遗传算法是一种模拟生物进化过程的启发式搜索算法,它通过选择、交叉和变异等操作,不断优化问题的解决方案。该算法将问题的解编码为染色体,随机生成初始种群,并定义适应度函数评估个体性能。随后,根据适应度选择个体繁殖,通过交叉生成新后代,并以一定概率进行变异,增加种群多样性。迭代此过程直至满足终止条件,最终得到最优解或近似最优解。遗传算法具有全局搜索能力强、鲁棒性高和编码简单等特点,适用于解决组合优化、参数优化等多种问题。 问题描述:使用遗传算法求解f(x)=x*cos(x)+2的最大值
导入必要的库:
import random
import math
定义出我们的目标函数:
def objective_function(x):
# 目标函数:f(x)=x*cos(x)+2
return x * math.cos(x) + 2
定义交叉与变异算法:
def crossover(parent1, parent2, crossover_step):
# 交叉操作(单点交叉)
child1 = float(str(parent1)[:crossover_step] + str(parent2)[crossover_step:])
child2 = float(str(parent2)[:crossover_step] + str(parent1)[crossover_step:])
return child1, child2
def mutate(individual, mutation_rate, mutation_step):
"""
变异操作
:param individual: 种群个体
:param mutation_rate: 变异几率
:param mutation_step: 变异程度
:return: 变异后个体
"""
if random.random() < mutation_rate: # random.random()输出一个百分几率
individual = random.uniform(individual - mutation_step, individual + mutation_step) # 在一定范围内产生变异
return individual
定义遗传算法:
def genetic_algorithm(low, high, population_size, generations, mutation_rate, mutation_step, crossover_rate,
crossover_step):
"""
遗传算法
:param low: 种群最小值
:param high: 种群最大值
:param population_size: 种群大小(初始元素数量)
:param generations: 遗传代数(迭代进行次数)
:param mutation_rate: 变异几率
:param mutation_step: 变异程度(偏离原原本的程度)
:param crossover_rate: 交配几率
:param crossover_step: 交配程度(染色体交换的深度) int 表示交换的位数
:return: 符合算法的最佳值
"""
list_population = [random.uniform(low, high) for _ in range(population_size)]
list_scores = [objective_function(x) for x in list_population] # 初始化
for _ in range(generations): # 进行选择、交叉、变异
list_population_new = []
for _ in range(0, population_size, 2): # 因为是二二交配,所以步长为2
if len(list_population) > 1:
father, mother = random.sample(list_population, 2) # 在种群中任选两个个体进行交配
if random.random() < crossover_rate: # random.random()输出一个百分几率,表示是否发生交配
child1, child2 = crossover(father, mother, crossover_step) # 父母交配,孩子进行变异操作并加入新一代中
list_population_new.extend([mutate(child1, mutation_rate, mutation_step),
mutate(child2, mutation_rate, mutation_step)])
else: # 父母不交配则直接变异并作为新一代
list_population_new.extend([mutate(father, mutation_rate, mutation_step),
mutate(mother, mutation_rate, mutation_step)])
else: # 种群数量小于2时视为种群灭亡,无法繁殖
print("种群因过小而灭亡,无法迭代")
exit()
list_population += list_population_new # 将子代加入父代中
list_population_new = [] # 清空子代列表准备作其他用
list_scores = [objective_function(x) for x in list_population] # 进行压力测试(估价)
for i, v in enumerate(list_scores):
if v > sum(list_scores) / len(list_scores): # 将高于平均水平的个体保留,其他淘汰
list_population_new.append(list_population[i])
list_population = list_population_new # 被保留的个体作为新一代
answer = max(list_scores) # 最佳答案(因为是求最大值,所以使用max函数)
best_child = list_population[list_scores.index(answer)] # 最后一次迭代后的最佳子代
return best_child, answer
传入参数运行算法:
best_x, best_value = genetic_algorithm(-10, 10, 100, 100, 0.1, 1, 0.5, 6)
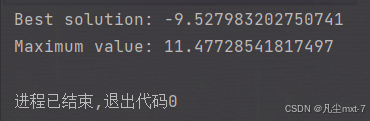
print("Best solution:", best_x)
print("Maximum value:", best_value)
PS:
1. 种群的交配方案有两种,一种是让种群中的个体两两交配产生新的个体,另一种是在种群中任取两个个体进行交配,选取次数为种群数量/2,代码中选取的是后者
2.未采用精英策略
运行结果:
有任何问题可向作者提出。






















 346
346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








