import os
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
import subprocess
import tempfile
import shutil
import random
import wave
import struct
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
# 尝试导入PyQt5,如果失败则提供友好的错误信息
try:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QVBoxLayout,
QHBoxLayout, QPushButton, QLabel, QFileDialog,
QMessageBox, QProgressBar, QGroupBox, QTextEdit,
QCheckBox, QListWidget, QListWidgetItem, QComboBox)
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt, QThread, pyqtSignal
from PyQt5.QtGui import QFont, QPalette, QColor, QIcon
except ImportError:
print("错误: 需要安装PyQt5库")
print("请运行: pip install PyQt5")
sys.exit(1)
# 尝试导入GPU相关库
try:
import pyopencl as cl
OPENCL_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
OPENCL_AVAILABLE = False
try:
import cupy as cp
CUDA_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
CUDA_AVAILABLE = False
# 尝试导入scipy
try:
import scipy.io.wavfile as wavfile
SCIPY_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
SCIPY_AVAILABLE = False
class AudioSteganography:
"""音频隐写处理类"""
@staticmethod
def embed_message(audio_path, message, output_path):
"""使用改进的LSB算法在音频中嵌入消息"""
try:
# 读取音频文件
with wave.open(audio_path, 'rb') as audio:
params = audio.getparams()
frames = audio.readframes(audio.getnframes())
# 将音频数据转换为字节数组
audio_data = bytearray(frames)
# 将消息转换为二进制
binary_message = ''.join(format(ord(char), '08b') for char in message)
binary_message += '00000000' # 添加终止符
# 检查音频容量是否足够
if len(binary_message) > len(audio_data) * 8:
raise ValueError("音频文件太小,无法嵌入消息")
# 使用改进的LSB算法嵌入消息(每4个样本嵌入1位)
sample_interval = 4 # 每4个样本嵌入1位
message_index = 0
for i in range(0, len(audio_data), sample_interval):
if message_index >= len(binary_message):
break
# 修改每个样本的最低有效位
audio_data[i] = (audio_data[i] & 0xFE) | int(binary_message[message_index])
message_index += 1
# 保存带有隐写信息的音频
with wave.open(output_path, 'wb') as output_audio:
output_audio.setparams(params)
output_audio.writeframes(bytes(audio_data))
return True, "音频隐写成功"
except Exception as e:
return False, f"音频隐写失败: {str(e)}"
@staticmethod
def extract_message(audio_path):
"""从音频中提取隐藏的消息"""
try:
# 读取音频文件
with wave.open(audio_path, 'rb') as audio:
frames = audio.readframes(audio.getnframes())
# 将音频数据转换为字节数组
audio_data = bytearray(frames)
# 提取LSB位
binary_message = ''
sample_interval = 4 # 与嵌入时保持一致
for i in range(0, len(audio_data), sample_interval):
binary_message += str(audio_data[i] & 1)
# 将二进制转换为字符
message = ''
for i in range(0, len(binary_message), 8):
byte = binary_message[i:i+8]
if len(byte) < 8:
break
char = chr(int(byte, 2))
if char == '\0': # 遇到终止符停止
break
message += char
return True, message
except Exception as e:
return False, f"消息提取失败: {str(e)}"
class VideoProcessor(QThread):
progress_updated = pyqtSignal(int)
status_updated = pyqtSignal(str)
finished = pyqtSignal(bool, str)
batch_progress = pyqtSignal(int, int) # 当前处理, 总计
def __init__(self, video_a_path, video_b_paths, output_dir, use_gpu=False, gpu_type="auto"):
super().__init__()
self.video_a_path = video_a_path
self.video_b_paths = video_b_paths
self.output_dir = output_dir
self.use_gpu = use_gpu
self.gpu_type = gpu_type
self.temp_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
self.gpu_context = None
self.gpu_queue = None
self.gpu_device = None
# 初始化GPU环境
if self.use_gpu:
self.init_gpu()
def init_gpu(self):
"""初始化GPU环境"""
try:
if self.gpu_type == "cuda" or (self.gpu_type == "auto" and CUDA_AVAILABLE):
# 使用CUDA
self.status_updated.emit("初始化CUDA环境...")
# 检查可用GPU
devices = cp.cuda.runtime.getDeviceCount()
if devices > 0:
self.status_updated.emit(f"找到 {devices} 个NVIDIA GPU")
# 使用第一个可用的GPU
cp.cuda.Device(0).use()
self.gpu_type = "cuda"
return True
else:
self.status_updated.emit("未找到NVIDIA GPU,尝试使用OpenCL")
self.gpu_type = "opencl"
if self.gpu_type == "opencl" or (self.gpu_type == "auto" and OPENCL_AVAILABLE):
# 使用OpenCL
self.status_updated.emit("初始化OpenCL环境...")
