万物皆可对象
一、理解“万事万物皆对象”
1.在Java语言范畴中,我们都将功能、结构等封装到类中,通过类的实例化,来调用具体的功能结构
>Scanner,String等
>文件:File
>网络资源:URL
2.涉及到Java语言与前端Html、后端的数据库交互时,前后端的结构在Java层面交互时,都体现为类、对象。
内存解析的说明
1.引用类型的变量,只可能存储两类值:null 或 地址值(含变量的类型)
匿名对象的使用
1.理解:我们创建的对象,没有显式的赋给一个变量名。即为匿名对象
2.特征:匿名对象只能调用一次。
3.使用:如下
public class InstanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone p = new Phone();
// p = null;
System.out.println(p);
p.sendEmail();
p.playGame();
//匿名对象
// new Phone().sendEmail();
// new Phone().playGame();
new Phone().price = 1999;
new Phone().showPrice();//0.0
//**********************************
PhoneMall mall = new PhoneMall();
// mall.show(p);
//匿名对象的使用
mall.show(new Phone());
}
}
class PhoneMall{
public void show(Phone phone){
phone.sendEmail();
phone.playGame();
}
}
class Phone{
double price;//价格
public void sendEmail(){
System.out.println("发送邮件");
}
public void playGame(){
System.out.println("玩游戏");
}
public void showPrice(){
System.out.println("手机价格为:" + price);
}
}
工具类的自定义
工具类的定义
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* 自定义数组的工具类
*
*/
public class ArrayUtil {
// 求数组的最大值
public int getMax(int[] arr) {
int maxValue = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (maxValue < arr[i]) {
maxValue = arr[i];
}
}
return maxValue;
}
// 求数组的最小值
public int getMin(int[] arr) {
int minValue = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (minValue > arr[i]) {
minValue = arr[i];
}
}
return minValue;
}
// 求数组的总和
public int getSum(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
// 求数组的平均值
public int getAvg(int[] arr) {
return getSum(arr) / arr.length;
}
//如下的两个同名方法构成了重载
// 反转数组
public void reverse(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length / 2; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[arr.length - i - 1];
arr[arr.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
public void reverse(String[] arr){
}
// 复制数组
public int[] copy(int[] arr) {
int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
arr1[i] = arr[i];
}
return arr1;
}
// 数组排序
public void sort(int[] arr) {
// 冒泡排序
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// int temp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
// arr[j + 1] = temp;
//错误的:
// swap(arr[j],arr[j + 1]);
//正确的:
swap(arr,j,j + 1);
}
}
}
}
//错误的:交换数组中指定两个位置元素的值
// public void swap(int i,int j){
// int temp = i;
// i = j;
// j = temp;
// }
//正确的:交换数组中指定两个位置元素的值
public void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// 遍历数组
public void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 查找指定元素
public int getIndex(int[] arr, int dest) {
// 线性查找:
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (dest == arr[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;//返回一个负数,表示没有找到
}
}
工具类的测试
package com.atguigu.java;
public class ArrayUtilTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayUtil util = new ArrayUtil();
int[] arr = new int[]{32,34,32,5,3,54,654,-98,0,-53,5};
int max = util.getMax(arr);
System.out.println("最大值为:" + max);
System.out.println("排序前:");
util.print(arr);
util.sort(arr);
System.out.println("排序后:");
util.print(arr);
// System.out.println("查找:");
// int index = util.getIndex(arr, -5);
