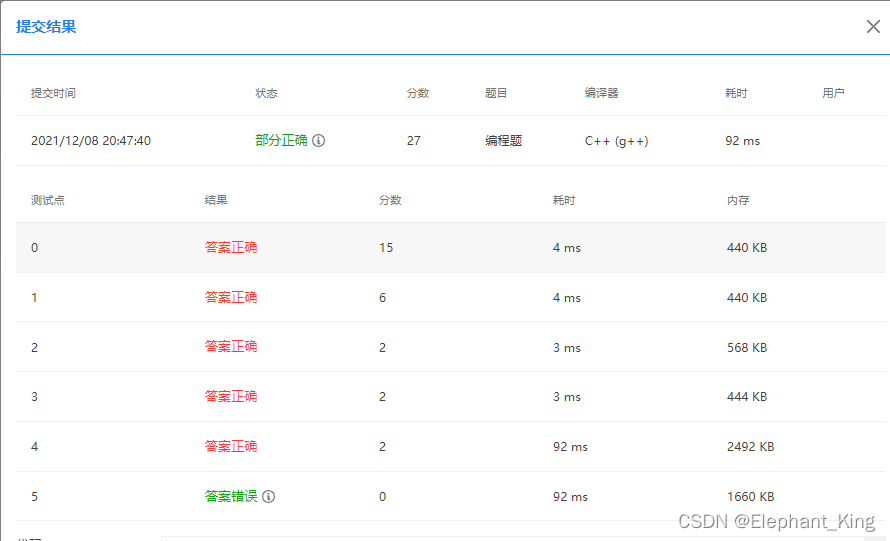
最后一个点也不知道哪错了
2021.12.17
呜呜呜信邪了,老老实实bfs了,注意内存超限就是数组开太大了,尽量别开太大
题解
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int g[65][1300][130];
int visited[65][1300][130];
int sum=0;
int m,n,l;
int t;
struct Node{
int x,y,z;
};
int X[6]={1,0,0,-1,0,0};
int Y[6]={0,1,0,0,-1,0};
int Z[6]={0,0,1,0,0,-1};
bool judge(int x,int y,int z){
if(x<0||x>=l||y<0||y>=m||z<0||z>=n) return false;
if(visited[x][y][z]||g[x][y][z]==0) return false;
return true;
}
int bfs(int x,int y,int z){
Node temp;
int cnt=0;
temp.x=x;
temp.y=y;
temp.z=z;
queue<Node> q;
q.push(temp);
while(!q.empty()){
Node top=q.front();
q.pop();
cnt++;
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
int tx=top.x+X[i];
int ty=top.y+Y[i];
int tz=top.z+Z[i];
if(judge(tx,ty,tz)){
q.push(Node{tx,ty,tz});
visited[tx][ty][tz]=1;
}
}
}
if(cnt>=t)
return cnt;
else
return 0;
}
int main(){
cin>>m>>n>>l>>t;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
scanf("%d",&g[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
if(g[i][j][k]==1&&visited[i][j][k]==0){
visited[i][j][k]=1;
ans+=bfs(i,j,k);
}
}
}
}
cout<<ans;
}






 本文探讨了如何利用BFS和DFS算法解决程序设计实验中的问题,即通过分析MRI图像,计算急性脑卒中核心区域的体积,仅计数体积小于特定阈值的区域。作者分享了解题思路和两种可能的代码实现,重点在于内存管理和正确遍历策略的选择。
本文探讨了如何利用BFS和DFS算法解决程序设计实验中的问题,即通过分析MRI图像,计算急性脑卒中核心区域的体积,仅计数体积小于特定阈值的区域。作者分享了解题思路和两种可能的代码实现,重点在于内存管理和正确遍历策略的选择。
















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