platforms = cl.get_platforms()
# 优先寻找Intel Arc显卡
intel_arc_found = False
for platform in platforms:
devices = platform.get_devices(device_type=cl.device_type.GPU)
for device in devices:
device_name = device.name
if "Intel" in device_name and ("Arc" in device_name or "A770" in device_name):
self.status_updated.emit(f"找到Intel Arc显卡: {device_name}")
self.gpu_context = cl.Context([device])
self.gpu_queue = cl.CommandQueue(self.gpu_context)
self.gpu_device = device
self.gpu_type = "opencl"
intel_arc_found = True
break
if intel_arc_found:
break
# 如果没有找到Intel Arc,寻找其他GPU
if not intel_arc_found:
for platform in platforms:
devices = platform.get_devices(device_type=cl.device_type.GPU)
if devices:
self.gpu_context = cl.Context(devices)
self.gpu_queue = cl.CommandQueue(self.gpu_context)
self.gpu_device = devices[0]
self.status_updated.emit(f"找到OpenCL GPU: {devices[0].name}")
self.gpu_type = "opencl"
return True
# 如果没有找到GPU,尝试使用CPU
if not intel_arc_found:
for platform in platforms:
devices = platform.get_devices(device_type=cl.device_type.CPU)
if devices:
self.gpu_context = cl.Context(devices)
self.gpu_queue = cl.CommandQueue(self.gpu_context)
self.gpu_device = devices[0]
self.status_updated.emit(f"使用OpenCL CPU: {devices[0].name}")
self.gpu_type = "opencl"
return True
self.status_updated.emit("未找到OpenCL设备,将使用CPU")
self.use_gpu = False
return False
else:
self.status_updated.emit("未安装GPU支持库,将使用CPU")
self.use_gpu = False
return False
except Exception as e:
self.status_updated.emit(f"GPU初始化失败: {str(e)},将使用CPU")
self.use_gpu = False
return False
def run(self):
try:
# 创建OK文件夹
ok_dir = os.path.join(self.output_dir, "OK")
os.makedirs(ok_dir, exist_ok=True)
total_videos = len(self.video_b_paths)
for idx, video_b_path in enumerate(self.video_b_paths):
output_filename = f"output_{os.path.basename(video_b_path).split('.')[0]}.mp4"
output_path = os.path.join(ok_dir, output_filename)
self.batch_progress.emit(idx + 1, total_videos)
self.status_updated.emit(f"处理视频 {idx + 1}/{total_videos}: {os.path.basename(video_b_path)}")
# 处理单个视频对
success, message = self.process_single_video(self.video_a_path, video_b_path, output_path)
if not success:
self.finished.emit(False, f"处理失败: {message}")
return
self.finished.emit(True, f"批量处理完成!共处理 {total_videos} 个视频,输出保存在 {ok_dir}")
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_details = traceback.format_exc()
self.finished.emit(False, f"处理过程中出现错误: {str(e)}\n详细信息:\n{error_details}")
finally:
# 清理临时文件
if os.path.exists(self.temp_dir):
try:
shutil.rmtree(self.temp_dir)
except:
pass
def process_single_video(self, video_a_path, video_b_path, output_path):
"""处理单个视频对"""
try:
self.status_updated.emit("开始处理视频...")
# 提取音频
self.status_updated.emit("提取音频...")
audio_path = self.extract_audio(video_a_path)
self.progress_updated.emit(10)
# 处理视频A
self.status_updated.emit("处理视频A...")
a_frames_dir = self.process_video_a(video_a_path)
self.progress_updated.emit(30)
# 处理视频B
self.status_updated.emit("处理视频B...")
b_frames_dir = self.process_video_b(video_b_path, len(os.listdir(a_frames_dir)))
self.progress_updated.emit(50)
# 嵌入隐写
self.status_updated.emit("嵌入隐写信息...")
stego_frames_dir = self.embed_steganography(a_frames_dir, b_frames_dir)
self.progress_updated.emit(70)
# 处理音频并合成最终视频
self.status_updated.emit("处理音频并合成最终视频...")
self.process_audio_and_assemble(stego_frames_dir, audio_path, output_path)
self.progress_updated.emit(90)
# 添加随机元数据
self.status_updated.emit("添加元数据...")
self.add_random_metadata(output_path)
self.progress_updated.emit(100)
return True, "处理完成"
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_details = traceback.format_exc()
return False, f"处理过程中出现错误: {str(e)}\n详细信息:\n{error_details}"
def extract_audio(self, video_path):
"""提取音频并转换为单声道"""
audio_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "audio.wav")
# 使用ffmpeg提取音频并转换为单声道
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-i', video_path,
'-vn', '-ac', '1', '-ar', '44100',
'-y', audio_path
]
try:
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True, capture_output=True)
return audio_path
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
# 如果提取失败,创建一个默认的音频文件
self.status_updated.emit("警告: 无法提取音频,将创建默认音频")
try:
# 创建一个1秒的静音音频
sample_rate = 44100
duration = 10 # 默认10秒
# 获取视频时长
probe_cmd = ['ffprobe', '-v', 'error', '-show_entries', 'format=duration', '-of', 'default=noprint_wrappers=1:nokey=1', video_path]
result = subprocess.run(probe_cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
if result.returncode == 0:
duration = float(result.stdout.strip())
# 生成静音
t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)
silence = np.zeros_like(t)
# 保存为WAV文件
if SCIPY_AVAILABLE:
wavfile.write(audio_path, sample_rate, silence.astype(np.float32))
else:
