0.reference
1.压缩列表初识
1.1 简介
压缩列表ziplist本质上就是一个字节数组,是Redis为了节约内存而设计的一种线性数据结构,可以包含多个元
素,每个元素可以是一个字节数组或一个整数。Redis的有序集合、散列和列表都直接或者间接使用了压缩列表。
当有序集合或散列表的元素个数比较少,且元素都是短字符串时,Redis便使用压缩列表作为其底层数据存储结
构。列表使用快速链表(quicklist)数据结构存储,而快速链表就是双向链表与压缩列表的组合。
1.2 测试相关命令
redis-server
redis-cli
hmset person name zhangsan gender 1 age 22
object encoding person
127.0.0.1:6379> hmset person name zhangsan gender 1 age 22
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding person
"ziplist"
注释与复习:
hmset是hset的批量设置形式,成功返回ok2. 压缩列表的设计与源码分析
2.1 压缩列表的存储结构
2.1.1 示意与字段含义
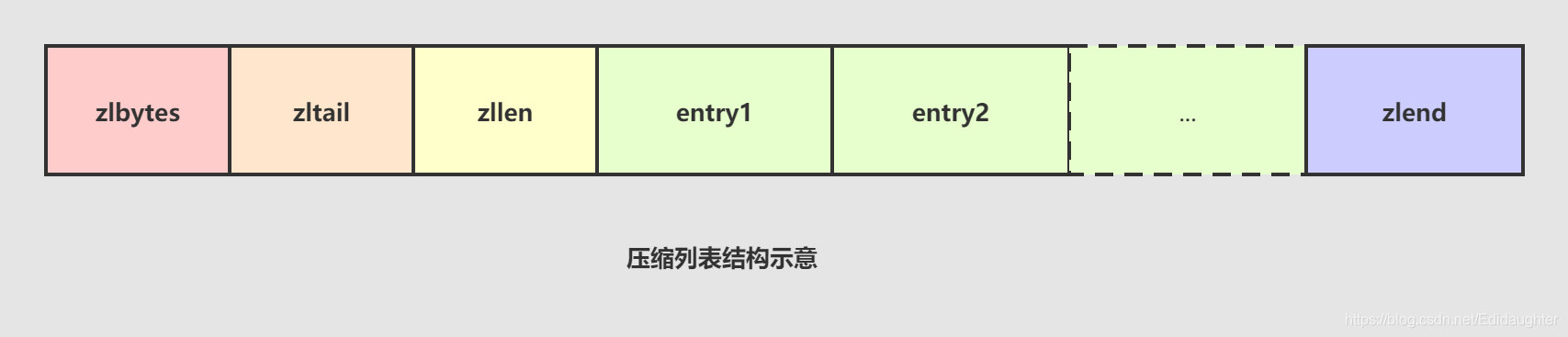
1)zlbytes:压缩列表的字节长度,占4个字节,因此压缩列表最多有2^32-1个字节。
2)zltail:压缩列表尾元素相对于压缩列表起始地址的偏移量,占4个字节。
3)zllen:压缩列表的元素个数,占2个字节。zllen无法存储元素个数超过65535(2^16-1)的压缩列表,必须
遍历整个压缩列表才能获取到元素个数。
4)entryX:压缩列表存储的元素,可以是字节数组或者整数,长度不限。entry的编码结构将在后面详细介绍。
5)zlend:压缩列表的结尾,占1个字节,恒为0xFF。2.1.2 字段的存取操作
假设char * zl(zl应该是ziplist的缩写)指向压缩列表首地址,Redis可通过以下宏定义实现压缩列表各个字段的存取操作:
/* Macro to determine if the entry is a string. String entries never start
* with "11" as most significant bits of the first byte. */
#define ZIP_IS_STR(enc) (((enc) & ZIP_STR_MASK) < ZIP_STR_MASK)
/* Utility macros. zl指向zlbytes字段*/
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))/* Return total bytes a ziplist is composed of. */
/* Return the offset of the last item inside the ziplist. */
/*zl+4 指向zltail字段*/
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
/* Return the length of a ziplist, or UINT16_MAX if the length cannot be
* determined without scanning the whole ziplist. */
/*zl+8 指向zllen字段*/
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
/* The size of a ziplist header: two 32 bit integers for the total
* bytes count and last item offset. One 16 bit integer for the number
* of items field. */
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))
/* Size of the "end of ziplist" entry. Just one byte. */
#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t))
/* Return the pointer to the first entry of a ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) ((zl)+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE)
