1.Robot Error Awareness Through Human Reactions: Implementation, Evaluation, and Recommendations
Authors: Maia Stiber, Russell Taylor, Chien-Ming Huang
Affiliations: Johns Hopkins University
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.05723
论文摘要
Effective error detection is crucial to prevent task disruption and maintain user trust. Traditional methods often rely on task-specific models or user reporting, which can be inflexible or slow. Recent research suggests social signals, naturally exhibited by users in response to robot errors, can enable more flexible, timely error detection. However, most studies rely on post hoc analysis, leaving their real-time effectiveness uncertain and lacking user-centric evaluation. In this work, we developed a proactive error detection system that combines user behavioral signals (facial action units and speech), user feedback, and error context for automatic error detection. In a study (), we compared our proactive system to a status quo reactive approach. Results show our system 1) reliably and flexibly detects error, 2) detects errors faster than the reactive approach, and 3) is perceived more favorably by users than the reactive one. We discuss recommendations for enabling robot error awareness in future HRI systems.
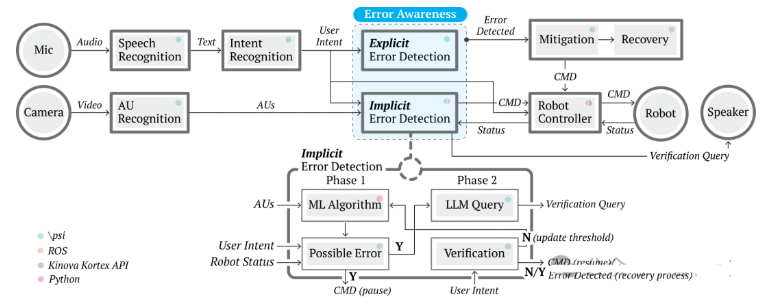
论文简评: 这篇关于人机交互中主动错误检测系统的论文,提出了通过隐式社会信号(面部动作单位和语音)来提高实时错误检测的方法。与传统的被动方法相比,该方法提高了错误检测的速度,并且用户感知到的效果也更好。作者通过一项包含28名参与者的用户研究验证了其系统的有效性,显示出该系统比传统方法更有效地提升了错误检测速度和用户体验。
这一创新性的方法不仅展示了积极的社会互动在增强人机协作中的真实误差检测的重要性,还为提升人机界面的用户体验提供了新的可能性。此外,这项研究的结果具有重要的应用价值,可以指导未来在人机协作中更好地利用社会信号以优化交互效果。
总的来说,这篇论文通过深入分析和实证研究,提出了一种基于社交信息的主动错误检测方法,这对改善人机交互的质量和效率具有重要意义。
2.Future-Conditioned Recommendations with Multi-Objective Controllable Decision Transformer
Authors: Chongming Gao, Kexin Huang, Ziang Fei, Jiaju Chen, Jiawei Chen, Jianshan Sun, Shuchang Liu, Qingpeng Cai, Peng Jiang
Affiliations: University of Science and Technology of China; Zhejiang University; Hefei University of Technology
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.07212
论文摘要
Securing long-term success is the ultimate aim of recommender systems, demanding strategies capable of foreseeing and shaping the impact of decisions on future user satisfaction. Current recommendation strategies grapple with two significant hurdles. First, the future impacts of recommendation decisions remain obscured, rendering it impractical to evaluate them through direct optimization of immediate metrics. Second, conflicts often emerge between multiple objectives, such as enhancing accuracy versus exploring diverse recommendations. Existing strategies, trapped in a “training, evaluation, and retraining” loop, grow more labor-intensive as objectives evolve.