# 使用wave模块创建WAV文件
with wave.open(audio_path, 'wb') as wav_file:
wav_file.setnchannels(1)
wav_file.setsampwidth(2)
wav_file.setframerate(sample_rate)
# 将静音数据转换为字节
max_amplitude = 32767 # 16位有符号整数的最大值
for sample in silence:
data = struct.pack('<h', int(sample * max_amplitude))
wav_file.writeframesraw(data)
return audio_path
except Exception as e2:
self.status_updated.emit(f"创建默认音频失败: {str(e2)}")
# 最后的手段,创建一个空的音频文件
open(audio_path, 'a').close()
return audio_path
def process_video_a(self, video_path):
"""处理视频A"""
# 创建输出目录
output_dir = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "video_a_frames")
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 获取视频信息
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
total_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
width, height = 1080, 2336
# 生成不可见黑色扰动背景
for i in range(total_frames):
# 创建带有轻微扰动的黑色背景
background = np.random.randint(0, 3, (height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 读取原始帧
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 调整原始帧大小并居中放置
h, w = frame.shape[:2]
scale = min((width-10)/w, (height-10)/h)
new_w, new_h = int(w * scale), int(h * scale)
resized_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (new_w, new_h))
# 将调整后的帧放置在背景上,设置不透明度为98%
x_offset = (width - new_w) // 2
y_offset = (height - new_h) // 2
# 创建叠加层
overlay = background.copy()
roi = overlay[y_offset:y_offset+new_h, x_offset:x_offset+new_w]
# 使用加权叠加实现98%不透明度
cv2.addWeighted(resized_frame, 0.98, roi, 0.02, 0, roi)
# 保存帧
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(output_dir, f"frame_{i:06d}.png"), overlay)
# 更新进度
if i % 10 == 0:
self.status_updated.emit(f"处理视频A帧: {i}/{total_frames}")
cap.release()
return output_dir
def process_video_b(self, video_path, total_frames_needed):
"""处理视频B"""
# 创建输出目录
output_dir = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "video_b_frames")
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 获取视频B的信息
cap_b = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
total_frames_b = int(cap_b.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
fps_b = cap_b.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
width, height = 1080, 2336
# 计算需要从视频B中提取的帧
start_frame = 0
if total_frames_b > total_frames_needed:
start_frame = random.randint(0, total_frames_b - total_frames_needed)
# 生成不可见黑色扰动背景并处理视频B
for i in range(total_frames_needed):
# 创建带有轻微扰动的黑色背景
background = np.random.randint(0, 3, (height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 读取原始帧(从适当的位置)
frame_idx = min(start_frame + i, total_frames_b - 1)
cap_b.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES, frame_idx)
ret, frame = cap_b.read()
if not ret:
break
# 调整原始帧大小并居中放置
h, w = frame.shape[:2]
scale = min((width-10)/w, (height-10)/h)
new_w, new_h = int(w * scale), int(h * scale)
resized_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (new_w, new_h))
# 将调整后的帧放置在背景上
x_offset = (width - new_w) // 2
y_offset = (height - new_h) // 2
# 创建叠加层
overlay = background.copy()
roi = overlay[y_offset:y_offset+new_h, x_offset:x_offset+new_w]
# 叠加帧
cv2.addWeighted(resized_frame, 1.0, roi, 0.0, 0, roi)
# 保存帧
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(output_dir, f"frame_{i:06d}.png"), overlay)
# 更新进度
if i % 10 == 0:
self.status_updated.emit(f"处理视频B帧: {i}/{total_frames_needed}")
cap_b.release()
return output_dir
def dct_embed_gpu(self, carrier, secret):
"""使用GPU加速的DCT隐写"""
if self.gpu_type == "cuda" and CUDA_AVAILABLE and self.use_gpu:
# 使用CuPy进行GPU加速
carrier_gpu = cp.asarray(carrier)
secret_gpu = cp.asarray(secret)
# 转换为YUV颜色空间
carrier_yuv = cp.zeros_like(carrier_gpu)
secret_yuv = cp.zeros_like(secret_gpu)
# RGB到YUV转换矩阵
transform = cp.array([[0.299, 0.587, 0.114],
[-0.14713, -0.28886, 0.436],
[0.615, -0.51499, -0.10001]])
# 应用转换矩阵
for i in range(carrier_gpu.shape[0]):
for j in range(carrier_gpu.shape[1]):
carrier_yuv[i, j] = cp.dot(transform, carrier_gpu[i, j])
secret_yuv[i, j] = cp.dot(transform, secret_gpu[i, j])
# 只使用Y通道进行DCT变换
carrier_y = carrier_yuv[:,:,0].astype(cp.float32)
secret_y = secret_yuv[:,:,0].astype(cp.float32)
# 对载体和秘密图像进行DCT变换
carrier_dct = cp.fft.dct(cp.fft.dct(carrier_y, axis=0), axis=1)
secret_dct = cp.fft.dct(cp.fft.dct(secret_y, axis=0), axis=1)
# 嵌入强度因子
alpha = 0.03
# 在DCT域中嵌入秘密图像
stego_dct = carrier_dct + alpha * secret_dct
# 进行逆DCT变换
stego_y = cp.fft.idct(cp.fft.idct(stego_dct, axis=1), axis=0)
# 将结果放回YUV图像中
stego_yuv = carrier_yuv.copy()
stego_yuv[:,:,0] = stego_y
# YUV到RGB转换矩阵
inv_transform = cp.linalg.inv(transform)
# 转换回RGB颜色空间
stego_bgr = cp.zeros_like(stego_yuv)
for i in range(stego_yuv.shape[0]):
for j in range(stego_yuv.shape[1]):
stego_bgr[i, j] = cp.dot(inv_transform, stego_yuv[i, j])
return cp.clip(stego_bgr, 0, 255).astype(cp.uint8).get()
