前驱课程
面相对象的堆数组
1 原始堆数组的缺点:
1) 原始堆数组 其长度是固定不变的。
2) 使用指针管理元素,数据和操作散落一地。这样的数组,使用起来也很不方便。
2 如何实现一个面向对象的动态数组
下面我们要实现的类叫 Vector。这个类有下面的一些功能。
现在,我们也开始考虑如何实现下面的这些功能。
1 返回元素数量 size
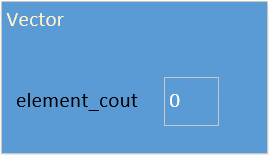
数组的元素数量,我们可以用一个成员变量 element_cout 来记录。
每当元素增加一个的时候,我们记得把这个成员变量的值加1。
class Vector
{
int size();// 返回元素数量
private:
int element_cout = 0;// 存储元素数量
};
2 添加元素 push_back()
为了盛放元素,我们需要创建一个动态数组。但是一开始这个数组多大比较好呢?
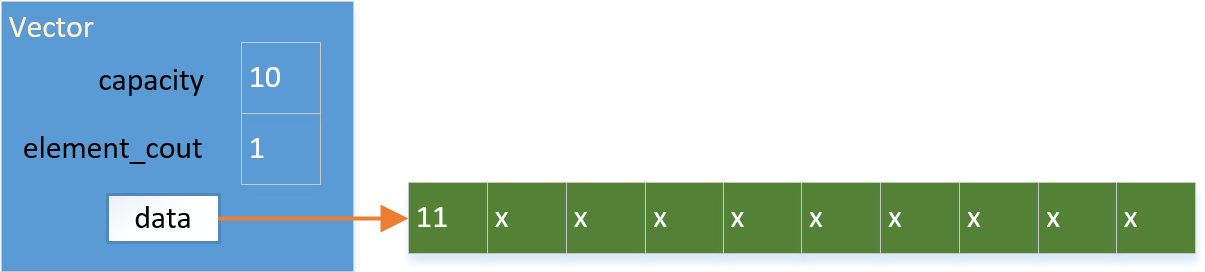
我们把数组初始容量 capacity 设为10. 当这些元素用完了(capacity == element_count)以后再扩容。
第一次push_back的时候,容器的容量是10,元素个数为0,因为还没有存任何数据;
class Vector
{
private:
int element_cout=0;
int capacity=0;
int* data=nullptr;
};

3 添加元素到容器里
使用push_back(i)来把元素放到容器里的过程如下
添加整数11到容器中:
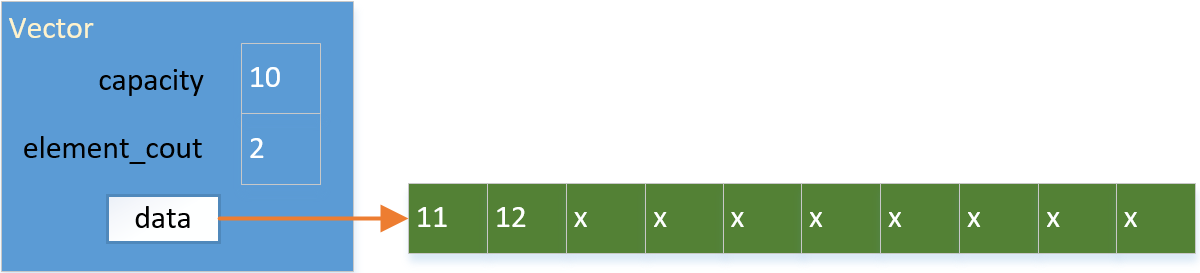
添加整数12到容器中:
一直添加,直到添加20到容器中:
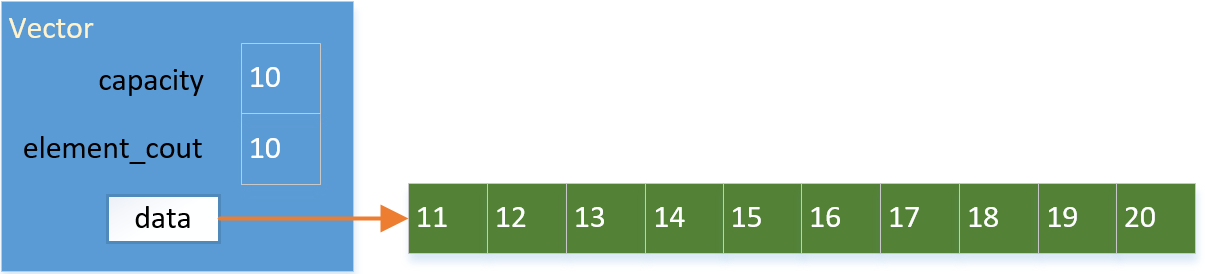