// if(index >= 0){
// System.out.println("找到了,索引地址为:" + index);
// }else{
// System.out.println("未找到");
// }
// util.reverse(arr);
}
}
方法的重载
public void getSum(int i,int j);
public void getSum(double d1,double d2);
public void getSum(String s ,int i);
public void getSum(int i,String s);
public class OverLoadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OverLoadTest test = new OverLoadTest();
test.getSum(1,2);
}
//如下的4个方法构成了重载
public void getSum(int i,int j){
System.out.println("1");
}
public void getSum(double d1,double d2){
System.out.println("2");
}
public void getSum(String s ,int i){
System.out.println("3");
}
public void getSum(int i,String s){
System.out.println("4");
}
//如下的3个方法不能与上述4个方法构成重载
// public int getSum(int i,int j){
// return 0;
// }
// public void getSum(int m,int n){
//
// }
// private void getSum(int i,int j){
//
// }
}
可变个数的形参
public void show(int i,String …strs);
public void show(String … strs);
/*
* 可变个数形参的方法
*
* 1.jdk 5.0新增的内容
* 2.具体使用:
* 2.1 可变个数形参的格式:数据类型 ... 变量名
* 2.2 当调用可变个数形参的方法时,传入的参数个数可以是:0个,1个,2个,。。。
* 2.3 可变个数形参的方法与本类中方法名相同,形参不同的方法之间构成重载
* 2.4 可变个数形参的方法与本类中方法名相同,形参类型也相同的数组之间不构成重载。换句话说,二者不能共存。
* 2.5 可变个数形参在方法的形参中,必须声明在末尾
* 2.6 可变个数形参在方法的形参中,最多只能声明一个可变形参。
*
*/
public class MethodArgsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MethodArgsTest test = new MethodArgsTest();
test.show(12);
// test.show("hello");
// test.show("hello","world");
// test.show();
test.show(new String[]{"AA","BB","CC"});
}
public void show(int i){
}
public void show(String s){
System.out.println("show(String)");
}
public void show(String ... strs){
System.out.println("show(String ... strs)");
for(int i = 0;i < strs.length;i++){
System.out.println(strs[i]);
}
}
//不能与上一个方法同时存在
// public void show(String[] strs){
//
// }
//The variable argument type String of the method
//show must be the last parameter
// public void show(String ...strs,int i){
//
// }
}
值传递
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
*
* 关于变量的赋值:
*
* 如果变量是基本数据类型,此时赋值的是变量所保存的数据值。
* 如果变量是引用数据类型,此时赋值的是变量所保存的数据的地址值。
*
*/
public class ValueTransferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("***********基本数据类型:****************");
int m = 10;
int n = m;
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
System.out.println("***********引用数据类型:****************");
Order o1 = new Order();
o1.orderId = 1001;
Order o2 = o1;//赋值以后,o1和o2的地址值相同,都指向了堆空间中同一个对象实体。
System.out.println("o1.orderId = " + o1.orderId + ",o2.orderId = " +o2.orderId);
o2.orderId = 1002;
System.out.println("o1.orderId = " + o1.orderId + ",o2.orderId = " +o2.orderId);
}
}
class Order{
int orderId;
}
基本数据类型:*****
m = 10, n = 10
m = 10, n = 20
引用数据类型:*****
o1.orderId = 1001,o2.orderId = 1001
o1.orderId = 1002,o2.orderId = 1002
第二个说明代码
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* 方法的形参的传递机制:值传递
*
* 1.形参:方法定义时,声明的小括号内的参数
* 实参:方法调用时,实际传递给形参的数据
*
* 2.值传递机制:
* 如果参数是基本数据类型,此时实参赋给形参的是实参真实存储的数据值。
* 如果参数是引用数据类型,此时实参赋给形参的是实参存储数据的地址值。
*
*/
public class ValueTransferTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m = 10;
int n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
//交换两个变量的值的操作
