LRU缓存-keep-alive实现原理
keep-alive是Vue.js的一个内置组件。它能够将不活动的组件实例保存在u内存中,而不是直接销毁,它是一个抽象组件,不会被渲染到真实DOM中,也不会出现在父组件链中。简单地说,keep-alive用于保存组件的渲染状态,避免组件反复创建和渲染,有效提高系统性能。
keep-alive的max属性,用于限制可以缓存多少组件实例,一旦这个数字达到了上限,在新实例被创建之前,已缓存组件中最久没有被访问的实例会被销毁掉
LRU缓存淘汰算法
LRU缓存淘汰算法:根据数据的历史记录来淘汰数据,重点在于保护最近被访问/使用过的数据,淘汰阶段最久被访问的数据
主体思想:如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高
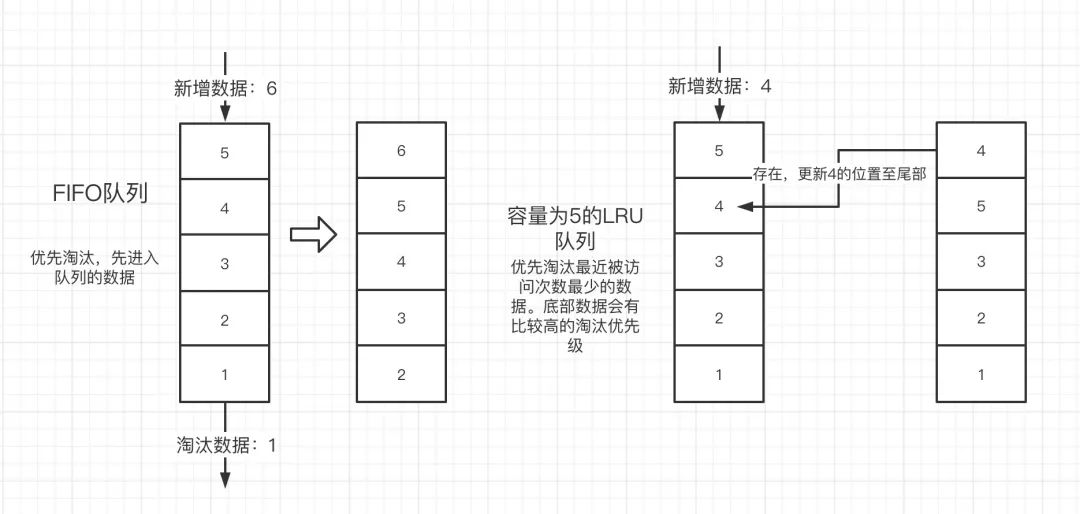
1、新数据插入到链表尾部
2、每当命中缓存(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表尾部
3、当链表满的时候,将链表头部数据丢弃
实现LRU的数据结构
hashMap+双向链表 考虑可能需要频繁删除一个元素,并将这个元素的前一个结点指向下一个节点,所以使用双链接最合适
class LRUCache {
capacity; //容量
cache; //缓存
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new Map();
}
get(key) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
let temp = this.cache.get(key);
this.cache.delete(key);
this.cache.set(key, temp);
return map;
}
return -1;
}
put(key, value) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
this.cache.delete(key);
} else if (this.cache.size >= this.capacity) {
this.cache.delete(this.cache.keys().next().value);
}
this.cache.set(key, value);
}
}
Vue中的Keep-Alive
原理:
1.使用LRU缓存机制进行缓存,max限制缓存表的最大容量
2.根据设定的include/exclude(如果有)进行条件匹配,决定是否缓存。不匹配直接返回组件实例
3.根据组件ID和tag生成缓存Key,并在缓存对象中查找是否已缓存过该组件实例。如果存在,直接去除缓存值并更新该key再this.keys中的位置(更新key的位置是实现LRU置换策略的关键)
4.获取节点名称,或者根据节点cid等信息喷出当前组件名称
5.获取keep-alive包裹着第一个子组件对象及其组件名
const KeepAliveImpl = {
name: "KeepAlive",
props: {
include: [String, RegExp, Array],
exclude: [String, RegExp, Array],
max: [String, Number],
},
setup(props, { slots }) {
const cache = new Map();
const keys = new Set();
let current = null;
//当props上的include或者exclude变化时移除缓存
watch(
() => [propos.include, props.exclude],
([include, exclude]) => {
include && pruneCache((name) => matches(include, name));
exclude && pruneCache((name) => !matches(exclude, name));
},
{ flush: "post", deep: true }
);
let pendingCacheKey = null;
const cacheSubtree = () => {
if (pendingCacheKey != null) {
cache.set(pendingCacheKey, getInnerChild(instance.subTree));
}
};
onMounted(cacheSubtree);
onUpdated(cacheSubtree);
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
// 卸载缓存表里的所有组件和其中的子树...
