1.Nginx中的连接池
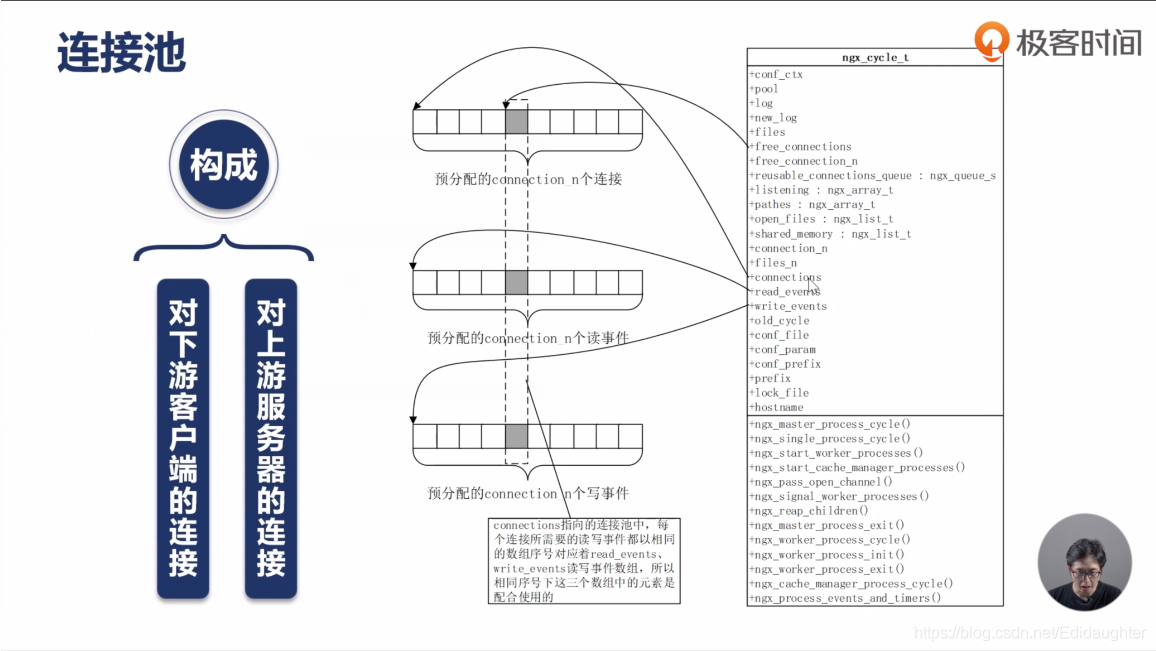
2.连接池中的数据结构
(1)每一个worker进程中都有一个ngx_cycle_t.
(2)查看 http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#worker_connections可以看到配置说明
是这样的:
Syntax: worker_connections number;
Default: worker_connections 512;
Context: events
Sets the maximum number of simultaneous connections that can be opened by a worker process.
It should be kept in mind that this number includes all connections (e.g. connections
with proxied servers, among others), not only connections with clients. Another
consideration is that the actual number of simultaneous connections cannot exceed the
current limit on the maximum number of open files, which can be changed by
worker_rlimit_nofile.
翻译就是说:
设置一个worker进程可以同时打开的最大连接数,必须要注意的是这个数字应该是所有的连接数(比如说:包括
代理的上游服务器的,或者其他的),而不仅仅是与客户端的连接.另外要注意的一点是:实际同时连接数不能
超过进程能够打开的最大文件数,这个最大文件数可以通过worker_rlimit_nofile来设置.
说明:默认配置512是非常小的,我们的Nginx面向的是至少万计百万计算的,所以往往我们是需要修改这个的.
如果我们Nginx做反向代理的时候,一个客户端会消耗两个连接.
(3)ngx_connection_t *connections;是我们所说的连接池.
每一个连接自动对应一个读事件和一个写事件,所以在ngx_cycle_t中,还有read_events和write_events数组.他们
指向的数组的大小也是和worker_connections的配置是一样的.
(4)连接池,读事件池和写事件池是如何联系起来的呢?
它们都是有序号的,通过序号关联起来.