// int temp = m ;
// m = n;
// n = temp;
ValueTransferTest1 test = new ValueTransferTest1();
test.swap(m, n);
System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n);
}
public void swap(int m,int n){
int temp = m ;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
}
m = 10, n = 20
m = 10, n = 20
第三个说明代码:想要改变两个值,必须使用引用型变量
package com.atguigu.java;
public class ValueTransferTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
data.m = 10;
data.n = 20;
System.out.println("m = " + data.m + ", n = " + data.n);
//交换m和n的值
// int temp = data.m;
// data.m = data.n;
// data.n = temp;
ValueTransferTest2 test = new ValueTransferTest2();
test.swap(data);
System.out.println("m = " + data.m + ", n = " + data.n);
}
public void swap(Data data){
int temp = data.m;
data.m = data.n;
data.n = temp;
}
}
class Data{
int m;
int n;
}
m = 10, n = 20
m = 20, n = 10
封装性的说明
封装性的体现:需要权限修饰符的配合
- Java的四种权限修饰符的权限(从小到大):private、缺省、protected、public。
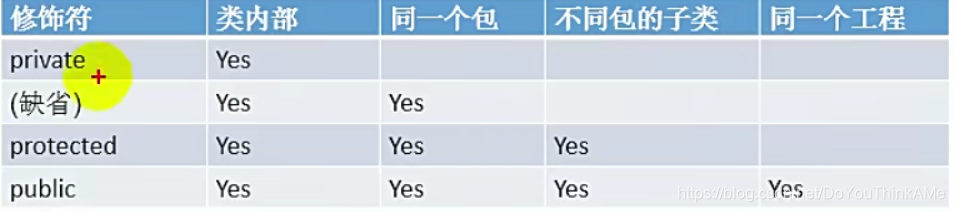
- 四种权限修饰符可以用来修饰类和类的内部结构:属性、 方法 、 构造器 、 内部类。
- 具体的,四种都可以用来修饰内部结构:属性,构造器 、 构造器 、 内部类。
- 修饰类的话,只能使用:缺省 、 public 。
代码测试:
Order
package com.atguigu.java;
public class Order {
private int orderPrivate;
int orderDefault;
public int orderPublic;
private void methodPrivate(){
orderPrivate = 1;
orderDefault = 2;
orderPublic = 3;
}
void methodDefault(){
orderPrivate = 1;
orderDefault = 2;
orderPublic = 3;
}
public void methodPublic(){
orderPrivate = 1;
orderDefault = 2;
orderPublic = 3;
}
}
Ordertest
package com.atguigu.java;
public class OrderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//首先要创建Order的对象
Order order = new Order();
order.orderDefault = 1;
order.orderPublic = 2;
//出了Order类之后,私有的结构就不可以调用了
// order.orderPrivate = 3;//The field Order.orderPrivate is not visible
order.methodDefault();
order.methodPublic();
//出了Order类之后,私有的结构就不可以调用了
// order.methodPrivate();//The method methodPrivate() from the type Order is not visible
}
}
另外一个包内:只有public能用
package java1;
import com.atguigu.java.Order;
public class OrderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Order order = new Order();
order.orderPublic = 2;
// 出了Order类所属的包之后,私有的结构、缺省声明的结构就不可以调用了
// order.orderDefault = 1;
// order.orderPrivate = 3;//The field Order.orderPrivate is not visible
order.methodPublic();
// 出了Order类所属的包之后,私有的结构、缺省声明的结构就不可以调用了
// order.methodDefault();
// order.methodPrivate();//The method methodPrivate() from the type Order is not visible
}
}
总结封装性:Java提供了四种权限修饰符来修饰类及类的内部结构,体现了类及类的内部结构的可见性的大小;
封装性的练习:
Person:
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 1.创建程序,在其中定义两个类:Person和PersonTest类。定义如下:
* 用setAge()设置人的合法年龄(0~130),用getAge()返回人的年龄。
*
* 2.练习2:
* 2.1. 在前面定义的Person类中添加构造器,利用构造器设置所有人的age属性初始值都为18。
* 2.2. 修改上题中类和构造器,增加name属性,使得每次创建Person对象的同时初始化对象的age属性值和name属性值。
*
*/
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
public Person(){
age = 18;
}
public Person(String n,int a){
name = n;
age = a;
}
public void setAge(int a){
if(a < 0 || a > 130){
// throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据非法!");
System.out.println("传入的数据非法!");
return;
}
age = a;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
//绝对不要这样写!!