elif self.gpu_type == "opencl" and OPENCL_AVAILABLE and self.use_gpu and self.gpu_context:
# 使用OpenCL进行GPU加速,特别优化Intel Arc显卡
return self.dct_embed_opencl(carrier, secret)
else:
# 使用CPU版本
return self.dct_embed_cpu(carrier, secret)
def dct_embed_opencl(self, carrier, secret):
"""使用OpenCL进行DCT隐写,特别优化Intel Arc显卡"""
try:
# 将图像转换为YUV颜色空间
carrier_yuv = cv2.cvtColor(carrier, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV)
secret_yuv = cv2.cvtColor(secret, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV)
# 只使用Y通道进行DCT变换
carrier_y = carrier_yuv[:,:,0].astype(np.float32)
secret_y = secret_yuv[:,:,0].ast(np.float32)
# 创建OpenCL缓冲区
carrier_buffer = cl.Buffer(self.gpu_context, cl.mem_flags.READ_ONLY | cl.mem_flags.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=carrier_y)
secret_buffer = cl.Buffer(self.gpu_context, cl.mem_flags.READ_ONLY | cl.mem_flags.COPY_HOST_PTR, hostbuf=secret_y)
# 创建输出缓冲区
stego_dct_buffer = cl.Buffer(self.gpu_context, cl.mem_flags.WRITE_ONLY, carrier_y.nbytes)
stego_y_buffer = cl.Buffer(self.gpu_context, cl.mem_flags.WRITE_ONLY, carrier_y.nbytes)
# 编译OpenCL程序 - 修复了内核代码中的语法错误
dct_program = cl.Program(self.gpu_context, """
__kernel void dct_embed(__global float* carrier, __global float* secret,
__global float* stego_dct, __global float* stego_y,
float alpha, int width, int height) {
int x = get_global_id(0);
int y = get_global_id(1);
int idx = y * width + x;
// DCT变换 (简化实现)
// 在实际应用中,这里应该实现完整的2D DCT算法
// 这里使用简化的DCT近似
float dct_carrier = carrier[idx] * cos((2*x+1)*y*M_PI/(2*width));
float dct_secret = secret[idx] * cos((2*x+1)*y*M_PI/(2*width));
// 嵌入秘密图像
stego_dct[idx] = dct_carrier + alpha * dct_secret;
// 逆DCT变换
stego_y[idx] = stego_dct[idx] * cos((2*x+1)*y*M_PI/(2*width));
}
""").build()
# 设置内核参数
width, height = carrier_y.shape[1], carrier_y.shape[0]
alpha = np.float32(0.03)
# 执行内核
dct_program.dct_embed(self.gpu_queue, carrier_y.shape, None,
carrier_buffer, secret_buffer, stego_dct_buffer,
stego_y_buffer, alpha, np.int32(width), np.int32(height))
# 读取结果
stego_y = np.empty_like(carrier_y)
cl.enqueue_copy(self.gpu_queue, stego_y, stego_y_buffer)
# 将结果放回YUV图像中
stego_yuv = carrier_yuv.copy()
stego_yuv[:,:,0] = stego_y
# 转换回BGR颜色空间
stego_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(stego_yuv, cv2.COLOR_YUV2BGR)
return np.clip(stego_bgr, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
except Exception as e:
self.status_updated.emit(f"OpenCL处理失败: {str(e)},将使用CPU")
return self.dct_embed_cpu(carrier, secret)
def dct_embed_cpu(self, carrier, secret):
"""在DCT域中嵌入秘密图像(CPU版本)"""
# 将图像转换为YUV颜色空间
carrier_yuv = cv2.cvtColor(carrier, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV)
secret_yuv = cv2.cvtColor(secret, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YUV)
# 只使用Y通道进行DCT变换
carrier_y = carrier_yuv[:,:,0].astype(np.float32)
secret_y = secret_yuv[:,:,0].astype(np.float32)
# 对载体和秘密图像进行DCT变换
carrier_dct = cv2.dct(carrier_y)
secret_dct = cv2.dct(secret_y)
# 嵌入强度因子
alpha = 0.03
# 在DCT域中嵌入秘密图像
stego_dct = carrier_dct + alpha * secret_dct
# 进行逆DCT变换
stego_y = cv2.idct(stego_dct)
# 将结果放回YUV图像中
stego_yuv = carrier_yuv.copy()
stego_yuv[:,:,0] = stego_y
# 转换回BGR颜色空间
stego_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(stego_yuv, cv2.COLOR_YUV2BGR)
return np.clip(stego_bgr, 0, 255).ast(np.uint8)
def embed_steganography(self, a_frames_dir, b_frames_dir):
"""嵌入隐写信息"""
# 创建输出目录
output_dir = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "stego_frames")
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 获取帧列表
a_frames = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(a_frames_dir) if f.endswith('.png')])
total_frames = len(a_frames)
for i, frame_name in enumerate(a_frames):
# 读取A视频帧
carrier_frame = cv2.imread(os.path.join(a_frames_dir, frame_name))
# 读取B视频帧
secret_frame = cv2.imread(os.path.join(b_frames_dir, frame_name))
# 调整秘密图像大小以匹配载体图像
secret_frame = cv2.resize(secret_frame, (carrier_frame.shape[1], carrier_frame.shape[0]))
# 在DCT域中嵌入秘密图像
if self.use_gpu:
stego_frame = self.dct_embed_gpu(carrier_frame, secret_frame)
else:
stego_frame = self.dct_embed_cpu(carrier_frame, secret_frame)
# 添加数字水印(版权保护)- 透明度极低,人眼几乎不可见
stego_frame = self.add_watermark(stego_frame)
# 保存处理后的帧
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(output_dir, frame_name), stego_frame)
# 更新进度
if i % 10 == 0:
self.status_updated.emit(f"嵌入隐写帧: {i}/{total_frames}")
return output_dir
def add_watermark(self, image):
"""添加数字水印 - 透明度极低,人眼几乎不可见"""
# 将OpenCV图像转换为PIL图像
pil_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# 创建一个绘图对象
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(pil_image, 'RGBA')
# 使用默认字体
try:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
# 尝试加载系统字体
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 20)