(5)ngx_connection_s这个结构体在64位操作系统中占用的内存大约是232个字节,具体的版本不同可能会
有微小的差异,每一个struct ngx_event_s在64位操作系统中占用的内存大约是96个字节,所以当我们
使用一个连接的时候消耗的资源大约是(232+96*2)个字节.
我们的worker_connections配置的为num,初始化的时候就会预分配内存大约就是n*(232+96*2)bytes内存.
(6)关注ngx_event_s中的handler这个成员,这是一个回调方法,很多第三方模块会把这个handler设为自己
的实现;
(7)关注ngx_event_s中的timer这个成员,这是一个定时器,当我们对http请求做读超时和写超时等设置的时
候,其实我们是在操作它们的读事件和写事件中的timer,这个timer就是nginx实现超时机制的定时器.它的
数据类型是ngx_rbtree_node_t,是红黑树的中的一个节点.
这里的定时器也是可以配置的,就是这个设置:
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#client_header_timeout
配置方法:
Syntax: client_header_timeout time;
Default: client_header_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server
为什么不是:
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#client_body_timeout
呢?
(8)ngx_connection_s中的off_t sent;这个变量时我们通常所说的bytes_sent变量,
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html内置变量中的bytes_sent,
表达这个连接上已经向客户端发送了多少字节,通常access_log中记录nginx处理的请求中,会
记录这个变量.
screen -r nginx是啥意思?,配置文件中的log_forma定义一个日志格式的时候可以用到这个
内置变量.
(9)当我们配置高并发的Nginx时,必须把connection的数目配置到足够大,当做反向或正向代理服务
器的时候,记得需要正确计算;
Nginx中很多的结构体的成员和我们的内置变量是能够一一对应,比如说刚刚提到的bytes_sent,
body_bytes_sent,都是我们在access_log或者openresty中lua写的代码中获取到Nginx内置变量
时经常使用到的方法.
===========================================================================================================
find . -name "*h" | xargs grep "ngx_cycle_t"
find . -name "*h" | xargs grep "struct ngx_cycle_s"
中找到数据的定义在下面两个文件中:
/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/core/ngx_core.h
/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/core/ngx_cycle.h
(1)ngx_core.h
typedef struct ngx_cycle_s ngx_cycle_t;
(2)
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx;
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_log_t *log;
ngx_log_t new_log;
ngx_uint_t log_use_stderr; /* unsigned log_use_stderr:1; */
ngx_connection_t **files;
ngx_connection_t *free_connections;
ngx_uint_t free_connection_n;
ngx_module_t **modules;
ngx_uint_t modules_n;
ngx_uint_t modules_used; /* unsigned modules_used:1; */
ngx_queue_t reusable_connections_queue;
ngx_uint_t reusable_connections_n;
ngx_array_t listening;
ngx_array_t paths;
ngx_array_t config_dump;
ngx_rbtree_t config_dump_rbtree;
ngx_rbtree_node_t config_dump_sentinel;
ngx_list_t open_files;
ngx_list_t shared_memory;
ngx_uint_t connection_n;
ngx_uint_t files_n;
ngx_connection_t *connections;//这个就是我们所说的连接池
ngx_event_t *read_events;//读事件池
ngx_event_t *write_events;//写事件池
ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle;
ngx_str_t conf_file;
ngx_str_t conf_param;
ngx_str_t conf_prefix;
ngx_str_t prefix;
ngx_str_t lock_file;
ngx_str_t hostname;
};
find . -name "*h" | xargs grep "ngx_connection_s"
find . -name "*h" | xargs grep "ngx_connection_t"
(1)/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/core/ngx_core.h
(2)/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/core/ngx_connection.h
(1)typedef struct ngx_connection_s ngx_connection_t;
(2)
struct ngx_connection_s {
void *data;
ngx_event_t *read; // 读事件
ngx_event_t *write;// 写事件
ngx_socket_t fd;
ngx_recv_pt recv;
ngx_send_pt send;// 抽象解耦OS底层方法
ngx_recv_chain_pt recv_chain;
ngx_send_chain_pt send_chain;
ngx_listening_t *listening;
off_t sent;//off_t可以理解成无符号整型,表达这个连接上已经发送了多少字节,时配置中的bytes_sent变量
ngx_log_t *log;
ngx_pool_t *pool;
int type;
