类的成员变量分为值类型和引用类型。
浅克隆
浅克隆是将原型对象的成员变量为值类型复制一份给克隆对象,而成员变量为引用对象的引用地址复制给克隆对象,说白了就是共享引用对象。
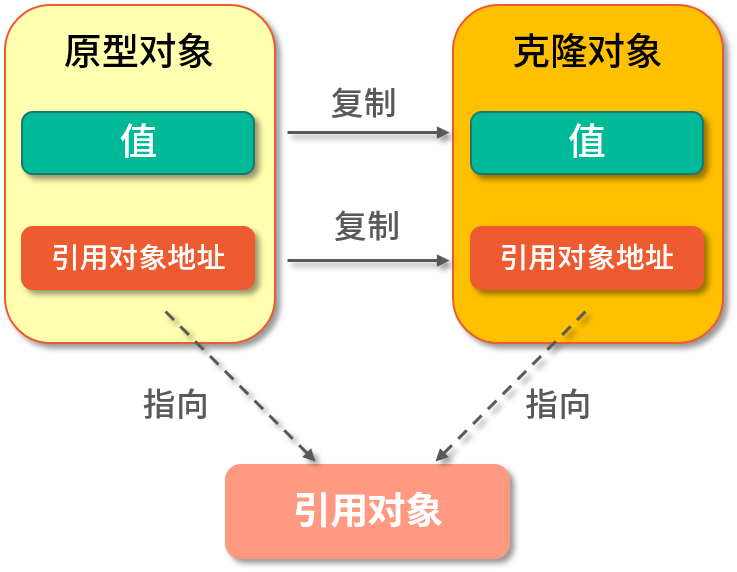
深克隆
深克隆就是原型对象不管成员变量是什么类型都要复制一份克隆对象,原型对象和克隆对象是两个完全独立的对象。

JAVA实现克隆条件
1、实现Cloneable接口。
2、重写Ojbect类中clone()方法。
Object.clone()几点特点
1、对于所有对象来说,x.clone() !=x 应当返回 true,因为克隆对象与原对象不是同一个对象;
2、对于所有对象来说,x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass() 应当返回 true,因为克隆对象与原对象的类型是一样的;
3、对于所有对象来说,x.clone().equals(x) 应当返回 true,因为使用 equals 比较时,它们的值都是相同的。
Arrays.copyOf()的克隆方式
@Data
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = {new Student(1,"哈哈哈")};
Student[] students1 = Arrays.copyOf(students,students.length);
students1[0].setId(2);
System.out.println("原型对象:" + students[0].getId());
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + students1[0].getId() );
}
}

结果显示,修改克隆对象的值,原型对象的值也随着改变。
数组属于比较特殊的引用类型, Arrays.copyOf()只是把引用地址复制了一份给克隆对象。 Arrays.copyOf()属于浅克隆。资源共享。
浅克隆的实现
Object的clone()可以直接实现浅克隆。
深克隆的实现
深克隆可以有很多种方式进行实现:
-
所有对象都实现克隆方法;
-
通过构造方法实现深克隆;
-
使用 JDK 自带的字节流实现深克隆;
-
使用第三方工具实现深克隆,比如 Apache Commons Lang;
-
使用 JSON 工具类实现深克隆,比如 Gson、FastJSON 等。
1、所有对象都实现克隆方法;
import lombok.Data;
public class CloneExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Address address = new Address(1,"广州");
People people = new People(1,"Java", address);
// 克隆
People people1 = people.clone();
// 修改原型
people1.address.setCity("深圳");
// 输出比对结果
System.out.println("原型对象:" + people.address.getCity());
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + people1.address.getCity());
}
// 用户类
@Data
static class People implements Cloneable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
@Override
protected People clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
People people = (People)super.clone();
System.out.println(this.address.clone());
people.setAddress(this.address.clone());
return people;
}
}
// 地址类
@Data
static class Address implements Cloneable{
private Integer id;
private String city;
public Address(Integer id, String city) {
this.id = id;
this.city = city;
}
@Override
protected Address clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Address)super.clone();
}
}
}