except:
pass
except:
pass
# 添加水印文本 - 使用极低的透明度 (约0.5%)
watermark_text = "Copyright Protected"
# 获取文本尺寸
try:
# 对于较新版本的Pillow
bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), watermark_text, font=font)
text_width = bbox[2] - bbox[0]
text_height = bbox[3] - bbox[1]
except:
# 对于较旧版本的Pillow
try:
text_width, text_height = draw.textsize(watermark_text, font=font)
except:
# 如果所有方法都失败,使用估计值
text_width, text_height = 150, 20
# 在多个位置添加水印
positions = [
(10, 10), # 左上角
(image.shape[1] - text_width - 10, 10), # 右上角
(10, image.shape[0] - text_height - 10), # 左下角
(image.shape[1] - text_width - 10, image.shape[0] - text_height - 10) # 右下角
]
for position in positions:
# 添加文本 - 使用极低的透明度 (约0.5%)
draw.text(position, watermark_text, (255, 255, 255, 2), font=font) # 透明度从5降低到2
# 转换回OpenCV图像
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pil_image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def process_audio_and_assemble(self, frames_dir, audio_path, output_path):
"""处理音频并合成最终视频"""
# 生成随机噪声音频
noise_audio_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "noise_audio.wav")
# 获取音频信息
try:
cmd = ['ffprobe', '-i', audio_path, '-show_entries', 'format=duration', '-v', 'quiet', '-of', 'csv=p=0']
result = subprocess.run(cmd, capture_output=True, text=True)
duration = float(result.stdout.strip())
# 生成随机噪声(极低音量)
sample_rate = 44100
t = np.linspace(0, duration, int(sample_rate * duration), endpoint=False)
noise = 0.0005 * np.random.randn(len(t)) # 极低音量噪声
# 保存噪声音频
if SCIPY_AVAILABLE:
wavfile.write(noise_audio_path, sample_rate, noise.astype(np.float32))
else:
# 使用wave模块创建WAV文件
with wave.open(noise_audio_path, 'wb') as wav_file:
wav_file.setnchannels(1)
wav_file.setsampwidth(2)
wav_file.setframerate(sample_rate)
# 将噪声数据转换为字节
max_amplitude = 32767 # 16位有签名整数的最大值
for sample in noise:
data = struct.pack('<h', int(sample * max_amplitude))
wav_file.writeframesraw(data)
except:
# 如果生成噪声失败,创建一个空的音频文件
open(noise_audio_path, 'a').close()
# 在音频中嵌入隐写信息
stego_audio_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "stego_audio.wav")
message = "HiddenSteganoMessage2023"
success, msg = AudioSteganography.embed_message(audio_path, message, stego_audio_path)
if not success:
self.status_updated.emit(f"音频隐写警告: {msg}")
stego_audio_path = audio_path # 使用原始音频
# 合并音频(左声道为隐写音频,右声道为噪声)
mixed_audio_path = os.path.join(self.temp_dir, "mixed_audio.wav")
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-y',
'-i', stego_audio_path,
'-i', noise_audio_path,
'-filter_complex', '[0:a][1:a]amerge=inputs=2,pan=stereo|c0<c0+c1|c1<c2+c3[aout]',
'-map', '[aout]',
mixed_audio_path
]
try:
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True, capture_output=True)
except:
# 如果合并失败,使用隐写音频
mixed_audio_path = stego_audio_path
# 使用ffmpeg从帧序列创建视频
frame_pattern = os.path.join(frames_dir, "frame_%06d.png")
# 生成随机比特率 (5000-7000kbps)
bitrate = random.randint(5000, 7000)
self.status_updated.emit(f"使用比特率: {bitrate}kbps")
# 使用H.264编码和指定的参数
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-y',
'-framerate', '30',
'-i', frame_pattern,
'-i', mixed_audio_path,
'-c:v', 'libx264',
'-pix_fmt', 'yuv420p',
'-crf', '18', # 较低CRF值以获得更高质量
'-preset', 'fast' if not self.use_gpu else 'medium',
'-b:v', f'{bitrate}k',
'-maxrate', f'{bitrate + 1000}k',
'-bufsize', f'{bitrate * 2}k',
'-s', '1080x2336',
'-c:a', 'aac',
'-b:a', '128k',
'-metadata', 'title=Processed Video',
output_path
]
try:
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True, capture_output=True)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
# 如果添加音频失败,尝试创建没有音频的视频
cmd_no_audio = [
'ffmpeg', '-y',
'-framerate', '30',
'-i', frame_pattern,
'-c:v', 'libx264',
'-pix_fmt', 'yuv420p',
'-crf', '18',
'-preset', 'fast' if not self.use_gpu else 'medium',
'-b:v', f'{bitrate}k',
'-maxrate', f'{bitrate + 1000}k',
'-bufsize', f'{bitrate * 2}k',
'-s', '1080x2336',
'-metadata', 'title=Processed Video',
output_path
]
subprocess.run(cmd_no_audio, check=True, capture_output=True)
# 添加声纹去重处理(简化实现)
self.add_voiceprint_processing(output_path)
def add_voiceprint_processing(self, video_path):
"""添加声纹去重处理(简化实现)"""
# 在实际应用中,这里应该实现复杂的声纹处理算法
# 这里只是一个简单的示例,添加一些元数据标记
temp_output = video_path + ".temp.mp4"
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-i', video_path,
'-metadata', 'voiceprint_processed=true',
'-metadata', 'voiceprint_hash=' + ''.join(random.choices('0123456789abcdef', k=32)),
'-codec', 'copy',
'-y', temp_output
]
try:
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True, capture_output=True)
# 替换原文件
os.replace(temp_output, video_path)
except:
# 如果添加元数据失败,保持原文件不变
if os.path.exists(temp_output):
os.remove(temp_output)
def add_random_metadata(self, video_path):
"""添加随机元数据到视频文件"""
metadata_options = {
