学习章节
https://bioconductor.github.io/BiocWorkshops/introduction-to-bioconductor-annotation-resources.html
文章目录
1. Introduction to Bioconductor annotation resources
参考资料
- The AnnotationDbi vignette
- The biomaRt vignette
- The GenomicFeatures vignette.
1.1 本次练习所使用到的R包
- AnnotationDbi
- AnnotationHub
- BSgenome
- biomaRt
- ensembldb
- org.Hs.eg.db
- TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene
- EnsDb.Hsapiens.v79
- EnsDb.Mmusculus.v79
- Homo.sapiens
- BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19
- hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db
1.2 学习目的
- Understand what sort of annotation data are available
- Understand the difference between annotation sources (NCBI and EBI/EMBL)
- Gain familiarity with the various ways to query annotation packages
- Get some practice making queries
2. Annotation WorkShop
2.1 What do we mean by annotation-常规用处
Annotation实质就是我们为自己已经获得的某些数据的ID号添加上功能或者位置信息
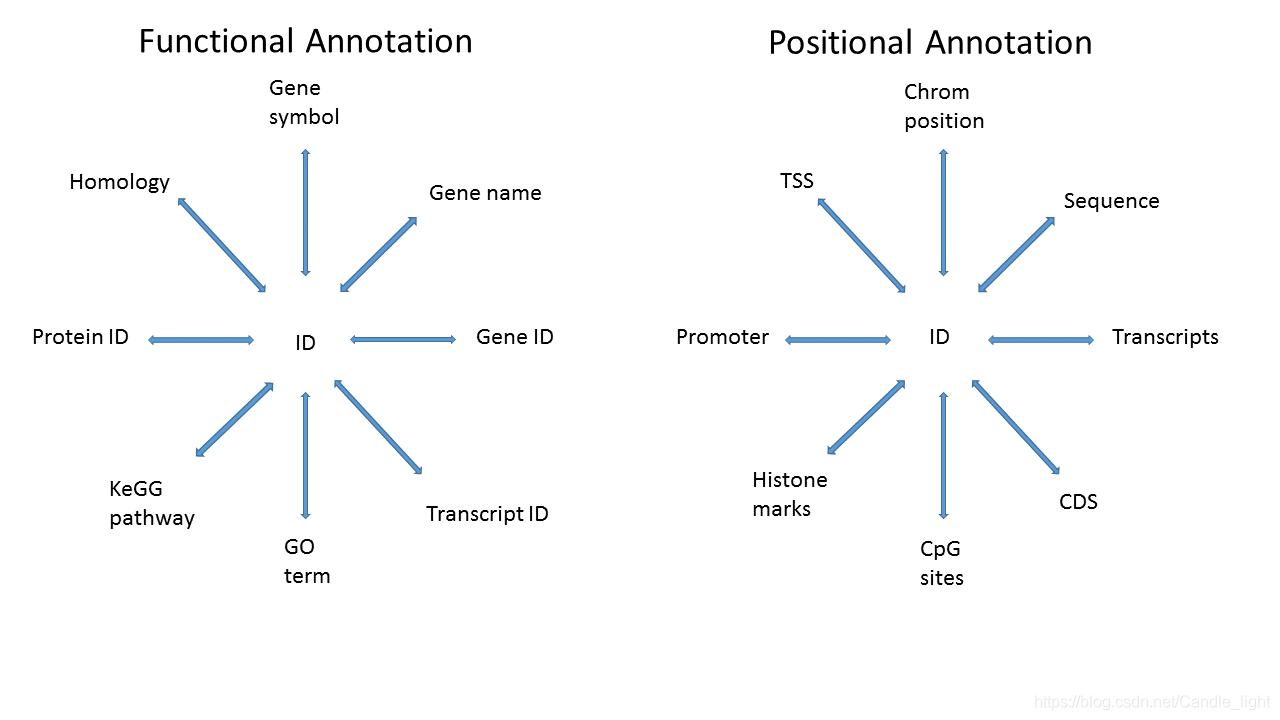
2.2 What do we mean by annotation-特殊用途
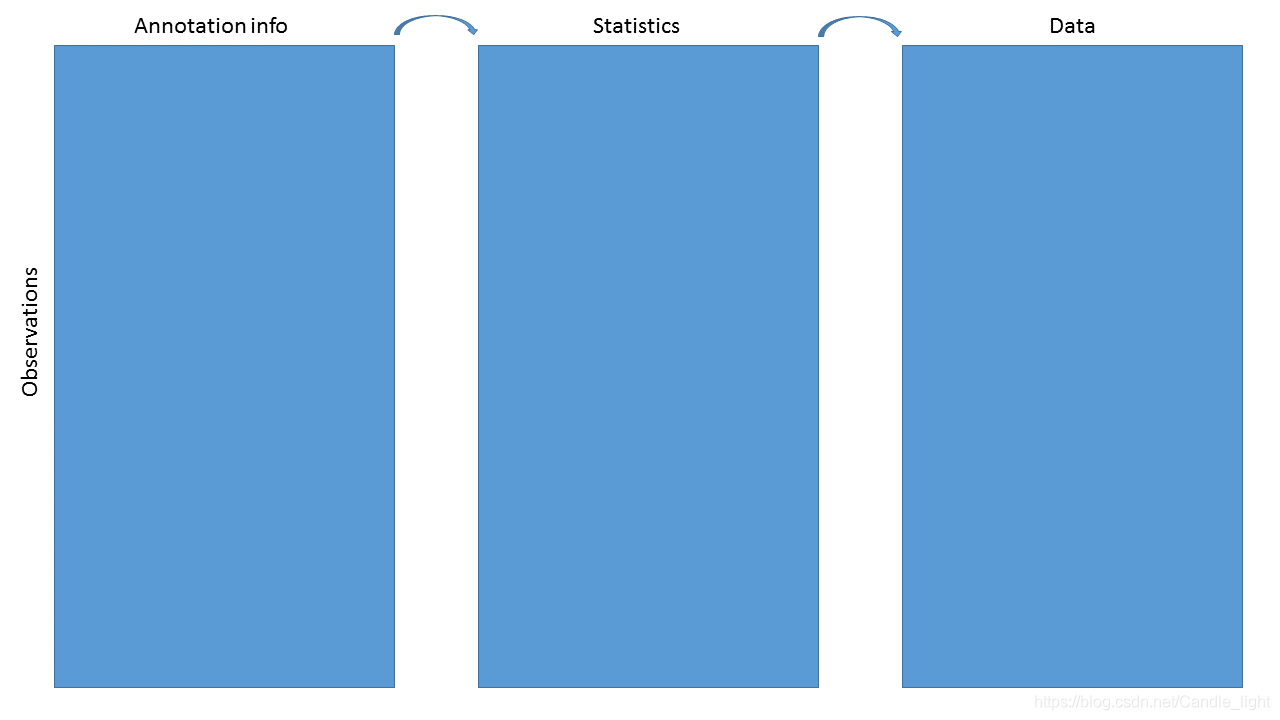
为数据和统计数据,添加其他有用的信息(不只是ID号),注释完成的结果可能是一个data.frame的数据框,一个Html的网页,或者是一个RangedSummarizedExperiment对象