让所有引用对象都是实现克隆,从而实现克隆对象实现深克隆。
2、通过构造方法实现深克隆;
// 调用构造函数克隆对象
People p2 = new People(p1.getId(), p1.getName(),
new Address(p1.getAddress().getId(), p1.getAddress().getCity()));
创建克隆对象的时候直接赋值,是一种笨方法。
3、使用 JDK 自带的字节流实现深克隆;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.*;
public class CloneExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Address address = new Address(1,"广州");
People people1 = new People(1,"Java", address);
// 通过字节流实现克隆
People people2 = (People) StreamClone.clone(people1);
// 修改原型
people1.getAddress().setCity("深圳");
// 输出比对结果
System.out.println("原型对象:" + people1.address.getCity());
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + people2.address.getCity());
}
static class StreamClone{
/**
* 通过字节流实现克隆
*/
public static <T extends Serializable > T clone(People people) {
T cloneObj = null;
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oos.writeObject(people);
oos.close();
// 分配内存,写入原型对象,生成新对象
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bo.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
// 返回生成的新对象
cloneObj = (T) oi.readObject();
oi.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return cloneObj;
}
}
// 用户类
@Data
static class People implements Serializable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
}
// 地址类
@Data
static class Address implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String city;
public Address(Integer id, String city) {
this.id = id;
this.city = city;
}
}
}

通过字节流将原型对象的值写进内存,然后再从内存中读取数据进行克隆。因为是从内存中读取值所以不存在共享内存地址。
注意:原型对象以及引用对象都要实现Serializable 接口,标识自己可以被序列化,否则会抛出异常 (java.io.NotSerializableException)。
4、使用第三方工具实现深克隆,比如 Apache Commons Lang;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.SerializationUtils;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 深克隆实现方式四:通过 apache.commons.lang 实现
*/
public class CloneExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Address address = new Address(1,"广州");
People people1 = new People(1,"Java", address);
// 通过字节流实现克隆
People people2 = (People) SerializationUtils.clone(people1);
// 修改原型
people1.getAddress().setCity("深圳");
// 输出比对结果
System.out.println("原型对象:" + people1.address.getCity());
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + people2.address.getCity());
}
// 用户类
@Data
static class People implements Serializable{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
}
// 地址类
@Data
static class Address implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String city;
public Address(Integer id, String city) {
this.id = id;
this.city = city;
}
}
}

可以看出此方法和第三种实现方式类似,都需要实现 Serializable 接口,都是通过字节流的方式实现的,只不过这种实现方式是第三方提供了现成的方法,让我们可以直接调用。
5、使用 JSON 工具类实现深克隆,比如 Gson、FastJSON 等。
import lombok.Data;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class CloneExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Address address = new Address(1,"广州");
People people1 = new People(1,"Java", address);
// 通过字节流实现克隆
Gson gson = new Gson();
People people2 = gson.fromJson(gson.toJson(people1), People.class);
// 修改原型
people1.getAddress().setCity("深圳");
// 输出比对结果
System.out.println("原型对象:" + people1.address.getCity());
System.out.println("克隆对象:" + people2.address.getCity());
}
// 用户类
@Data
static class People implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public People(Integer id, String name, Address address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
}
// 地址类
@Data
static class Address implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String city;
public Address(Integer id, String city) {
this.id = id;
this.city = city;
}
}
}

这种方式就是将原型对象装成JSON格式数据,再有JSON格式数据生成克隆对象,借助第三方数据存储,进行克隆。
本文是根据下面链接进行学习编写:
https://kaiwu.lagou.com/course/courseInfo.htm?courseId=59#/detail/pc?id=1767







 本文深入探讨了浅克隆和深克隆的概念,详细讲解了JAVA实现克隆的条件及Object.clone()的特点,并通过多种方式展示了如何实现深克隆,包括自定义克隆方法、构造方法、字节流、第三方工具及JSON工具类。
本文深入探讨了浅克隆和深克隆的概念,详细讲解了JAVA实现克隆的条件及Object.clone()的特点,并通过多种方式展示了如何实现深克隆,包括自定义克隆方法、构造方法、字节流、第三方工具及JSON工具类。
















 203
203

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