});
return () => {
// 省略部分代码,以下是缓存逻辑
pendingCacheKey = null;
const children = slots.default();
let vnode = children[0];
const comp = vnode.type;
const name = getName(comp);
const { include, exclude, max } = props;
// key 值是 KeepAlive 子节点创建时添加的,作为缓存节点的唯一标识
const key = vnode.key == null ? comp : vnode.key;
// 通过 key 值获取缓存节点
const cachedVNode = cache.get(key);
if (cachedVNode) {
// 缓存存在,则使用缓存装载数据
vnode.el = cachedVNode.el;
vnode.component = cachedVNode.component;
if (vnode.transition) {
// 递归更新子树上的 transition hooks
setTransitionHooks(vnode, vnode.transition);
}
// 阻止 vNode 节点作为新节点被挂载
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE;
// 刷新key的优先级
keys.delete(key);
keys.add(key);
} else {
keys.add(key);
// 属性配置 max 值,删除最久不用的 key ,这很符合 LRU 的思想
if (max && keys.size > parseInt(max, 10)) {
pruneCacheEntry(keys.values().next().value);
}
}
// 避免 vNode 被卸载
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE;
current = vnode;
return vnode;
};
},
};
// 遍历缓存表
function pruneCache(filter?: (name: string) => boolean) {
cache.forEach((vnode, key) => {
const name = getComponentName(vnode.type as ConcreteComponent);
if (name && (!filter || !filter(name))) {
// !filter(name) 即 name 在 includes 或不在 excludes 中
pruneCacheEntry(key);
}
});
}
// 依据 key 值从缓存表中移除对应组件
function pruneCacheEntry(key: CacheKey) {
const cached = cache.get(key) as VNode;
if (!current || cached.type !== current.type) {
/* 当前没有处在 activated 状态的组件
* 或者当前处在 activated 组件不是要删除的 key 时
* 卸载这个组件
*/
unmount(cached); // unmount方法里同样包含了 resetShapeFlag
} else if (current) {
// 当前组件在未来应该不再被 keepAlive 缓存
// 虽然仍在 keepAlive 的容量中但是需要刷新当前组件的优先级
resetShapeFlag(current);
// resetShapeFlag
}
cache.delete(key);
keys.delete(key);
}
function resetShapeFlag(vnode: VNode) {
let shapeFlag = vnode.shapeFlag; // shapeFlag 是 VNode 的标识
// ... 清除组件的 shapeFlag
}
总结
使用 KeepAlive 后,被 KeepAlive 包裹的组件在经过第一次渲染后,它的 vnode 以及 DOM 都会被缓存起来,然后再下一次再次渲染该组件的时候,直接从缓存中拿到对应的 vnode 和 DOM,然后渲染,并不需要再走一次组件初始化,render 和 patch 等一系列流程,减少了 script 的执行时间,性能更好。
缓存过程:
1.声明有序集合keys作为缓存容器,存入组件的唯一key值
2.在缓存容器keys中,越靠前的key值越意味着被访问的越少也越优先被淘汰
3.渲染函数执行时,若命中缓存时,则从keys中删除当前命中的key,并往keys末尾追加key值,刷新该key的优先级
4.未命中缓存时,则 keys 追加缓存数据 key 值,若此时缓存数据长度大于 max 最大值,则删除最旧的数据
5.当触发beforeMount/update生命周期,缓存当前activated组建的子树的数据





















 3530
3530

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








