0. AAC介绍
AAC音频文件的每一帧都由一个ADTS头和AAC ES(AAC音频数据)组成。
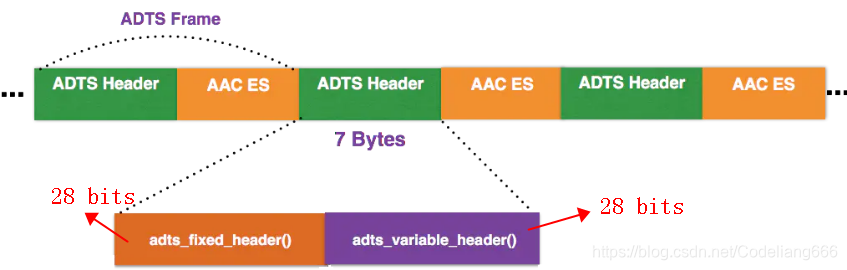
以下是wiki的介绍:https://wiki.multimedia.cx/index.php?title=ADTS
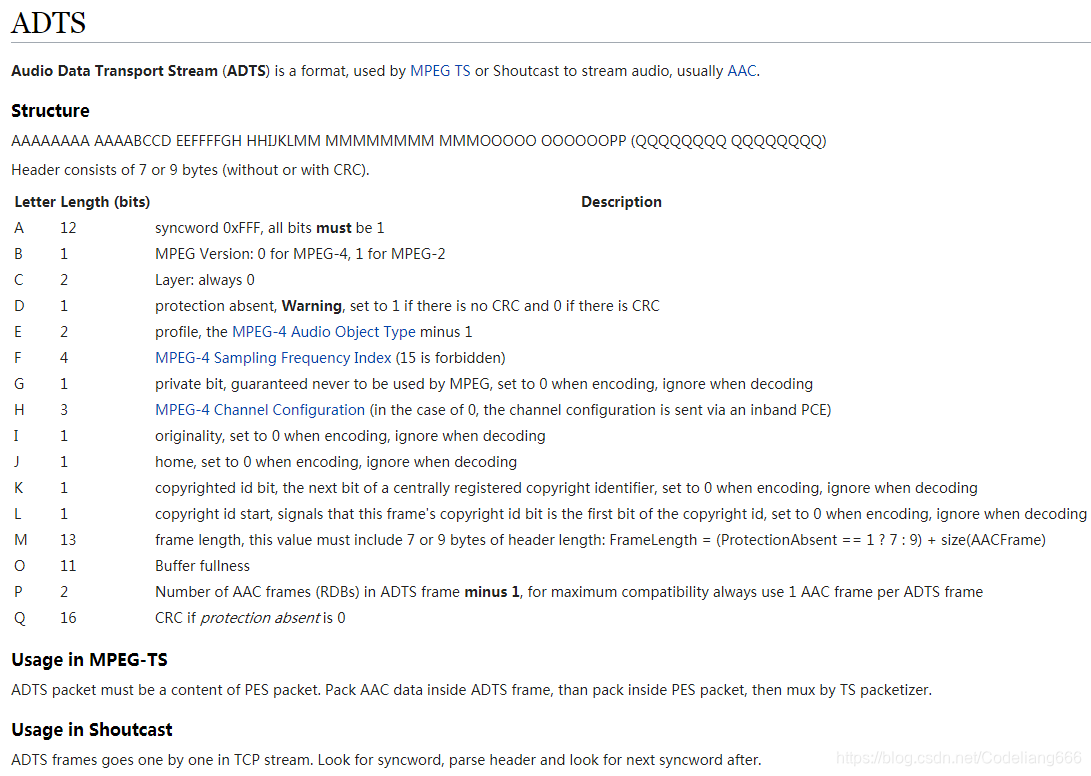
0.1 其包括固定头信息:adts_fixed_header()
ADTS头的固定头信息在每个帧中都是一样的。

syncword:帧同步标识一个帧的开始,固定为0xFFF
ID:MPEG 标示符。0表示MPEG-4,1表示MPEG-2
layer:固定为’00’
protection_absent:标识是否进行误码校验。0表示有CRC校验,1表示没有CRC校验
profile:标识使用哪个级别的AAC。1: AAC Main 2:AAC LC (Low Complexity) 3:AAC SSR (Scalable Sample Rate) 4:AAC LTP (Long Term Prediction)
sampling_frequency_index:标识使用的采样率的下标
private_bit:私有位,编码时设置为0,解码时忽略
channel_configuration:标识声道数
original_copy:编码时设置为0,解码时忽略
home:编码时设置为0,解码时忽略
0.2 可变头信息:adts_variable_header()