// public int doAge(int a){
// age = a;
// return age;
// }
public void setName(String n){
name = n;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
PersonTest:
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 在PersonTest类中实例化Person类的对象b,
* 调用setAge()和getAge()方法,体会Java的封装性。
*
*/
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
// p1.age = 1;编译不通过
p1.setAge(12);
System.out.println("年龄为:" + p1.getAge());
// p1.doAge(122);
Person p2 = new Person("Tom", 21);
System.out.println("name = " + p2.getName() + ",age = " + p2.getAge());
}
}
构造器(或构造方法)
类的结构之三:
构造器(或构造方法、constructor)的使用
construct:建设、建造。 construction:CCB constructor:建设者一、构造器的作用:
1.创建对象
2.初始化对象的信息二、说明:
1.如果没有显式的定义类的构造器的话,则系统默认提供一个空参的构造器
2.定义构造器的格式:权限修饰符 类名(形参列表){}
3.一个类中定义的多个构造器,彼此构成重载
4.一旦我们显式的定义了类的构造器之后,系统就不再提供默认的空参构造器
5.一个类中,至少会有一个构造器。
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建类的对象:new + 构造器
Person p = new Person();
p.eat();
Person p1 = new Person("Tom");
System.out.println(p1.name);
}
}
class Person{
//属性
String name;
int age;
//构造器
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person().....");
}
//主要的地方
//如果这个功能是固定的话直接在创造构造器的时候直接赋给
public Person(String n){
name = n;
}
//
public Person(String n,int a){
name = n;
age = a;
}
//方法
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("人可以学习");
}
}
Person()…
人吃饭
Tom
构造器的练习
2.练习2:
2.1. 在前面定义的Person类中添加构造器,利用构造器设置所有人的age属性初始值都为18。
2.2. 修改上题中类和构造器,增加name属性,使得每次创建Person对象的同时初始化对象的age属性值和name属性值。
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
public Person(){
age = 18;
}
public Person(String n,int a){
name = n;
age = a;
}
public void setName(String n){
name = n;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p2 = new Person("Tom", 21);
System.out.println("name = " + p2.getName() + ",age = " + p2.getAge());
}
}
练习二
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 编写两个类,TriAngle和TriAngleTest,其中TriAngle类中声明私有的底边长base和高height,同时声明公共方法访问私有变量。
* 此外,提供类必要的构造器。另一个类中使用这些公共方法,计算三角形的面积。
*/
public class TriAngle { //angle:角 angel:天使
private double base;//底边长
private double height;//高
public TriAngle(){
}
public TriAngle(double b,double h){
base = b;
height = h;
}
public void setBase(double b){
base = b;
}
public double getBase(){
return base;
}
public void setHeight(double h){
height = h;
}
public double getHeight(){
return height;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer;
