题目描述
输入一颗二叉树的跟节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)。


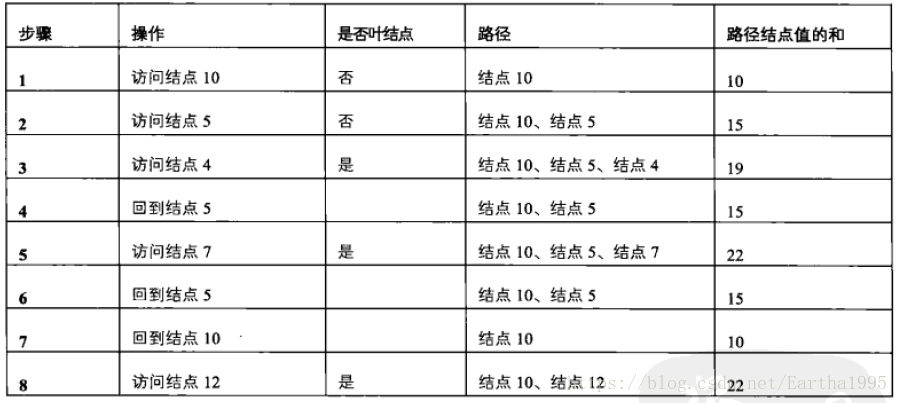

#include<cstdlib>
#include<vector>
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {
vector<vector<int> > path;
if(root == NULL) return path;
int currentSum = 0;
vector<int> temp;
FindTreePath(root, expectNumber, path, temp, currentSum);
return path;
}
void FindTreePath(TreeNode* pRoot,int expectNumber, vector<vector<int> > & path, vector<int> temp,
int currentSum)
{
currentSum += pRoot->val;
temp.push_back(pRoot->val);
// 如果是叶节点,并且路径上节点的和等于输入的值
// 重启一行路径
bool isLeaf = pRoot->left == NULL && pRoot->right == NULL;
if(currentSum == expectNumber && isLeaf)
{
path.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
}
// 如果不是叶节点,则遍历它的子节点
if(pRoot->left != NULL)
FindTreePath(pRoot->left, expectNumber, path, temp, currentSum);
if(pRoot->right != NULL)
FindTreePath(pRoot->right, expectNumber, path, temp, currentSum);
// 在返回到父节点之前,在路径上删除当前节点,
// 并在currentSum中减去当前节点的值
currentSum -= pRoot->val;
//if(temp.size() > 0)
temp.pop_back();
}
};
这里又定义了一个成员函数,用于递归调用。
其他解法:
#include<cstdlib>
#include<vector>
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > buffer;
vector<int> tmp;
vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {
if(root==NULL)
return buffer;
tmp.push_back(root->val);
if((expectNumber-root->val)==0 && root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
{
buffer.push_back(tmp);
}
FindPath(root->left,expectNumber-root->val);
FindPath(root->right,expectNumber-root->val);
if(tmp.size()!=0)
tmp.pop_back();
return buffer;
}
};























 378
378

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