copyrighted_id_bit:编码时设置为0,解码时忽略
copyrighted_id_start:编码时设置为0,解码时忽略
aac_frame_length:ADTS帧长度包括ADTS长度和AAC声音数据长度的和(单位是字节)。即 aac_frame_length = (protection_absent == 0 ? 9 : 7) + audio_data_length
adts_buffer_fullness:固定为0x7FF。表示是码率可变的码流
number_of_raw_data_blocks_in_frame:表示当前帧有number_of_raw_data_blocks_in_frame + 1 个原始帧(一个AAC原始帧包含一段时间内1024个采样及相关数据)。
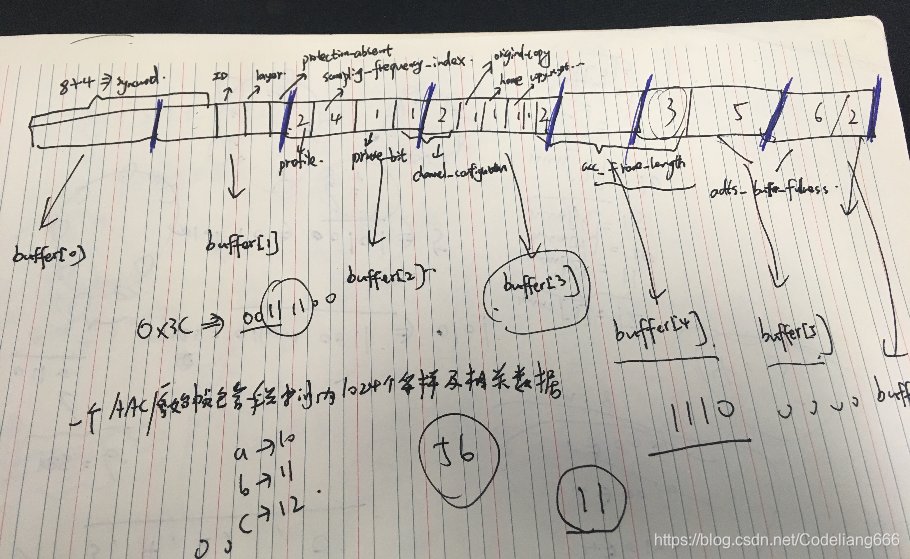
这个ADTS头信息有点难理解,建议在小本本上画一画,就能搞清楚下面这部分代码了。
//Sync words
if ((buffer[0] == 0xff) && ((buffer[1] & 0xf0) == 0xf0)) {
size |= ((buffer[3] & 0x03) << 11); //high 2 bit
size |= buffer[4] << 3; //middle 8 bit
size |= ((buffer[5] & 0xe0) >> 5); //low 3bit
//size存储的是aac_frame_length,即ADTS长度和AAC声音数据长度的和
break;
}
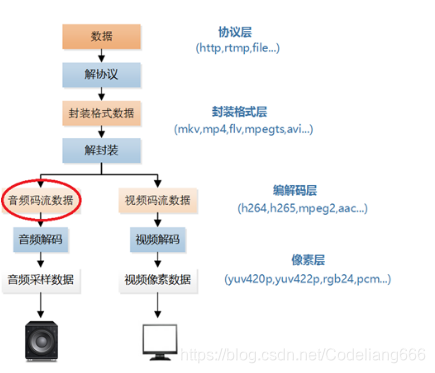
0.3 音频码流在视频播放器的位置
1. 代码
extern "C"
{
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
#endif
}
extern "C" {
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
}
int getADTSframe(unsigned char* buffer, int buf_size, unsigned char* data, int* data_size) {
// buffer是每次传进来的1024*1024字节的数据
// buf_size是成功读取1个字节的总的个数,这里读取成功即1024*1024,
//也可能末尾读着读着没了,那就没这么多
// data即传进来的aacframe,空间大小是1024*5个字节
// data_size是aac_frame_length:ADTS帧长度包括ADTS长度和AAC声音数据长度的和
//
int size = 0;
// 避免空指针,这个代码是有意义的,在实际的android开发中,
// 有时候遇到系统稳定性问题,比如死机,解dump会发现空指针,
// 我们找到函数的位置,然后加这个避免空指针的代码即可解决.
if (!buffer || !data || !data_size) {
return -1;
}
while (1) {
if (buf_size < 7) {
//ADTS头一般是7个字节,如果对数据进行CRC校验,还需要2个Byte的校验码,
//所以ADTS头实际长度是7个字节或者9个字节,
//所以若传进来的buf_size<7,那么也就没必要继续解析文件头了
return -1;
}
//Sync words
if ((buffer[0] == 0xff) && ((buffer[1] & 0xf0) == 0xf0)) {
size |= ((buffer[3] & 0x03) << 11); //high 2 bit
size |= buffer[4] << 3; //middle 8 bit
size |= ((buffer[5] & 0xe0) >> 5); //low 3bit
//size存储的是aac_frame_length,即ADTS长度和AAC声音数据长度的和
break;
}
--buf_size;
++buffer;
}
if (buf_size < size) {
//数据分割,若小于一个aac_frame_length帧长度,直接return
return 1;
}
memcpy(data, buffer, size);
//由buffer所指内存区域复制size个字节到data所指内存区域
//把重要信息存到aacframe指针里面
//需要知道profile以及sampling_frequency_index
*data_size = size;
return 0;
}
int simplest_aac_parser(const char* url)
{
int data_size = 0;
int size = 0;
int cnt = 0;
int offset = 0;
//FILE *myout=fopen("output_log.txt","wb+");
FILE* myout = stdout;
unsigned char* aacframe = (unsigned char*)malloc(1024 * 10);
unsigned char* aacbuffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(1024 * 2048);
FILE* ifile = fopen(url, "rb");
if (!ifile) {
printf("Open file error");
return -1;
}
printf("-----+- ADTS Frame Table -+------+\n");
printf(" NUM | Profile | Frequency| Size |\n");
printf("-----+---------+----------+------+\n");