public class TriAngleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TriAngle t1 = new TriAngle();
t1.setBase(2.0);
t1.setHeight(2.4);
// t1.base = 2.5;//The field TriAngle.base is not visible
// t1.height = 4.3;
System.out.println("base : " + t1.getBase() + ",height : " + t1.getHeight());
TriAngle t2 = new TriAngle(5.1,5.6);
System.out.println("base : " + t2.getBase() + ",height : " + t2.getHeight());
}
}
总结:属性赋值的先后顺序
① 默认初始化
② 显式初始化
③ 构造器中初始化
④ 通过"对象.方法" 或 "对象.属性"的方式,赋值
以上操作的先后顺序:① - ② - ③ - ④
JavaBean
JavaBean是一种Java语言写成的可重用组件。
所谓JavaBean,是指符合如下标准的Java类:
1 类是公共的
2 有一个无参的公共的构造器
3 有属性,且有对应的get、set方法
//构造器的权限和类的权限相同
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
public Customer(){
}
public void setId(int i){
id = i;
}
public int getId(){
return id;
}
public void setName(String n){
name = n;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
this
- this关键字的使用:
- 1.this可以用来修饰、调用:属性、方法、构造器
- 2.this修饰属性和方法:
this理解为:当前对象 或 当前正在创建的对象- 2.1 在类的方法中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用当前对象属性或方法。但是,
通常情况下,我们都选择省略"this."。特殊情况下,如果方法的形参和类的属性同名时,我们必须显式
的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。- 2.2 在类的构造器中,我们可以使用"this.属性"或"this.方法"的方式,调用当前正在创建的对象属性或方法。
但是,通常情况下,我们都选择省略"this."。特殊情况下,如果构造器的形参和类的属性同名时,我们必须显式
的使用"this.变量"的方式,表明此变量是属性,而非形参。- 3 this调用构造器
① 我们在类的构造器中,可以显式的使用"this(形参列表)"方式,调用本类中指定的其他构造器
② 构造器中不能通过"this(形参列表)“方式调用自己
③ 如果一个类中有n个构造器,则最多有 n - 1构造器中使用了"this(形参列表)”
④ ※规定:"this(形参列表)“必须声明在当前构造器的首行
⑤ ※构造器内部,最多只能声明一个"this(形参列表)”,用来调用其他的构造器
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setAge(1);
System.out.println(p1.getAge());
p1.eat();
System.out.println();
Person p2 = new Person("Jerry",20);
System.out.println(p2.getAge());
}
}
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
// this.eat();
String info = "Person初始化时,需要考虑如下的1,2,3,4...(共40行代码)";
System.out.println(info);
}
public Person(String name){
//this调构造器必须在首行
this();//调用构造器Person();
//this表示方法或者属性
this.name = name;
}
public Person(int age){
this();//调用构造器Person();
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name,int age){
this(age);//调用构造器Person(int age);
this.name = name;
//this.age = age;
//Person初始化时,需要考虑如下的1,2,3,4...(共40行代码)
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;//this可以省略
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;//this可以省略
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