'creation_time': ['2023-01-15T10:30:00', '2023-02-20T14:45:30', '2023-03-10T09:15:45'],
'location': ['New York, USA', 'London, UK', 'Tokyo, Japan', 'Paris, France'],
'device': ['iPhone 14 Pro', 'Samsung Galaxy S23', 'Canon EOS R5', 'Sony A7IV'],
'description': ['Beautiful landscape', 'Urban exploration', 'Nature documentary', 'Travel vlog'],
'encoder': ['H.264', 'HEVC', 'AV1', 'VP9']
}
# 随机选择元数据
selected_metadata = {
'creation_time': random.choice(metadata_options['creation_time']),
'location': random.choice(metadata_options['location']),
'device': random.choice(metadata_options['device']),
'description': random.choice(metadata_options['description']),
'encoder': random.choice(metadata_options['encoder'])
}
# 创建临时输出文件
temp_output = video_path + ".temp.mp4"
# 使用ffmpeg添加元数据
cmd = [
'ffmpeg', '-i', video_path,
'-metadata', f'creation_time={selected_metadata["creation_time"]}',
'-metadata', f'location={selected_metadata["location"]}',
'-metadata', f'device={selected_metadata["device"]}',
'-metadata', f'description={selected_metadata["description"]}',
'-metadata', f'encoder={selected_metadata["encoder"]}',
'-codec', 'copy',
'-y', temp_output
]
try:
subprocess.run(cmd, check=True, capture_output=True)
# 替换原文件
os.replace(temp_output, video_path)
except:
# 如果添加元数据失败,保持原文件不变
if os.path.exists(temp_output):
os.remove(temp_output)
class VideoSteganographyApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.video_a_path = ""
self.video_b_paths = []
self.output_dir = ""
self.use_gpu = False
self.gpu_type = "auto"
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle('视频隐写处理工具 - 最终版')
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 900, 800)
# 设置应用程序图标
if hasattr(sys, '_MEIPASS'):
# 打包后的路径
icon_path = os.path.join(sys._MEIPASS, 'app_icon.ico')
else:
# 开发时的路径
icon_path = 'app_icon.ico'
if os.path.exists(icon_path):
self.setWindowIcon(QIcon(icon_path))
# 设置暗色主题样式
self.setStyleSheet("""
QMainWindow {
background-color: #2b2b2b;
color: #cccccc;
}
QGroupBox {
font-weight: bold;
border: 2px solid #444444;
border-radius: 5px;
margin-top: 1ex;
padding-top: 10px;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
}
QGroupBox::title {
subcontrol-origin: margin;
left: 10px;
padding: 0 5px 0 5px;
color: #ffffff;
}
QPushButton {
background-color: #4CAF50;
border: none;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 16px;
margin: 4px 2px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
QPushButton:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
QPushButton:disabled {
background-color: #555555;
}
QPushButton:checked {
background-color: #2196F3;
}
QLabel {
padding: 5px;
color: #cccccc;
}
QProgressBar {
border: 2px solid #444444;
border-radius: 5px;
text-align: center;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
}
QProgressBar::chunk {
background-color: #4CAF50;
width: 10px;
}
QCheckBox {
padding: 5px;
color: #cccccc;
}
QCheckBox::indicator {
width: 15px;
height: 15px;
}
QCheckBox::indicator:unchecked {
border: 1px solid #555555;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
}
QCheckBox::indicator:checked {
border: 1px solid #555555;
background-color: #4CAF50;
}
QListWidget {
border: 1px solid #444444;
border-radius: 3px;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
color: #cccccc;
}
QComboBox {
border: 1px solid #444444;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 5px;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
color: #cccccc;
}
QComboBox QAbstractItemView {
border: 1px solid #444444;
background-color: #3c3c3c;
color: #cccccc;
selection-background-color: #4CAF50;
}
QTextEdit {
background-color: #3c3c3c;
color: #cccccc;
border: 1px solid #444444;
border-radius: 3px;
}
""")
central_widget = QWidget()
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
layout = QVBoxLayout(central_widget)
# 标题
title_label = QLabel("视频隐写处理工具 - 最终版")
title_label.setAlignment(Qt.AlignCenter)
title_font = QFont()
title_font.setPointSize(20)
title_font.setBold(True)
title_label.setFont(title_font)
layout.addWidget(title_label)
# 加速选项
acceleration_group = QGroupBox("加速选项")
acceleration_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.gpu_checkbox = QCheckBox("使用GPU加速")
self.gpu_checkbox.setChecked(False)
self.gpu_checkbox.stateChanged.connect(self.toggle_gpu_acceleration)
acceleration_layout.addWidget(self.gpu_checkbox)
self.gpu_type_combo = QComboBox()
self.gpu_type_combo.addItems(["自动检测", "NVIDIA CUDA", "OpenCL (Intel/AMD)"])
self.gpu_type_combo.currentIndexChanged.connect(self.change_gpu_type)
acceleration_layout.addWidget(QLabel("GPU类型:"))
acceleration_layout.addWidget(self.gpu_type_combo)
acceleration_group.setLayout(acceleration_layout)
layout.addWidget(acceleration_group)
# 视频A选择区域
video_a_group = QGroupBox("视频A (主视频)")