2.3 Data containers
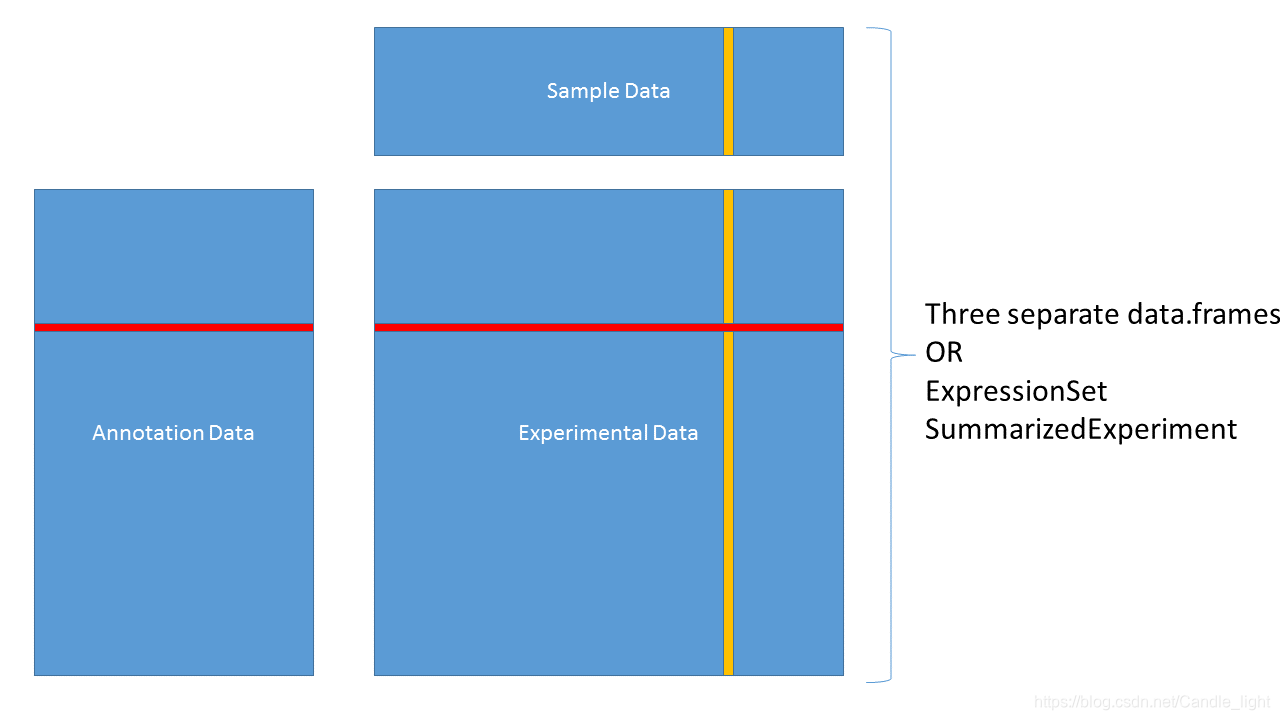
2.4 ExpressionSet
setwd("E:/GitHub/Bioinformatics-1000days/day3/")
load("eset.Rdata")
eset
## use exprs() to check the expression data
head(exprs(eset))
#> ExpressionSet (storageMode: lockedEnvironment)
#> assayData: 33552 features, 6 samples
#> element names: exprs
#> protocolData: none
#> phenoData
#> sampleNames: GSM2194079 GSM2194080 ... GSM2194084 (6 total)
#> varLabels: title characteristics_ch1.1
#> varMetadata: labelDescription
#> featureData
#> featureNames: 16657436 16657440 ... 17118478 (33552 total)
#> fvarLabels: PROBEID ENTREZID SYMBOL GENENAME
#> fvarMetadata: labelDescription
#> experimentData: use 'experimentData(object)'
#> Annotation: pd.hugene.2.0.st
## use phenoData to check the pheno data
head(pData(phenoData(eset)))
#> title characteristics_ch1.1
#> GSM2194079 SW620-miR625-rep1 shRNA: miR-625-3p
#> GSM2194080 SW620-miR625-rep2 shRNA: miR-625-3p
#> GSM2194081 SW620-miR625-rep3 shRNA: miR-625-3p
#> GSM2194082 SW620-scramble-rep1 shRNA: scramble
#> GSM2194083 SW620-scramble-rep2 shRNA: scramble
#> GSM2194084 SW620-scramble-rep3 shRNA: scramble