此时容器再也没有剩余的空间可以添加元素了,需要扩容。
扩容如果要保持元素挨在一起存放,只能另起一个更大的炉灶,把现在的数据拷贝过去。
(1)先开辟更大的空间
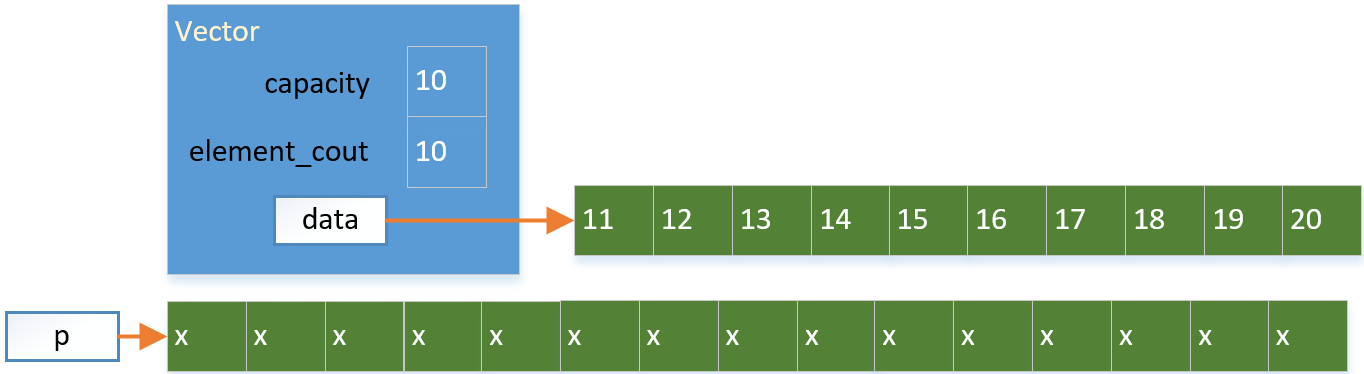
(2)拷贝原来的数据到新地方:
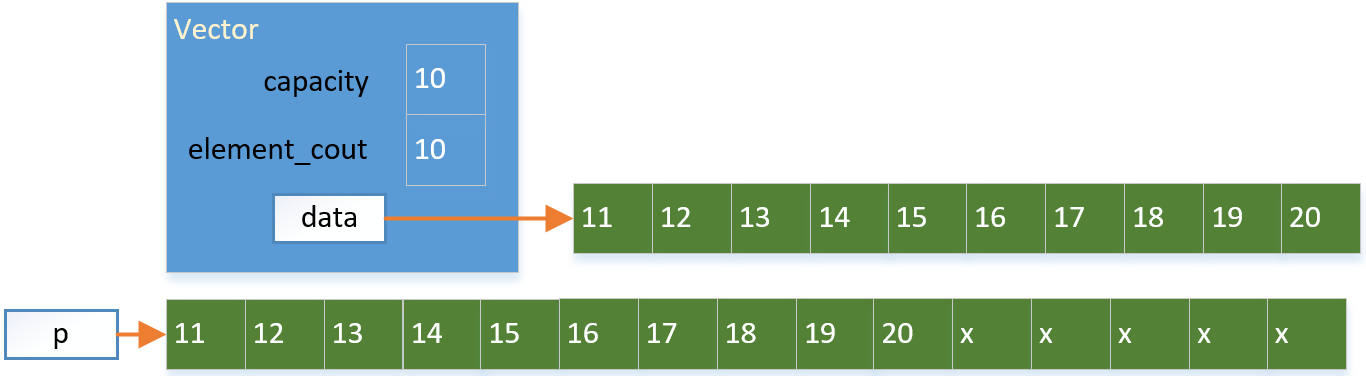
(3)添加新元素到新空间的末尾,更新元素数量
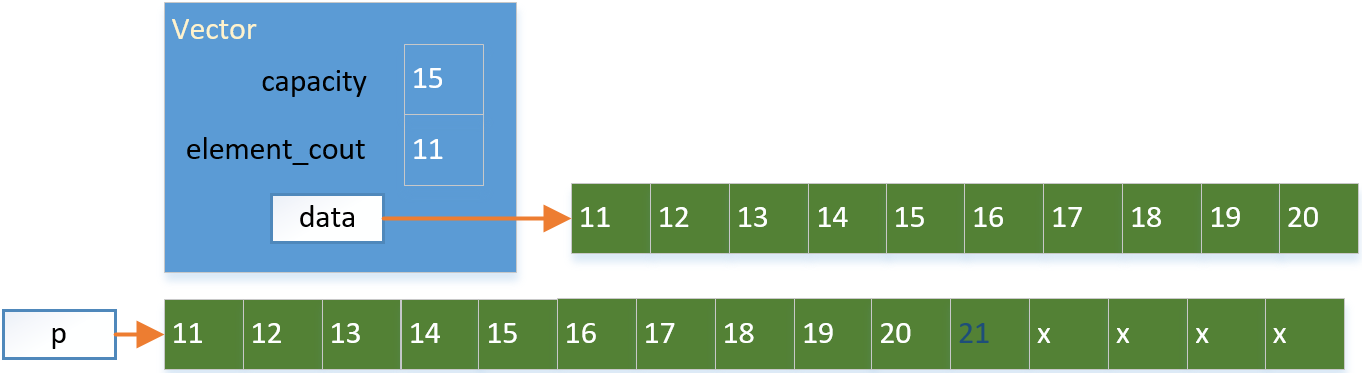
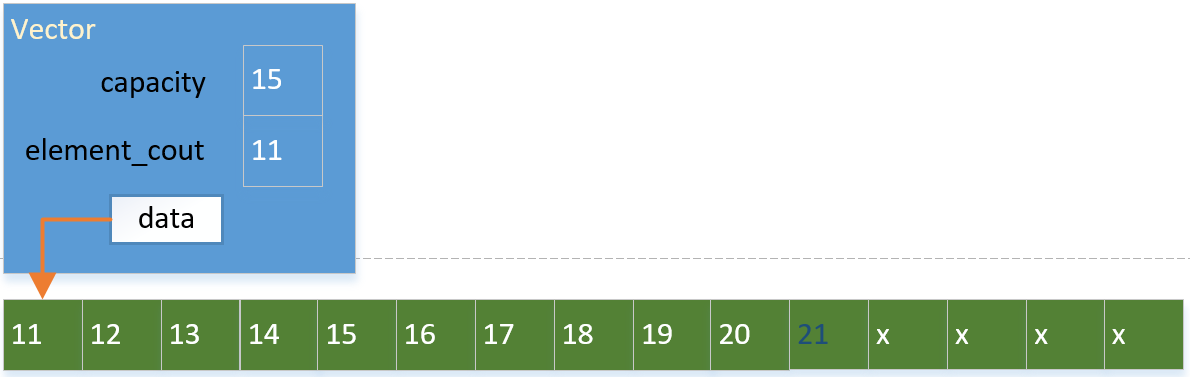
(4)释放原来的空间,接管新空间
delete[] m_data;
m_data = p;
4 访问元素
自定义的类型class/struct Vector是不可以使用下标操作符[]的。
Vector a;
a[0];// 编译报错!!!!