/* Return the pointer to the last entry of a ziplist, using the
* last entry offset inside the ziplist header. */
/*zl+zltail指向尾元素首地址,intrev32ifbe使得数据存储统一采用小端法*/
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
/* Return the pointer to the last byte of a ziplist, which is, the
* end of ziplist FF entry. */
/*压缩列表最后一个字段即为zlend字段*/
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl))-1)
/* Increment the number of items field in the ziplist header. Note that this
* macro should never overflow the unsigned 16 bit integer, since entries are
* always pushed one at a time. When UINT16_MAX is reached we want the count
* to stay there to signal that a full scan is needed to get the number of
* items inside the ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,incr) { \
if (ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) < UINT16_MAX) \
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = intrev16ifbe(intrev16ifbe(ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl))+incr); \
}
部分注释摘抄:
(1)ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) --zl指向zlbytes字段
(2)ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)--zl+4 指向zltail字段
(3)ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) --zl+8 指向zllen字段
(4)ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) --zl+zltail指向尾元素首地址,intrev32ifbe使得数据存储统一采用小端法
(5)ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl) --压缩列表最后一个字段即为zlend字段2.1.3 压缩列表元素entryX的编码结构
了解了压缩列表的基本结构,我们可以很容易地获得压缩列表的字节长度、元素个数等,那么如何遍历压缩列表
呢?对于任意一个元素,我们如何判断其存储的是什么类型呢?我们又如何获取字节数组的长度呢?回答这些问
题之前,需要先了解压缩列表元素的编码结构: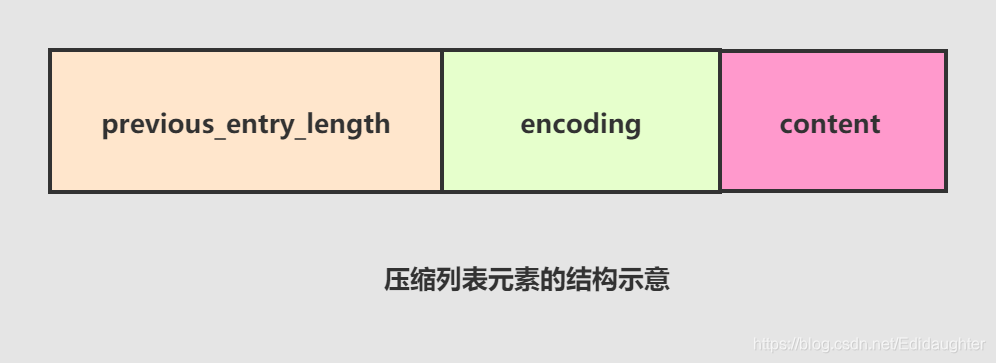
1.previous_entry_length
表示前一个元素的字节长度,占1个或者5个字节.
当前一个元素的长度小于254字节时,用1个字节表示;
当前一个元素的长度大于或等于254字节时,用5个字节来表示,此时previous_entry_length字段的第1个字节是
固定的0xFE,后面4个字节才真正表示前一个元素的长度;
假设已知当前元素的首地址为p,那么p-previous_entry_length就是前一个元素的首地址,从而实现压缩列表从
尾到头的遍历.
2.encoding
表示当前元素的编码,即content字段存储的数据类型(整数或者字节数组),数据内容存储在content字段.
为了节约内存,encoding字段同样长度可变.