video_a_layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.video_a_label = QLabel("未选择文件")
video_a_layout.addWidget(self.video_a_label)
video_a_btn = QPushButton("选择视频A")
video_a_btn.clicked.connect(self.select_video_a)
video_a_layout.addWidget(video_a_btn)
video_a_group.setLayout(video_a_layout)
layout.addWidget(video_a_group)
# 视频B选择区域
video_b_group = QGroupBox("视频B (隐写视频 - 可多选)")
video_b_layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.video_b_list = QListWidget()
video_b_layout.addWidget(self.video_b_list)
video_b_btn_layout = QHBoxLayout()
add_video_b_btn = QPushButton("添加视频B")
add_video_b_btn.clicked.connect(self.add_video_b)
video_b_btn_layout.addWidget(add_video_b_btn)
remove_video_b_btn = QPushButton("移除选中")
remove_video_b_btn.clicked.connect(self.remove_video_b)
video_b_btn_layout.addWidget(remove_video_b_btn)
clear_video_b_btn = QPushButton("清空列表")
clear_video_b_btn.clicked.connect(self.clear_video_b)
video_b_btn_layout.addWidget(clear_video_b_btn)
video_b_layout.addLayout(video_b_btn_layout)
video_b_group.setLayout(video_b_layout)
layout.addWidget(video_b_group)
# 输出选择区域
output_group = QGroupBox("输出设置")
output_layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.output_label = QLabel("未选择输出目录")
output_layout.addWidget(self.output_label)
output_btn = QPushButton("选择输出目录")
output_btn.clicked.connect(self.select_output)
output_layout.addWidget(output_btn)
output_group.setLayout(output_layout)
layout.addWidget(output_group)
# 进度区域
progress_group = QGroupBox("处理进度")
progress_layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.batch_label = QLabel("准备就绪")
progress_layout.addWidget(self.batch_label)
self.status_label = QLabel("等待开始...")
progress_layout.addWidget(self.status_label)
self.progress_bar = QProgressBar()
self.progress_bar.setValue(0)
progress_layout.addWidget(self.progress_bar)
progress_group.setLayout(progress_layout)
layout.addWidget(progress_group)
# 处理按钮
self.process_btn = QPushButton("开始批量处理")
self.process_btn.clicked.connect(self.process_videos)
self.process_btn.setEnabled(False)
layout.addWidget(self.process_btn)
# 日志区域
log_group = QGroupBox("处理日志")
log_layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.log_text = QTextEdit()
self.log_text.setReadOnly(True)
log_layout.addWidget(self.log_text)
log_group.setLayout(log_layout)
layout.addWidget(log_group)
# 初始化日志
self.log_text.append("应用程序已启动")
self.log_text.append(f"CUDA可用: {CUDA_AVAILABLE}")
self.log_text.append(f"OpenCL可用: {OPENCL_AVAILABLE}")
self.log_text.append(f"Scipy可用: {SCIPY_AVAILABLE}")
def toggle_gpu_acceleration(self, state):
self.use_gpu = (state == Qt.Checked)
if self.use_gpu:
self.log_text.append("已启用GPU加速")
else:
self.log_text.append("已禁用GPU加速,使用CPU处理")
def change_gpu_type(self, index):
if index == 0:
self.gpu_type = "auto"
self.log_text.append("GPU类型: 自动检测")
elif index == 1:
self.gpu_type = "cuda"
self.log_text.append("GPU类型: NVIDIA CUDA")
elif index == 2:
self.gpu_type = "opencl"
self.log_text.append("GPU类型: OpenCL (Intel/AMD)")
def select_video_a(self):
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择视频A文件", "", "视频文件 (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov *.mkv)"
)
if file_path:
self.video_a_path = file_path
self.video_a_label.setText(f"已选择: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
self.log_text.append(f"已选择视频A: {file_path}")
self.check_ready()
def add_video_b(self):
file_paths, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileNames(
self, "选择视频B文件", "", "视频文件 (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov *.mkv)"
)
if file_paths:
for file_path in file_paths:
if file_path not in self.video_b_paths:
self.video_b_paths.append(file_path)
self.video_b_list.addItem(os.path.basename(file_path))
self.log_text.append(f"已添加视频B: {file_path}")
self.check_ready()
def remove_video_b(self):
selected_items = self.video_b_list.selectedItems()
for item in selected_items:
index = self.video_b_list.row(item)
removed_path = self.video_b_paths.pop(index)
self.video_b_list.takeItem(index)
self.log_text.append(f"已移除视频B: {removed_path}")
self.check_ready()
def clear_video_b(self):
self.video_b_paths.clear()
self.video_b_list.clear()
self.log_text.append("已清空视频B列表")
self.check_ready()
def select_output(self):
dir_path = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(
self, "选择输出目录"
)
if dir_path:
self.output_dir = dir_path
self.output_label.setText(f"输出目录: {dir_path}")
self.log_text.append(f"已选择输出目录: {dir_path}")
self.check_ready()
def check_ready(self):
if self.video_a_path and self.video_b_paths and self.output_dir:
self.process_btn.setEnabled(True)
else:
self.process_btn.setEnabled(False)
def process_videos(self):
self.process_btn.setEnabled(False)
self.log_text.append("开始批量处理视频...")