this.study();//this可以省略
}
public void study(){
System.out.println("人学习");
}
}
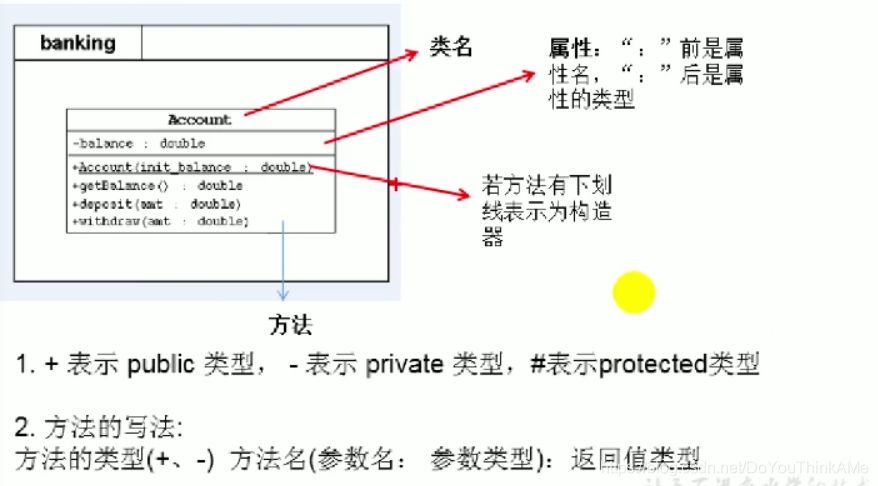
UMR类图
class中快速添加get 和 set
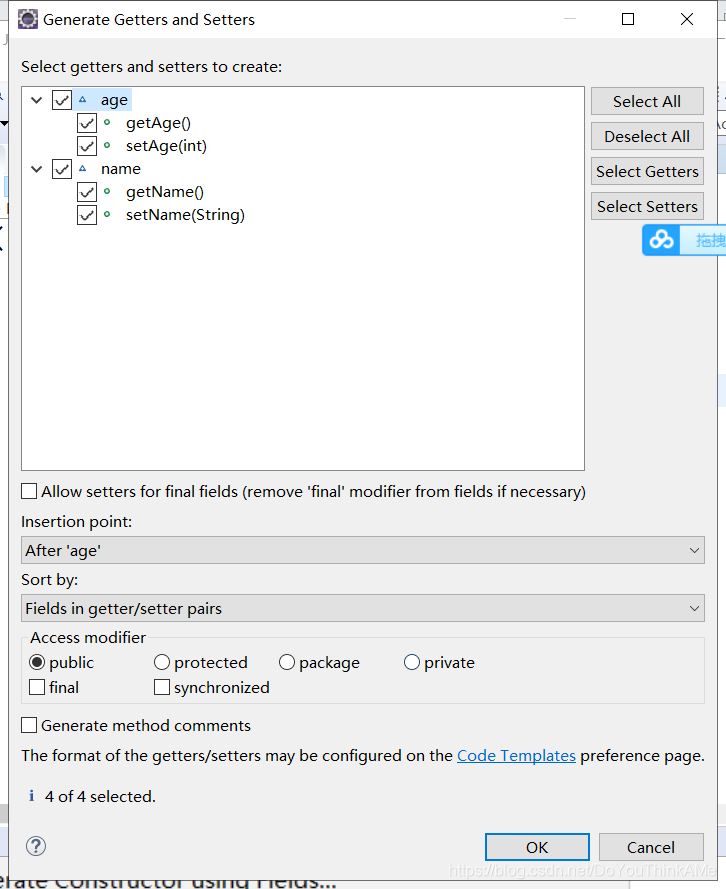
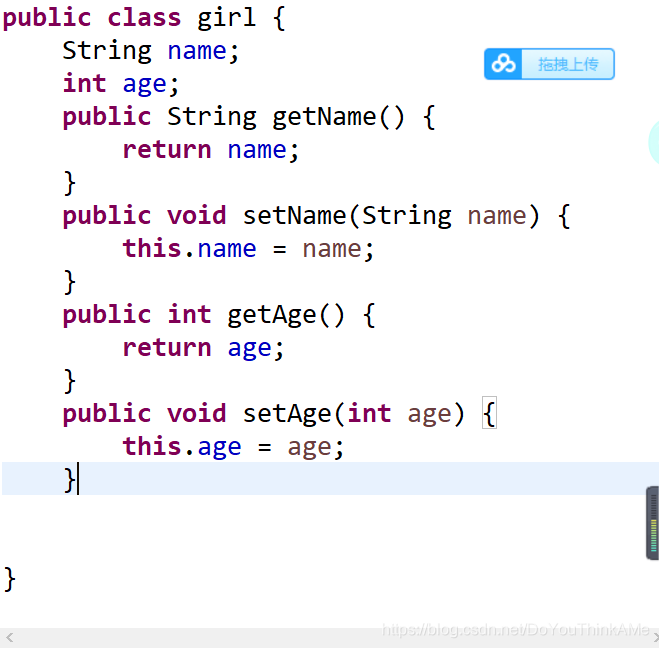
class中快速添加构造器
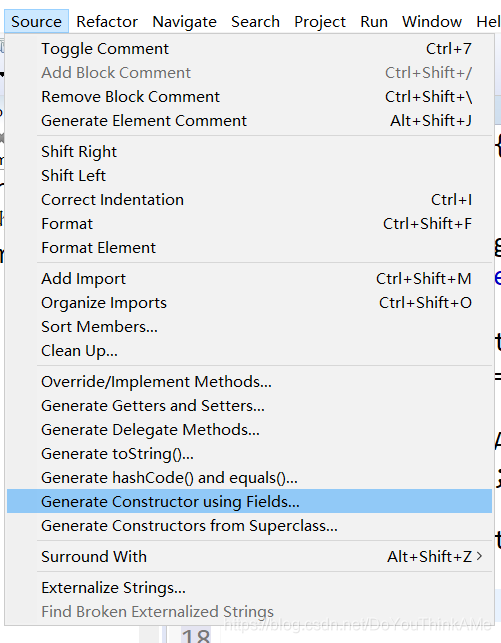
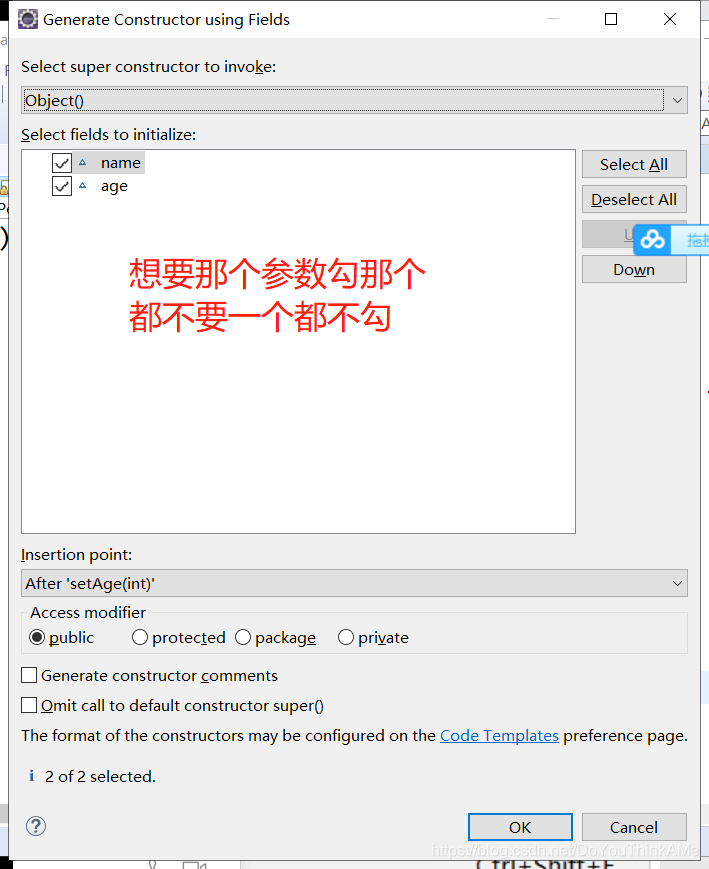
this的练习
package com.atguigu.java2;
public class Girl {
private String name;
private int age;
public Girl() {
}
public Girl(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void marry(Boy boy){
System.out.println("我想嫁给" + boy.getName());
boy.marry(this);
}
/**
*
* @Description 比较两个对象的大小
* @author shkstart
* @date 2019年1月18日下午4:02:09
* @param girl
* @return 正数:当前对象大; 负数:当前对象小 ; 0:当前对象与形参对象相等
*/
public int compare(Girl girl){
// if(this.age > girl.age){
// return 1;
// }else if(this.age < girl.age){
// return -1;
// }else{
// return 0;
// }
return this.age - girl.age;
}
}
package com.atguigu.java2;
public class Boy {
private String name;
private int age;
public Boy() {
}
public Boy(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Boy(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void marry(Girl girl){
System.out.println("我想娶" + girl.getName());
}
public void shout(){
if(this.age >= 22){
System.out.println("你可以去合法登记结婚了!");
}else{
System.out.println("先多谈谈恋爱~~");
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.java2;
public class BoyGirlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy = new Boy("罗密欧", 21);
boy.shout();
Girl girl = new Girl("朱丽叶", 18);
girl.marry(boy);
Girl girl1 = new Girl("祝英台",19);
int compare = girl.compare(girl1);
if(compare > 0){
System.out.println(girl.getName() + "大");
}else if(compare < 0){
System.out.println(girl1.getName() + "大");
}else{
System.out.println("一样大");
}
}
}
重要练习
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 写一个测试程序。
(1) 创建一个Customer ,名字叫 Jane Smith,
他有一个账号为1000,余额为2000元,年利率为 1.23% 的账户。
(2) 对Jane Smith操作。
存入 100 元,再取出960元。再取出2000元。
打印出Jane Smith 的基本信息
成功存入 :100.0
成功取出:960.0
余额不足,取款失败
Customer [Smith, Jane] has a account: id is 1000,
annualInterestRate is 1.23%, balance is 1140.0
*/
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer cust = new Customer("Jane", "Smith");
Account acct = new Account(1000, 2000, 0.0123);
cust.setAccount(acct);
cust.getAccount().deposit(100);
cust.getAccount().withdraw(960);
cust.getAccount().withdraw(2000);