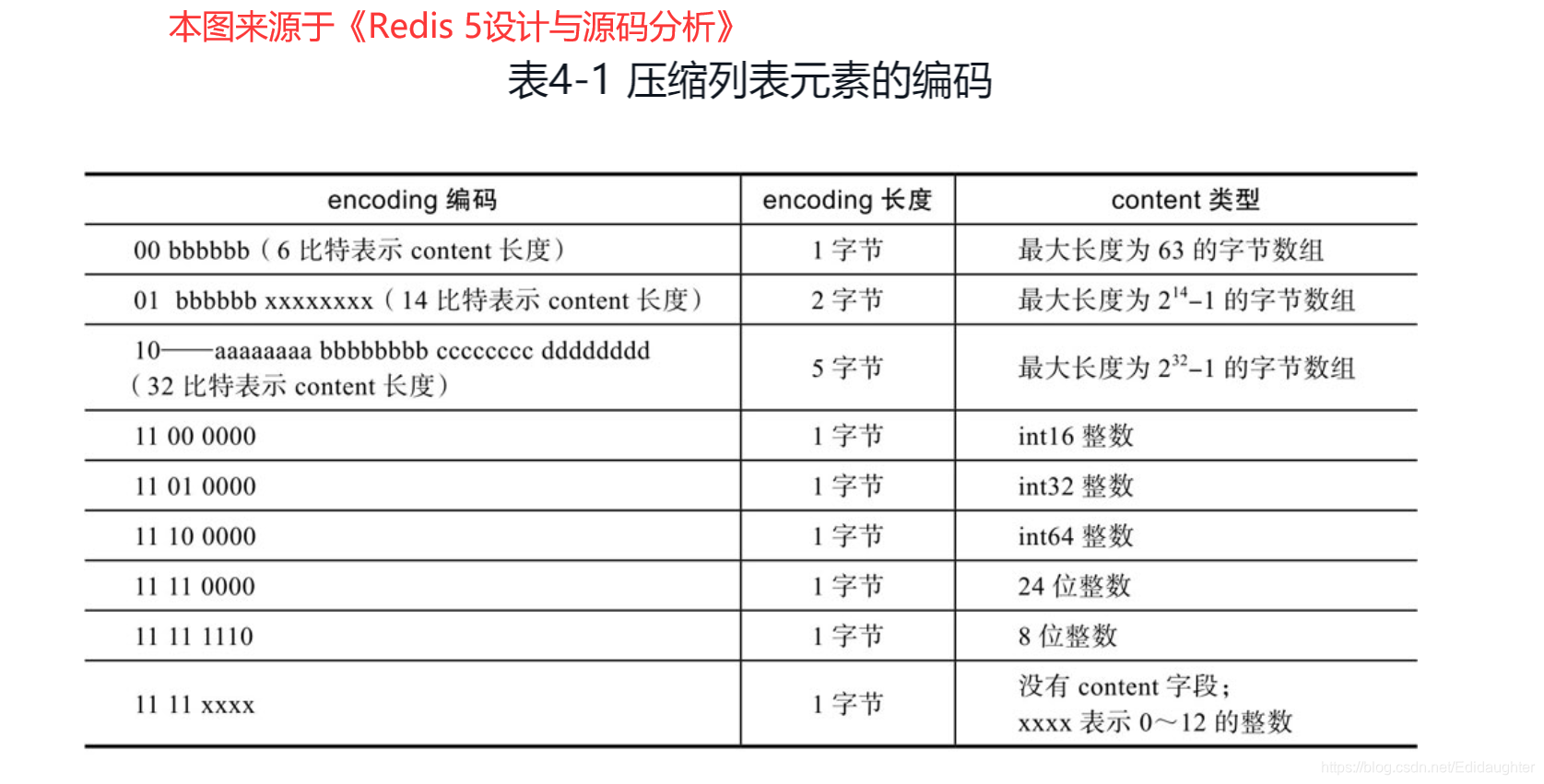
2.1
分析上面从书中截取来的图中的encoding编码,可以看出,encoding字段的
第1个字节的前2位,可以判断content字段存储的是整数或者字节数组(及其最大长度),
00-长度范围为0-63的字节数组;
01-长度范围为64-16383的字节数组;
11-长度方位为16384-4294967295的字节数组;
11-整数
2.2
content存储的是字节数组时,后续字节标识字节数组的实际长度;当content存储的是整数时,可根据第3、
第4位判断整数的具体类型。而当encoding字段标识当前元素存储的是0~12的立即数时,数据直接存储在
encoding字段的最后4位,此时没有content字段。
2.3
参照encoding字段的编码表格,Redis预定义了以下常量对应encoding字段的各编码类型:
#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0
#define ZIP_INT_MASK 0x30
#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6)
#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6)
#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6)
#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe
说明:
2^6 - 1 = 63
2^14 - 1 = 16383
2^32 - 1 = 4294967295
2.1.4 entryX经解码后的结构体定义zlentry
typedef struct zlentry {
unsigned int prevrawlensize; // previous_entry_length字段的长度
unsigned int prevrawlen; // previous_entry_length字段存储的内容
unsigned int lensize; // encoding字段的长度
unsigned int len; // encoding字段的存储的内容
unsigned int headersize; // 当前元素的首部长度,是previous_entry_length字段长度与encoding字段长度之和
unsigned char encoding; // 当前元素的编码
unsigned char *p; // 当前元素首地址
} zlentry;
说明:
1.encoding的含义
Set to ZIP_STR_* or ZIP_INT_* depending on the entry encoding.