为此需要使用操作符重载。
对操作符[]的重载是一个特殊的成员函数,有固定的格式。
给你的类添加一个下面的成员函数,就可以使用下标操作符了:
int& operator[](int n) { return data[n]; }
有了上面的成员函数,下面的代码就可以正常工作了:
Vector a;
a[0];// OK
5 清空元素 clear
清空元素会让数组回到初始状态,也就是capacity为0,size为0;
如果原来有元素,需要释放原来的全部动态内存。
此时 容量为0,大小为0。
注意:用户可以连续两次调用clear,而不应该出现问题。
完整代码和测试用例如下
#include<iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
// >>>>>>>>>>>>> do not care the code about memory leak checking. begin <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
struct MemoryNode{
void* ptr = 0;
bool m_released = false;
size_t byte_count = 0;
char file[100] = { 0 };
int line = -1;
bool is_array = false;
MemoryNode* next = nullptr;
};
struct MemoryList{
~MemoryList(){
bool exist_leak = false;
auto temp = head.next;
while (temp){
if (temp->m_released == false){
cout << "memory leak " << temp->byte_count << " byte(s) !!!" << endl;
exist_leak = true;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
if (!exist_leak){
cout << "OK good job ! No memory leak." << endl;
}
}
static MemoryNode* C_NewNode(void* ptr, size_t size, const char* file, int line, bool is_array){
auto pnode = (MemoryNode*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryNode));
pnode->ptr = ptr;
pnode->m_released = false;
pnode->byte_count = size;
for (char* p = pnode->file; *file != '\0'; p++, file++) {*p = *file;}
pnode->line = line;
pnode->is_array = is_array;
pnode->next = nullptr;
return pnode;
}
void push_back(MemoryNode* pnode){
if (tail == nullptr){
head.next = tail = pnode;
}else{
tail->next = pnode;
tail = tail->next;
}
++m_size;
}
MemoryNode* find(void* ptr){
auto temp = head.next;
while (temp){
if (temp->ptr == ptr){
return temp;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
int m_size = 0;
MemoryNode head;
MemoryNode* tail = nullptr;
};
static MemoryList g_MemoryList;
void* operator new(size_t size, char const* file, int line){
void* ptr = malloc(size);
auto pnode = MemoryList::C_NewNode(ptr, size, file, line, false);
g_MemoryList.push_back(pnode);
return ptr;
}
void* operator new[](std::size_t size, char const* file, int line){
void* ptr = malloc(size);
auto pnode = MemoryList::C_NewNode(ptr, size, file, line, true);
g_MemoryList.push_back(pnode);
return ptr;
}
void operator delete(void* ptr) noexcept{
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
cout << "can not delete nullptr !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
auto node = g_MemoryList.find(ptr);
if (node == nullptr){
cout << "you want to free memory which is not allocated from new !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
else
{
if (node->is_array){
cout << "momory allocated at line " << node->line << ", you want to free memory by delete not delete[] which is allocatd from new[] !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
if (node->m_released){
cout << "momory allocated at line " << node->line << ", you want to free one memory twice !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
node->m_released = true;
}
}
void operator delete(void*, std::size_t)
{
assert(false);
}
void operator delete[](void*, std::size_t)
{
assert(false);
}
void operator delete[](void* ptr) noexcept{
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
cout << "can not delete nullptr !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
auto node = g_MemoryList.find(ptr);
if (node == nullptr){
cout << "you want to free memory which is not allocated from new !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
else{
if (!node->is_array){
cout << "momory allocated at line " << node->line << ", you want to free memory by delete[] not delete which is allocatd from new !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
if (node->m_released){
cout << "momory allocated at line " << node->line << ", you want to free one memory twice !!!" << endl;
assert(false);
}
node->m_released = true;
}
}
void operator delete(void* pMem, const char* pszFilename, int nLine){
cout << (int*)pMem << pszFilename << nLine << endl;
free(pMem);
assert(false);
}
void operator delete[](void* pMem, const char* pszFilename, int nLine){
cout << (int*)pMem << pszFilename << nLine << endl;
free(pMem);
assert(false);
}
#define new new(__FILE__, __LINE__)
void check_do(bool b, int line = __LINE__) { if (b) { cout << "line:" << line << " Pass" << endl; } else { cout << "line:" << line << " Ohh! not passed!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" << " " << endl; exit(0); } }
#define check(msg) check_do(msg, __LINE__);
// >>>>>>>>>>>>> do not care the code about memory leak checking. begin <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<
//注意:禁止修改Vector的定义,包括禁止给Vector添加成员变量;
//可以添加私有成员函数,如果你认为需要的话
struct Vector
{
public:
Vector();