System.out.println("Customer[" + cust.getLastName() + "," + cust.getFirstName() +
"] has a account: id is " + cust.getAccount().getId() + ",annualInterestRate is "+
cust.getAccount().getAnnualInterestRate() * 100 + "% ,balance is " + cust.getAccount().getBalance());
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String f,String l){
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer;
public class Account {
private int id;//账号
private double balance;//余额
private double annualInterestRate;//年利率
public Account (int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate ){
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
//在提款方法withdraw中,需要判断用户余额是否能够满足提款数额的要求,如果不能,应给出提示。
public void withdraw (double amount){//取钱
if(balance < amount){
System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");
return;
}
balance -= amount;
System.out.println("成功取出:" + amount);
}
public void deposit (double amount){//存钱
if(amount > 0){
balance += amount;
System.out.println("成功存入:" + amount);
}
}
}
更重要的练习
package com.atguigu.exer4;
public class BankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank bank = new Bank();
bank.addCustomer("Jane", "Smith");
//连续操作
bank.getCustomer(0).setAccount(new Account(2000));
bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().withdraw(500);
double balance = bank.getCustomer(0).getAccount().getBalance();
System.out.println("客户:" + bank.getCustomer(0).getFirstName() + "的账户余额为:" + balance);
System.out.println("***********************");
bank.addCustomer("万里", "杨");
System.out.println("银行客户的个数为:" + bank.getNumOfCustomers());
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer4;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(String f, String l) {
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer4;
public class Account {
private double balance;
public Account(double init_balance){
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public double getBalance(){
return balance;
}
//存钱操作
public void deposit(double amt){
if(amt > 0){
balance += amt;
System.out.println("存钱成功");
}
}
//取钱操作
public void withdraw(double amt){
if(balance >= amt){
balance -= amt;
System.out.println("取钱成功");
}else{
System.out.println("余额不足");
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer4;
public class Bank {
private Customer[] customers;// 存放多个客户的数组
