无锁并发演进背景
随着系统高并发的压力越来越大,传统同步机制在高并发场景下的性能瓶颈和缺点可能会逐渐显露:
(1)性能损耗:synchronized等锁机制会导致线程阻塞和上下文切换,在高并发场景下性能损耗显著。
(2)锁粒度粗:锁通常需要保护整个代码块或方法,而实际可能只需保护单个变量的操作。
(3)易用性差:ReentrantLock等锁,开发者需手动管理锁的获取与释放,易引发死锁或锁竞争。
现代CPU提供原子指令(如CAS),允许无锁实现线程安全操作,原子类由此诞生,原子类基于CAS实现非阻塞同步,避免线程阻塞。原子类是Java为平衡性能与线程安全在并发编程领域的重要演进,其设计初衷是提供更轻量、高效的同步方案。接下来我们就对java中的原子类进行学习。
原子类的基本概念
原子类(Atomic Classes)之所以被称为“原子类”,源于其操作具备不可分割性的原子特性。原子类的方法(如incrementAndGet()、compareAndSet())能够确保在多线程环境下,对共享变量的操作要么完全执行,要么完全不执行,调用这些方法就像调用一个加了synchronized的方法一样,不会被其他线程干扰或观察到中间状态。
jdk1.5之后引入了原子类,Java并发包(java.util.concurrent.atomic)中的原子类的类名均以Atomic前缀标识(如AtomicInteger),明确其线程安全且不可分割的操作语义,开发者一眼就可以理解其用途。
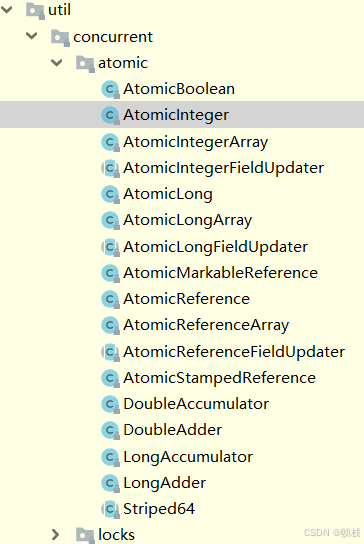
核心原子类详解
从上图可以看出,int、long、boolean这三种数据类型提供了对应的AtomicInteger、AtomicLong、AtomicBoolean原子类型,这三个是核心的原子类型。下面我们来详细学习下这三个原子类的核心api方法。
认识AtomicInteger类
/**
* An {@code int} value that may be updated atomically. See the
* {@link VarHandle} specification for descriptions of the properties
* of atomic accesses. An {@code AtomicInteger} is used in
* applications such as atomically incremented counters, and cannot be
* used as a replacement for an {@link java.lang.Integer}. However,
* this class does extend {@code Number} to allow uniform access by
* tools and utilities that deal with numerically-based classes.
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
...
}
一个可以原子更新的整数值,常用于需要原子递增的计数器等场景,但不能作为java.lang.Integer的替代品。不过,该类继承了Number,以便工具和实用程序能够以统一的方式处理基于数值的类。(Number是java.lang包中的抽象类,作为所有数值包装类的父类,提供统一的数值转换接口)。
初始化与值操作方法
(1)AtomicInteger(int initialValue)
/**
* Creates a new AtomicInteger with the given initial value.
*
* @param initialValue the initial value
*/
public AtomicInteger(int initialValue) {
value = initialValue;
}
/**
* Creates a new AtomicInteger with initial value {@code 0}.
*/
public AtomicInteger() {
}
提供了两个创建AtomicInteger对象的构造函数,可以根据给定的整型值创建AtomicInteger对象,或者创建初始值为0的AtomicInteger对象。
(2)set(int newValue)
/**
* Sets the value to {@code newValue},
* with memory effects as specified by {@link VarHandle#setVolatile}.
*
* @param newValue the new value
*/
public final void set(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
调用该方法强制更新AtomicInteger对象的值(立即可见)。
(3)lazySet(int newValue)
/**
* Sets the value to {@code newValue},
* with memory effects as specified by {@link VarHandle#setRelease}.
*
* @param newValue the new value
* @since 1.6
*/
public final void lazySet(int newValue) {
U.putIntRelease(this, VALUE, newValue);
}
调用该方法会延迟更新AtomicInteger对象的值(不保证立即可见)。
(4)int get()
/**
* Returns the current value,
* with memory effects as specified by {@link VarHandle#getVolatile}.
*
* @return the current value
*/
public final int get() {
return value




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 703
703

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