Vector(int n, int value);
Vector(const Vector& from);//deep copy
Vector& operator=(const Vector& from);//deep copy
~Vector();
int size() const;
//只读元素
//参考 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/539451614
const int& operator[](int n)const { return m_data[n]; }
//写入元素
int& operator[](int n) { return m_data[n]; }
void push_back(int value);
bool empty() const;
void clear();
private:
void copy(const Vector& from);
private:
int m_size = 0;
int m_capacity = 0;
int* m_data = nullptr;
//请忽略下面这个成员变量,这个成员变量不影响你的实现,当它不存在即可。
};
//默认构造函数什么也不需要做,只用来保证可以创建对象的时候无需提供参数
Vector::Vector()
{
}
Vector::Vector(int n, int value)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
Vector::Vector(const Vector& from)
{
copy(from);
}
Vector::~Vector()
{
//释放动态内存,需用用 delete[]
//(4) your code
}
int Vector::size() const
{
return m_size;
}
void Vector::push_back(int value)
{
//1 如果capacity为0,则一次性开辟10个元素
//2 如果capacity容量没有用完 追加到最后
//3 如果capacity容量已经用完,开辟两倍capacity大小的容量,拷贝老数据,追加新数据
if (m_capacity == 0)
{
//(1) your code
cout << value << endl;//you must delete this line
}
else if (m_size < m_capacity)
{
//给最后一个元素的后面赋值为新元素value
//增加元素数量
//(5) your code
}
else
{
//每次内存不够用就翻倍
int* p = new int[2 * m_capacity];
//先把原来的每个元素拷贝到新地方
for (int j = 0; j < m_size; j++)
{
p[j] = m_data[j];
}
//把新添加的元素也添加到新地方
//(6) your code
//记得元素数量加1
//(7) your code
//容量翻倍
//(8) your code
//释放原来的内存
//(9) your code
//成员变量接管新开普的内存
//(10) your code
}
}
bool Vector::empty() const
{
return m_size == 0;
}
void Vector::clear()
{
//(11) your code 参考 清空元素部分的介绍;如果原来已经有容量了,需要先释放原来的空间;
}
void Vector::copy(const Vector& from)
{
//(2) your code 先调用 clear
this->m_size = from.m_size;//this line is just test code
}
Vector& Vector::operator = (const Vector& from)
{
if (&from == this)
{
return *this;
}
copy(from);
return *this;
}
void print(Vector& v, const char* msg)
{
std::cout << "The contents of " << msg << " are:";
for (int i = 0; i != v.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << ' ' << v[i];
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
void test1(void)
{
Vector v;
check(v.size() == 0);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
print(v, "v");
check(v.size() == 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
check(v[i] == i);
}
check(v.size() == 10);
}
void test2(void)
{
int n = 100000;
Vector v;
check(v.size() == 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
assert(v[i] == i);//这里必须用assert,否则会疯狂打印pass
}
check(v.size() == n);
}
void test3()
{
Vector a;
Vector first; // empty vector of ints
check(first.empty() == true && first.size() == 0);
Vector second(4, 100); // four ints with value 100
check(second.empty() == false);
check(second.size() == 4);
Vector fourth(second); // a copy of third
check(fourth.size() == second.size());
int myints[] = { 16,2,77,29 };
Vector fifth;
fifth.push_back(16);
fifth.push_back(2);
fifth.push_back(77);
fifth.push_back(29);
check(fifth.empty() == false);
check(fifth[0] == 16);
check(fifth[3] == 29);
check(fifth.size() == sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int));
print(fifth, "fifth");//The contents of fifth are:16 2 77 29
fifth.push_back(30);
check(fifth[4] == 30);
check(fifth.size() == 5);
print(fifth, "fifth");//The contents of fifth are:16 2 77 29 30
check(fifth.size() == sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int) + 1);
first = fifth = fifth;
print(first, "first");//The contents of first are:16 2 77 29 30
check(first.empty() == false && first.size() == fifth.size());
Vector a1;
a1.push_back(16);
a1.push_back(2);
a1.push_back(77);
a1.push_back(29);
{
Vector b(a1);
b.push_back(2);
check(b[4] == 2);
check(b[0] == 16);
}
{
Vector c;
c = a1;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
check(a1.size() == sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int));
{
Vector c;
c = fifth;
c[0] = 1;
check(c[0] == 1);
}
}
int main()
{
test1();
test2();
test3();
return 0;
}
正确完整输出如下
line:309 Pass
The contents of v are: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
line:315 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:318 Pass
line:320 Pass
line:326 Pass
line:335 Pass
line:343 Pass
line:345 Pass
line:346 Pass
line:348 Pass
line:357 Pass
line:358 Pass
line:359 Pass
line:360 Pass
The contents of fifth are: 16 2 77 29
line:363 Pass
line:364 Pass
The contents of fifth are: 16 2 77 29 30
line:366 Pass
The contents of first are: 16 2 77 29 30
line:369 Pass
line:379 Pass
line:380 Pass
line:387 Pass
line:392 Pass
OK good job ! No memory leak.




 本文介绍了如何在C++中实现一个面向对象的堆数组Vector,包括添加元素、获取元素数量、内存管理以及内存泄露检查。着重讲解了动态数组的扩展、内存分配和释放的过程。
本文介绍了如何在C++中实现一个面向对象的堆数组Vector,包括添加元素、获取元素数量、内存管理以及内存泄露检查。着重讲解了动态数组的扩展、内存分配和释放的过程。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?