private int numberOfCustomers;// 记录客户的个数
public Bank() {
customers = new Customer[10];
}
// 添加客户
public void addCustomer(String f, String l) {
Customer cust = new Customer(f, l);
// customers[numberOfCustomers] = cust;
// numberOfCustomers++;
// 或
customers[numberOfCustomers++] = cust;
}
// 获取客户的个数
public int getNumOfCustomers() {
return numberOfCustomers;
}
// 获取指定位置上的客户
public Customer getCustomer(int index) {
// return customers[index];//可能报异常
if (index >= 0 && index < numberOfCustomers) {
return customers[index];
}
return null;
}
}
package关键字 和 import关键字
一、package关键字的使用
1.为了更好的实现项目中类的管理,提供包的概念
2.使用package声明类或接口所属的包,声明在源文件的首行
3.包,属于标识符,遵循标识符的命名规则、规范(xxxyyyzzz)、“见名知意”
4.每"."一次,就代表一层文件目录。
补充:同一个包下,不能命名同名的接口、类。
不同的包下,可以命名同名的接口、类。
二、import关键字的使用
import:导入
- 在源文件中显式的使用import结构导入指定包下的类、接口
- 声明在包的声明和类的声明之间
- 如果需要导入多个结构,则并列写出即可
- 可以使用"xxx.*"的方式,表示可以导入xxx包下的所有结构
- 如果使用的类或接口是java.lang包下定义的,则可以省略import结构
- 如果使用的类或接口是本包下定义的,则可以省略import结构
- 如果在源文件中,使用了不同包下的同名的类,则必须至少有一个类需要以全类名的方式显示。
com.atguigu.exer3.Account acct1 = new com.atguigu.exer3.Account(1000,2000,0.0123);- 使用"xxx.*"方式表明可以调用xxx包下的所有结构。但是如果使用的是xxx子包下的结构,则仍需要显式导入
- import static:导入指定类或接口中的静态结构:属性或方法
package com.atguigu.java;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.*;
import com.atguigu.exer4.Account;
import com.atguigu.exer4.Bank;
import com.atguigu.java2.java3.Dog;
import static java.lang.System.*;
import static java.lang.Math.*;
public class PackageImportTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String info = Arrays.toString(new int[]{1,2,3});
Bank bank = new Bank();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Scanner s = null;
System.out.println("hello!");
Person p = new Person();
Account acct = new Account(1000);
//全类名的方式显示
com.atguigu.exer3.Account acct1 = new com.atguigu.exer3.Account(1000,2000,0.0123);
Date date = new Date();
java.sql.Date date1 = new java.sql.Date(5243523532535L);
Dog dog = new Dog();
Field field = null;
out.println("hello");
long num = round(123.434);
}
}




 本文探讨了Java中的对象概念,如何通过类实例化并调用方法,包括匿名对象的使用。还深入讲解了Java的封装性,展示了如何通过权限修饰符控制类的属性和方法的访问性。此外,还涵盖了构造器、方法重载、值传递以及JavaBean的特性。文章以实际代码示例为基础,解释了如何在不同场景下应用这些概念。
本文探讨了Java中的对象概念,如何通过类实例化并调用方法,包括匿名对象的使用。还深入讲解了Java的封装性,展示了如何通过权限修饰符控制类的属性和方法的访问性。此外,还涵盖了构造器、方法重载、值传递以及JavaBean的特性。文章以实际代码示例为基础,解释了如何在不同场景下应用这些概念。
















 208
208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