To address these challenges, we introduce a future-conditioned strategy for multi-objective controllable recommendations, allowing for the direct specification of future objectives and empowering the model to generate item sequences that align with these goals autoregressively. We present the Multi-Objective Controllable Decision Transformer (MocDT), an offline Reinforcement Learning (RL) model capable of autonomously learning the mapping from multiple objectives to item sequences, leveraging extensive offline data. Consequently, it can produce recommendations tailored to any specified objectives during the inference stage. Our empirical findings emphasize the controllable recommendation strategy’s ability to produce item sequences according to different objectives while maintaining performance that is competitive with current recommendation strategies across various objectives.
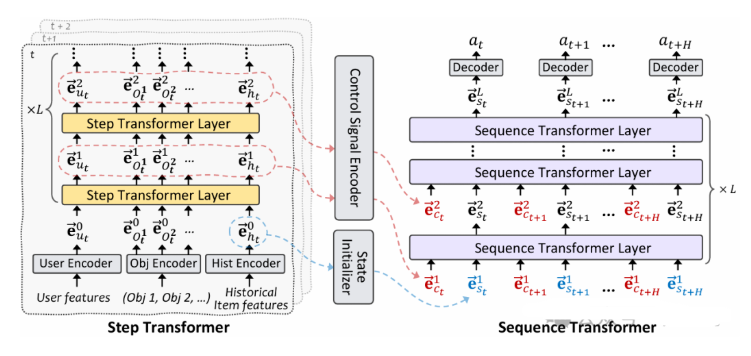
论文简评: 这篇关于Multi-Objective Controllable Decision Transformer(MocDT)的论文是一项创新性的研究成果,解决了传统推荐系统中面临的一个重要挑战——如何平衡多个目标。MocDT引入了一种控制信号以动态管理目标,从而有效应对这一问题。该框架不仅能够有效处理未来影响评估,也能解决多目标之间的冲突。此外,通过跨多个数据集的全面实验,证明了MocDT的有效性。总之,这篇文章为当前推荐系统优化方法提供了深入的思考,并提出了一个具有开创性的解决方案。
3.Natural Language-Assisted Multi-modal Medication Recommendation
Authors: Jie Tan, Yu Rong, Kangfei Zhao, Tian Bian, Tingyang Xu, Junzhou Huang, Hong Cheng, Helen Meng
Affiliations: The Chinese University of Hong Kong; DAMOAcademy, Alibaba Group; University of Texas at Arlington
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.07166
论文摘要
Combinatorial medication recommendation(CMR) is a fundamental task of healthcare, which offers opportunities for clinical physicians to provide more precise prescriptions for patients with intricate health conditions, particularly in the scenarios of long-term medical care. Previous research efforts have sought to extract meaningful information from electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitate combinatorial medication recommendations. Existing learning-based approaches further consider the chemical structures of medications, but ignore the textual medication descriptions in which the functionalities are clearly described. Furthermore, the textual knowledge derived from the EHRs of patients remains largely underutilized. To address these issues, we introduce the Natural Language-Assisted Multi-modal Medication Recommendation(NLA-MMR), a multi-modal alignment framework designed to learn knowledge from the patient view and medication view jointly. Specifically, NLA-MMR formulates CMR as an alignment problem from patient and medication modalities. In this vein, we employ pretrained language models(PLMs) to extract in-domain knowledge regarding patients and medications, serving as the foundational representation for both modalities. In the medication modality, we exploit both chemical structures and textual descriptions to create medication representations. In the patient modality, we generate the patient representations based on textual descriptions of diagnosis, procedure, and symptom. Extensive experiments conducted on three publicly accessible datasets demonstrate that NLA-MMR achieves new state-of-the-art performance, with a notable average improvement of 4.72% in Jaccard score. Our source code is publicly available on this https URL.