However for 4 bits immediate integers this can assume a range
of values and must be range-checked.
根据entry的解码被设置成ZIP_STR_*或 ZIP_INT_*.
但是对于4个bits位以内的数据可以被视为一个范围并且必须要检查范围.
2.1.5 函数zipEntry解码压缩列表的元素,存储于zlentry结构体
函数zipEntry用来解码压缩列表的元素,存储于zlentry结构体.
/* Return a struct with all information about an entry. */
void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;
e->p = p;
}第一步.解码previous_entry_length字段,此时入参ptr指向元素首地址;
/* Return the length of the previous element, and the number of bytes that
* are used in order to encode the previous element length.
* 'ptr' must point to the prevlen prefix of an entry (that encodes the
* length of the previous entry in order to navigate the elements backward).
* The length of the previous entry is stored in 'prevlen', the number of
* bytes needed to encode the previous entry length are stored in
* 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \
} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \
assert(sizeof((prevlen)) == 4); \
memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); \
memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); \
} \
} while(0);第二步 解码encoding字段逻辑,此时入参ptr指向元素首地址偏移previous_entry_length字段长度的位置;
/* Decode the entry encoding type and data length (string length for strings,
* number of bytes used for the integer for integer entries) encoded in 'ptr'.
* The 'encoding' variable will hold the entry encoding, the 'lensize'
* variable will hold the number of bytes required to encode the entry
* length, and the 'len' variable will hold the entry length. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \
(lensize) = 2; \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_32B) { \
(lensize) = 5; \
(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((ptr)[4]); \
} else { \
panic("Invalid string encoding 0x%02X", (encoding)); \
} \
} else { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); \
} \
} while(0);字节数组只根据ptr[0]的前2个比特即可判断类型,而判断整数类型需要ptr[0]的前4个比特,代码如下:
/* Return bytes needed to store integer encoded by 'encoding'. */
unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1;
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2;
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3;
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4;
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8;
}
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 0; /* 4 bit immediate */
panic("Invalid integer encoding 0x%02X", encoding);
return 0;
}3.基本操作
3.1 创建压缩列表ziplistNew
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))
#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t))
#define ZIP_END 255
/* Create a new empty ziplist. */
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {
// ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE = zlbytes + zltail + zllen
unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+ZIPLIST_END_SIZE;
unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes);
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes);
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE);
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0;
zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END; // ZIP_END 结尾标识符0XFF
return zl;
}
zlbytes,zltail,zllen见本文【2.1.1】所示内容.3.2 插入元素ziplistInsert
插入元素可以简要分为3个步骤:
① 将元素内容编码;
② 重新分配空间;
③ 复制数据。
3.3 删除元素ziplistDelete
压缩列表删除元素的API定义如下,函数输入参数zl指向压缩列表首地址;*p指向待删除元素的首地址(参数p同时可以作为输出参数);返回参数为压缩列表首地址。
unsigned char *ziplistDelete(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char **p) {
size_t offset = *p-zl;
zl = __ziplistDelete(zl,*p,1);
return zl;
}3.4 遍历压缩列表ziplistNext&ziplistPrev
遍历就是从头到尾(后向遍历)或者从尾到头(前向遍历)访问压缩列表中的每个元素。
压缩列表的遍历API定义如下,函数输入参数zl指向压缩列表首地址,p指向当前访问元素的首地址;
ziplistNext函数返回后一个元素的首地址,ziplistPrev返回前一个元素的首地址.
// 后向遍历
unsigned char *ziplistNext(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
((void) zl);
if (p[0] == ZIP_END) {
return NULL;
}
p += zipRawEntryLength(p);
if (p[0] == ZIP_END) {
return NULL;
}
return p;
}
// 前向遍历
unsigned char *ziplistPrev(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
if (p[0] == ZIP_END) {
p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
return (p[0] == ZIP_END) ? NULL : p;
} else if (p == ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl)) {
return NULL;
} else {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
assert(prevlen > 0);
return p-prevlen;
}
}





 介绍Redis中压缩列表(ziplist)的结构与实现原理,包括存储结构、编码方式及基本操作。
介绍Redis中压缩列表(ziplist)的结构与实现原理,包括存储结构、编码方式及基本操作。
















 3151
3151

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