struct sockaddr *sockaddr;
socklen_t socklen;
ngx_str_t addr_text;
ngx_str_t proxy_protocol_addr;
in_port_t proxy_protocol_port;
#if (NGX_SSL || NGX_COMPAT)
ngx_ssl_connection_t *ssl;
#endif
struct sockaddr *local_sockaddr;
socklen_t local_socklen;
ngx_buf_t *buffer;
ngx_queue_t queue;
ngx_atomic_uint_t number;
ngx_uint_t requests;
unsigned buffered:8;
unsigned log_error:3; /* ngx_connection_log_error_e */
unsigned timedout:1;
unsigned error:1;
unsigned destroyed:1;
unsigned idle:1;
unsigned reusable:1;
unsigned close:1;
unsigned shared:1;
unsigned sendfile:1;
unsigned sndlowat:1;
unsigned tcp_nodelay:2; /* ngx_connection_tcp_nodelay_e */
unsigned tcp_nopush:2; /* ngx_connection_tcp_nopush_e */
unsigned need_last_buf:1;
#if (NGX_HAVE_AIO_SENDFILE || NGX_COMPAT)
unsigned busy_count:2;
#endif
#if (NGX_THREADS || NGX_COMPAT)
ngx_thread_task_t *sendfile_task;
#endif
};
/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/core/ngx_core.h
/home/muten/module/nginx-1.13.7/src/event/ngx_event.h
(1)typedef struct ngx_event_s ngx_event_t;
(2)
struct ngx_event_s {
void *data;
unsigned write:1;
unsigned accept:1;
/* used to detect the stale events in kqueue and epoll */
unsigned instance:1;
/*
* the event was passed or would be passed to a kernel;
* in aio mode - operation was posted.
*/
unsigned active:1;
unsigned disabled:1;
/* the ready event; in aio mode 0 means that no operation can be posted */
unsigned ready:1;
unsigned oneshot:1;
/* aio operation is complete */
unsigned complete:1;
unsigned eof:1;
unsigned error:1;
unsigned timedout:1;
unsigned timer_set:1;
unsigned delayed:1;
unsigned deferred_accept:1;
/* the pending eof reported by kqueue, epoll or in aio chain operation */
unsigned pending_eof:1;
unsigned posted:1;
unsigned closed:1;
/* to test on worker exit */
unsigned channel:1;
unsigned resolver:1;
unsigned cancelable:1;
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE)
unsigned kq_vnode:1;
/* the pending errno reported by kqueue */
int kq_errno;
#endif
/*
* kqueue only:
* accept: number of sockets that wait to be accepted
* read: bytes to read when event is ready
* or lowat when event is set with NGX_LOWAT_EVENT flag
* write: available space in buffer when event is ready
* or lowat when event is set with NGX_LOWAT_EVENT flag
*
* epoll with EPOLLRDHUP:
* accept: 1 if accept many, 0 otherwise
* read: 1 if there can be data to read, 0 otherwise
*
* iocp: TODO
*
* otherwise:
* accept: 1 if accept many, 0 otherwise
*/
#if (NGX_HAVE_KQUEUE) || (NGX_HAVE_IOCP)
int available;
#else
unsigned available:1;
#endif
ngx_event_handler_pt handler;
#if (NGX_HAVE_IOCP)
ngx_event_ovlp_t ovlp;
#endif
ngx_uint_t index;
ngx_log_t *log;
ngx_rbtree_node_t timer;
/* the posted queue */
ngx_queue_t queue;
#if 0
/* the threads support */
/*
* the event thread context, we store it here
* if $(CC) does not understand __thread declaration
* and pthread_getspecific() is too costly
*/
void *thr_ctx;
#if (NGX_EVENT_T_PADDING)
/* event should not cross cache line in SMP */
uint32_t padding[NGX_EVENT_T_PADDING];
#endif
#endif
};





 本文解析了Nginx中的连接池实现原理,包括连接池的数据结构、与读写事件池的关系,以及如何通过配置调整以支持高并发场景。
本文解析了Nginx中的连接池实现原理,包括连接池的数据结构、与读写事件池的关系,以及如何通过配置调整以支持高并发场景。
















 1103
1103

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