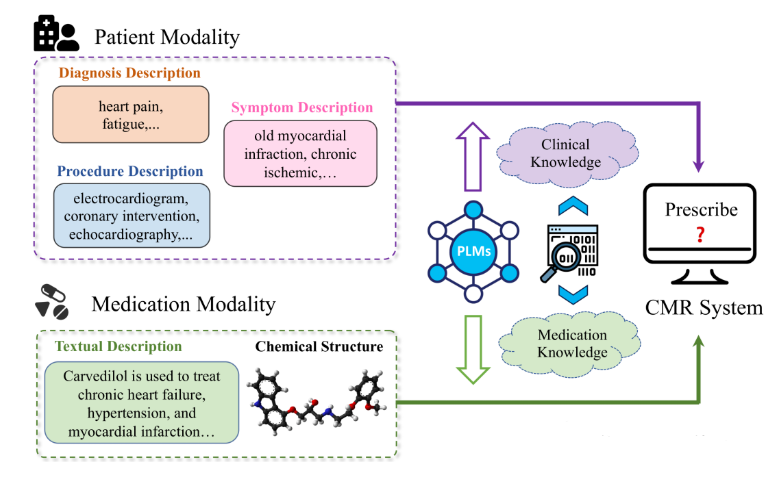
论文简评: 这篇论文介绍了一种名为Natural Language-Assisted Multi-modal Medication Recommendation(NLA-MMR)的框架,旨在通过整合文本药物描述、化学结构和电子健康记录(EHR)中的患者数据来增强复合性药物推荐。作者提出了一种多模态对齐方法,该方法通过联合学习患者的多种模态来获取知识,利用预训练的语言模型以提高表示学习的质量。
文章的关键在于引入了多个模态(文本描述和化学结构)来表示药物,并通过预先训练的语言模型提取这些模态的知识。此外,实验结果表明,此方法显著优于现有最先进的方法,尤其是在三个不同数据集上的表现。
总的来说,这篇论文提出了一种新颖的方法,有效融合了药物信息的多种模态,并充分利用预训练语言模型的优势,从而提升了复合性药物推荐的质量。
4.A Worrying Reproducibility Study of Intent-Aware Recommendation Models
Authors: Faisal Shehzad, Maurizio Ferrari Dacrema, Dietmar Jannach
Affiliations: University of Klagenfurt; Politecnico di Milano
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.10143
论文摘要
Lately, we have observed a growing interest in intent-aware recommender systems (IARS). The promise of such systems is that they are capable of generating better recommendations by predicting and considering the underlying motivations and short-term goals of consumers. From a technical perspective, various sophisticated neural models were recently proposed in this emerging and promising area. In the broader context of complex neural recommendation models, a growing number of research works unfortunately indicates that (i) reproducing such works is often difficult and (ii) that the true benefits of such models may be limited in reality, e.g., because the reported improvements were obtained through comparisons with untuned or weak baselines. In this work, we investigate if recent research in IARS is similarly affected by such problems. Specifically, we tried to reproduce five contemporary IARS models that were published in top-level outlets, and we benchmarked them against a number of traditional non-neural recommendation models. In two of the cases, running the provided code with the optimal hyperparameters reported in the paper did not yield the results reported in the paper. Worryingly, we find that all examined IARS approaches are consistently outperformed by at least one traditional model. These findings point to sustained methodological issues and to a pressing need for more rigorous scholarly practices.
论文简评: 这篇论文旨在探讨意图感知推荐系统(Intent-Aware Recommendation Systems, IARS)模型的可复现性问题,并揭示复杂模型往往无法超越传统方法的原因。研究者们对五篇发表于顶级会议的IARS模型进行了重复性检查,发现简单、传统的算法经常表现出更好的性能。这一结果对机器学习和推荐系统领域具有重要意义,因为它强调了改进现有研究方法学缺陷的重要性。通过深入分析和比较不同研究的结果,研究者们提出了许多值得讨论的问题,例如如何更好地理解和解决这些方法学问题等。总之,该文为改善当前研究环境提供了宝贵的见解和建议,积极推动了整个领域的进步。
5.Dynamic Multimodal Fusion via Meta-Learning Towards Micro-Video Recommendation
Authors: Han Liu, Yinwei Wei, Fan Liu, Wenjie Wang, Liqiang Nie, Tat-Seng Chua
Affiliations: Shandong University; NationalUniversity of Singapore; Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen)
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.07110
论文摘要
