实验目的和要求
了解静态联编的动态联编的概念。掌握动态联编的条件。
实验内容
1.分析并调试下列程序。
- //sy6_1.cpp
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Base
- {
- public:
- virtual void f(float x){cout<<"Base::f(float)"<<x<<endl;}
- void g(float x){cout<<"Base::g(float)"<<x<<endl;}
- void h(float x){cout<<"Base::h(float)"<<x<<endl;}
- };
- class Derived:public Base
- {
- public:
- virtual void f(float x){cout<<"Derived::f(float}"<<x<<endl;}
- void g(int x){cout<<"Derived::g(int)"<<x<<endl;}
- void h(float x){cout<<"Derived::h(float)"<<x<<endl;}
- };
- int main()
- {
- Derived d;
- Base *pb=&d;
- Derived *pd=&d;
- pb->f(3.14f);
- pd->f(3.14f);
- pb->g(3.14f);
- pb->h(3.14f);
- pd->h(3.14f);
- return 0;
- }
(1)找出以上程序中使用了重载和覆盖函数。
(2)写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。

程序的输出结果如下:
2
. 分析并调试下列程序
- //sy6_2.cpp
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Base
- {
- public:
- void f(int x){cout<<"Base::f(int)"<<x<<endl;}
- void f(float x){cout<<"Base::f(float)"<<x<<endl;}
- virtual void g(void){cout<<"Base::g(void)"<<endl;}
- };
- class Derived:public Base
- {
- public:
- virtual void g(void){cout<<"Derived::g(void}"<<endl;}
- };
- int main()
- {
- Derived d;
- Base *pb=&d;
- pb->f(42);
- pb->f(3.14f);
- pb->g();
- return 0;
- }
(1)找出以上程序中使用了重载和覆盖函数。
(2)写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。
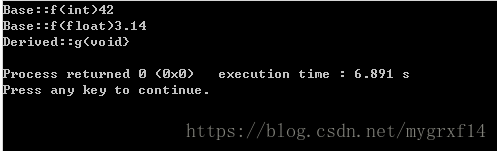
程序的输出结果如下:
3. 分析并调试下列程序
- //sy6_3.cpp
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Point
- {
- public:
- Point(double i,double j){x=i;y=j;}
- double Area(){return 0.0;}
- private:
- double x,y;
- };
- class Rectangle:public Point
- {
- public:
- Rectangle(double i,double j,double k,double l):Point(i,j){w=k;h=l;}
- double Area(){return w*h;}
- private:
- double w,h;
- };
- int main()
- {
- Point p(3.5,7);
- double A=p.Area();
- cout<<"Area= "<<A<<endl;
- Rectangle r(1.2,3,5,7.8);
- A=r.Area();
- cout<<"Area= "<<A<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。
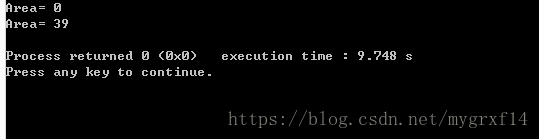
4. 分析并调试下列程序
- //sy6_4.cpp
- #include<iostream>
- using namespace std;
- const double PI=3.1415;
- class Shap
- {
- public:
- virtual double Area()=0;
- };
- class Triangle:public Shap
- {
- public:
- Triangle(double h,double w){H=h;W=w;}
- double Area(){return 0.5*H*W;}
- private:
- double H,W;
- };
- class Rectangle:public Shap
- {
- public:;
- Rectangle(double h,double w){H=h;W=w;}
- double Area(){return H*W;}
- private:
- double H,W;
- };
- class Circle:public Shap
- {
- public:
- Circle(double r){R=r;}
- double Area(){return PI*R*R;}
- private:
- double R;
- };
- class Square:public Shap
- {
- public:
- Square(double s){S=s;}
- double Area(){return S*S;}
- private:
- double S;
- };
- double Total(Shap *s[],int n)
- {
- double sum=0;
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- sum+=s[i]->Area();
- return sum;
- }
- int main()
- {
- Shap *s[5];
- s[0]=new Square(8.0);
- s[1]=new Rectangle(3.0,8.0);
- s[2]=new Square(12.0);
- s[3]=new Circle(8.0);
- s[4]=new Triangle(5.0,4.0);
- double sum=Total(s,5);
- cout<<"SUM = "<<sum<<endl;
- return 0;
- }
程序的输出结果如下:
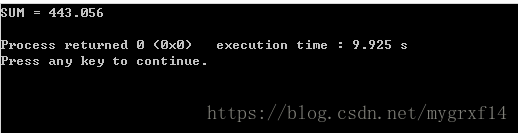
(1)指出抽象类。
(2)指出纯虚函数,并说明它的作用。
(3)每个类的作用是什么?整个程序的作用是什么?
5. 某学校对教师每个月工资的计算规定如下:固定工资+课时补贴;教授的固定工资为5000元,每个课时补贴50;副教授的固定工资为3000,每个课时补贴30元;讲师的固定工资为2000元,每个课时补贴20元。定义教师抽象类,派生不同职称的教师类,编写程序求若干个教师的月工资。(sy6_5.cpp)
6. 把实验5中的第4题的Shape类定义为抽象类,提供共同操作界面的纯虚函数。TwoDimShape类和ThreeDimShape类仍然抽象类,第3层具体类才能提供全部函数的实现。在测试函数中,使用基类指针实现不同派生类对象的操作。
分析与讨论
1.结合实验内容中第1题和第2题,说明重载与覆盖的区别。
2.总结静态联编和动态联编的区别和动态联编的条件。




 本文通过四个C++程序实例,详细分析了多态性和虚函数的运用,包括重载、覆盖的概念及实际效果。程序涉及基类与派生类之间的成员函数调用,展示了动态绑定和静态绑定的不同。通过对输出结果的解释,深入理解多态在面向对象编程中的作用。
本文通过四个C++程序实例,详细分析了多态性和虚函数的运用,包括重载、覆盖的概念及实际效果。程序涉及基类与派生类之间的成员函数调用,展示了动态绑定和静态绑定的不同。通过对输出结果的解释,深入理解多态在面向对象编程中的作用。
















 3612
3612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