self.processor = VideoProcessor(
self.video_a_path,
self.video_b_paths,
self.output_dir,
self.use_gpu,
self.gpu_type
)
self.processor.progress_updated.connect(self.update_progress)
self.processor.status_updated.connect(self.update_status)
self.processor.finished.connect(self.processing_finished)
self.processor.batch_progress.connect(self.update_batch_progress)
self.processor.start()
def update_progress(self, value):
self.progress_bar.setValue(value)
def update_status(self, message):
self.status_label.setText(message)
self.log_text.append(message)
def update_batch_progress(self, current, total):
self.batch_label.setText(f"处理进度: {current}/{total}")
self.log_text.append(f"开始处理第 {current} 个视频,共 {total} 个")
def processing_finished(self, success, message):
self.process_btn.setEnabled(True)
self.status_label.setText("处理完成" if success else "处理失败")
self.log_text.append(message)
if success:
QMessageBox.information(self, "成功", message)
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", message)
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# 设置应用程序样式为Fusion,支持暗色主题
app.setStyle('Fusion')
# 设置调色板为暗色主题
palette = QPalette()
palette.setColor(QPalette.Window, QColor(43, 43, 43))
palette.setColor(QPalette.WindowText, Qt.white)
palette.setColor(QPalette.Base, QColor(25, 25, 25))
palette.setColor(QPalette.AlternateBase, QColor(53, 53, 53))
palette.setColor(QPalette.ToolTipBase, Qt.white)
palette.setColor(QPalette.ToolTipText, Qt.white)
palette.setColor(QPalette.Text, Qt.white)
palette.setColor(QPalette.Button, QColor(53, 53, 53))
palette.setColor(QPalette.ButtonText, Qt.white)
palette.setColor(QPalette.BrightText, Qt.red)
palette.setColor(QPalette.Link, QColor(42, 130, 218))
palette.setColor(QPalette.Highlight, QColor(42, 130, 218))
palette.setColor(QPalette.HighlightedText, Qt.black)
app.setPalette(palette)
window = VideoSteganographyApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
生成的软件提示:
处理失败: 处理过程中出现错误: 'numpy.ndarray' object has no attribute 'ast'
详细信息:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 278, in process_single_video
File "main.py", line 642, in embed_steganography
File "main.py", line 616, in dct_embed_cpu
AttributeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object has no attribute 'ast'
请修正一下
最新发布
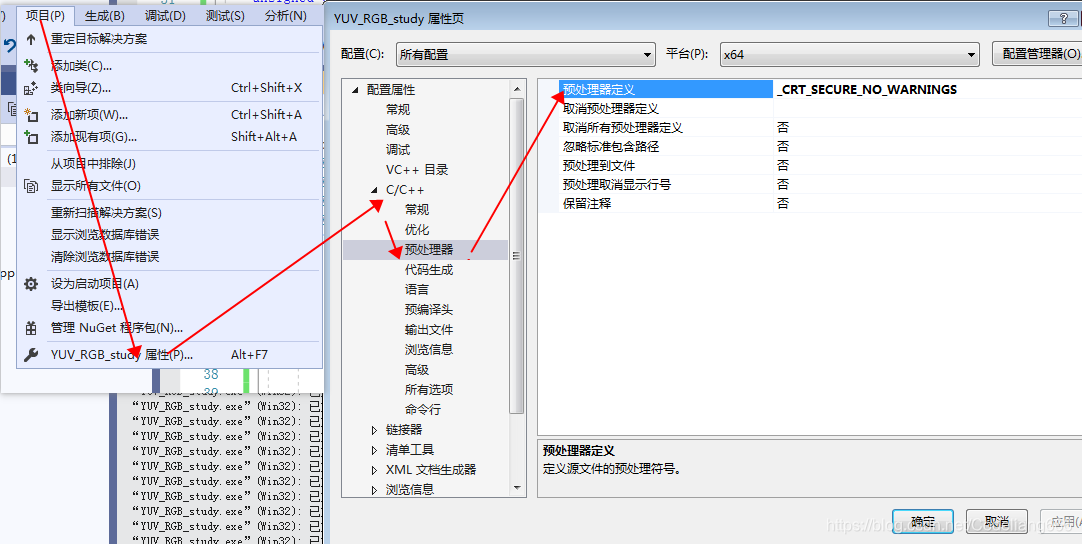
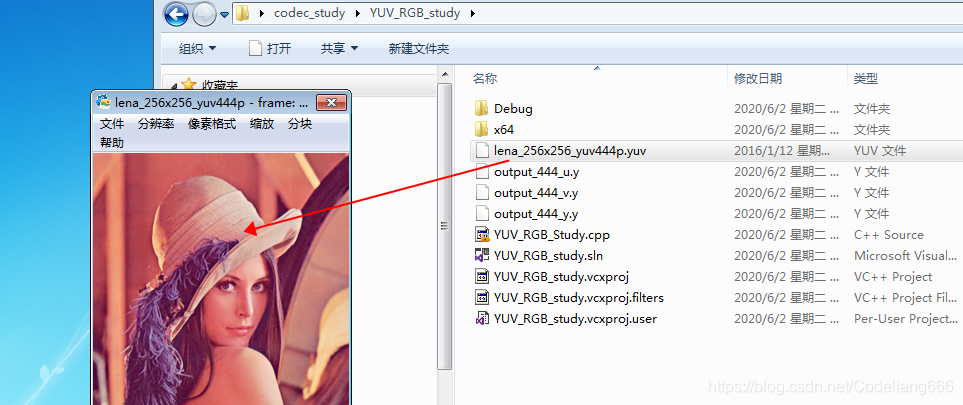





 本文详细介绍了如何使用C语言实现YUV444P格式图像的Y、U、V分量分离,提供了完整可运行的源代码,并指导解决编译问题,展示了分离后的各分量图像效果。
本文详细介绍了如何使用C语言实现YUV444P格式图像的Y、U、V分量分离,提供了完整可运行的源代码,并指导解决编译问题,展示了分离后的各分量图像效果。
















 590
590

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