Multimodal information (e.g., visual, acoustic, and textual) has been widely used to enhance representation learning for micro-video recommendation. For integrating multimodal information into a joint representation of micro-video, multimodal fusion plays a vital role in the existing micro-video recommendation approaches. However, the static multimodal fusion used in previous studies is insufficient to model the various relationships among multimodal information of different micro-videos. In this paper, we develop a novel meta-learning-based multimodal fusion framework called Meta Multimodal Fusion (MetaMMF), which dynamically assigns parameters to the multimodal fusion function for each micro-video during its representation learning. Specifically, MetaMMF treats the multimodal fusion of each micro-video as an independent task. Based on the meta information extracted from the multimodal features of the input task, MetaMMF parameterizes a neural network as the item-specific fusion function via a meta learner. We perform extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets, demonstrating significant improvements over several state-of-the-art multimodal recommendation models, like MMGCN, LATTICE, and InvRL. Furthermore, we enhance our model by adopting canonical polyadic decomposition to improve training efficiency and validate its effectiveness through experimental results. Codes are available at https://github.com/hanliu95/MetaMMF.
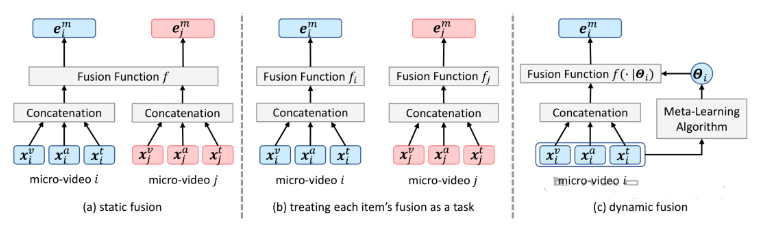
论文简评: 总的来说,本文提出了一种基于元学习的多模态融合框架(MetaMMF),该框架动态地为每个微视频分配参数到多模态融合函数中。与静态多模态融合方法相比,这种框架能够将每个微视频视为一个独立任务进行融合,从而提供更定制化的表示。通过在三个基准数据集上的实验,作者报告了对现有模型的显著改进。这些实验展示了MetaMMF的有效性,并表明它具有广泛的应用前景。总而言之,本文的研究工作具有重要的理论价值和实践意义,对解决微视频推荐问题作出了积极贡献。
6. 如何系统学习掌握AI大模型?
AI大模型作为人工智能领域的重要技术突破,正成为推动各行各业创新和转型的关键力量。抓住AI大模型的风口,掌握AI大模型的知识和技能将变得越来越重要。
学习AI大模型是一个系统的过程,需要从基础开始,逐步深入到更高级的技术。
这里给大家精心整理了一份
全面的AI大模型学习资源,包括:AI大模型全套学习路线图(从入门到实战)、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习、面试题等,资料免费分享!

1. 成长路线图&学习规划
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
这里,我们为新手和想要进一步提升的专业人士准备了一份详细的学习成长路线图和规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习成长路线。

2. 大模型经典PDF书籍
书籍和学习文档资料是学习大模型过程中必不可少的,我们精选了一系列深入探讨大模型技术的书籍和学习文档,它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。(书籍含电子版PDF)

3. 大模型视频教程
对于很多自学或者没有基础的同学来说,书籍这些纯文字类的学习教材会觉得比较晦涩难以理解,因此,我们提供了丰富的大模型视频教程,以动态、形象的方式展示技术概念,帮助你更快、更轻松地掌握核心知识。

4. 2024行业报告
行业分析主要包括对不同行业的现状、趋势、问题、机会等进行系统地调研和评估,以了解哪些行业更适合引入大模型的技术和应用,以及在哪些方面可以发挥大模型的优势。

5. 大模型项目实战
学以致用 ,当你的理论知识积累到一定程度,就需要通过项目实战,在实际操作中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作和职业发展打下坚实的基础。

6. 大模型面试题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。
在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我们将提供精心整理的大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以
微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码,免费领取【保证100%免费】





















 2915
2915

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