while (!feof(ifile)) {
data_size = fread(aacbuffer + offset, 1, 1024 * 2048 - offset, ifile);
unsigned char* input_data = aacbuffer;
while (1)
{
int ret = getADTSframe(input_data, data_size, aacframe, &size );
if (ret == -1) {
break;
}
else if (ret == 1) {
memcpy(aacbuffer, input_data, data_size);
offset = data_size;
break;
}
char profile_str[10] = { 0 };
char frequence_str[10] = { 0 };
unsigned char profile = aacframe[2] & 0xC0;
profile = profile >> 6;
//获取标识使用哪个级别的AAC。1: AAC Main
//2:AAC LC (Low Complexity)
//3:AAC SSR (Scalable Sample Rate)
//4:AAC LTP (Long Term Prediction)
switch (profile) {
case 0: sprintf(profile_str, "Main"); break;
case 1: sprintf(profile_str, "LC"); break;
case 2: sprintf(profile_str, "SSR"); break;
default:sprintf(profile_str, "unknown"); break;
}
unsigned char sampling_frequency_index = aacframe[2] & 0x3C;
sampling_frequency_index = sampling_frequency_index >> 2;
//获取标识使用的采样率的下标
switch (sampling_frequency_index) {
case 0: sprintf(frequence_str, "96000Hz"); break;
case 1: sprintf(frequence_str, "88200Hz"); break;
case 2: sprintf(frequence_str, "64000Hz"); break;
case 3: sprintf(frequence_str, "48000Hz"); break;
case 4: sprintf(frequence_str, "44100Hz"); break;
case 5: sprintf(frequence_str, "32000Hz"); break;
case 6: sprintf(frequence_str, "24000Hz"); break;
case 7: sprintf(frequence_str, "22050Hz"); break;
case 8: sprintf(frequence_str, "16000Hz"); break;
case 9: sprintf(frequence_str, "12000Hz"); break;
case 10: sprintf(frequence_str, "11025Hz"); break;
case 11: sprintf(frequence_str, "8000Hz"); break;
default:sprintf(frequence_str, "unknown"); break;
}
fprintf(myout, "%5d| %8s| %8s| %5d|\n", cnt, profile_str, frequence_str, size);
data_size -= size;
input_data += size;
cnt++;
}
}
fclose(ifile);
free(aacbuffer);
free(aacframe);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
simplest_aac_parser("nocturne.aac");
return 0;
}
nocturne.aac 音源获取链接: https://github.com/leixiaohua1020/simplest_mediadata_test
2. 结果
本程序的输入为一个AAC原始码流(裸流)的文件路径,输出为该码流中ADTS frame的统计数据
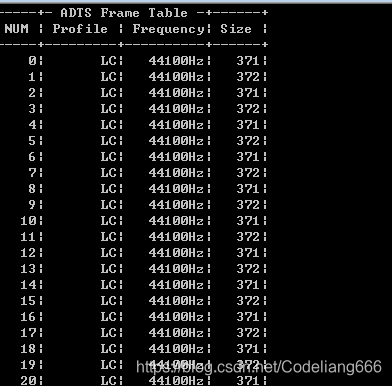
…
参考链接:
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/b5ca697535bd
- https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/leixiaohua1020/article/details/50535042?locationNum=3&fps=1





 本文深入讲解AAC音频文件的ADTS头结构,包括固定头信息和可变头信息的详细解析,以及如何通过代码实现AAC音频帧的定位和提取。文章提供了具体的C语言代码示例,演示如何从AAC原始码流中读取并解析ADTS帧。
本文深入讲解AAC音频文件的ADTS头结构,包括固定头信息和可变头信息的详细解析,以及如何通过代码实现AAC音频帧的定位和提取。文章提供了具体的C语言代码示例,演示如何从AAC原始码流中读取并解析ADTS帧。

















 276
276

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