## use pData() and featureData to check the featureData
## 例如基因的id,symbol之类的信息
head(pData(featureData(eset)))
函数解释
- phenoData() 返回一个包含变量值和变量元数据信息的
对象(object) - pData() pData返回一个
数据框(data.frame),其中每行代表一个样本,每列代表一个变量,如下所示
title characteristics_ch1.1
GSM2194079 SW620-miR625-rep1 shRNA: miR-625-3p
GSM2194080 SW620-miR625-rep2 shRNA: miR-625-3p
GSM2194081 SW620-miR625-rep3 shRNA: miR-625-3p
所以提取表型信息和feature信息的时候,首先用phenoData()和featureData()提取出相应的变量对象,然后一定要用pData()将对象中的信息返回成数据框格式的数据!
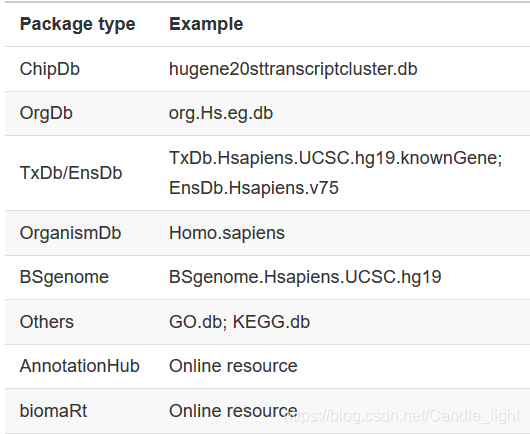
2.5 Annotation sources 注释资源
3. Interacting with AnnoDb packages
- 使用
select()函数提取数据 - 用法:
select(annopkg, keys, columns, keytype)
annopkg the annotation package(注释包)
keys keys are the IDs that we know
columns columns are the values we want
keytype is the type of key used(if the keytype is the central key, it can remain unspecified)
3.1 示例使用
假设我们现在分析了来自Affymetrix人类基因ST 2.0芯片的数据,并想知道这些芯片id所对应的基因是什么。(注:本次练习所选的probe id是随机选取的)
library(hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db)
set.seed(12345)
ids <- featureNames(eset)[sample(1:25000, 5)]
ids
select(hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db, ids, "SYMBOL")
#> 'select()' returned 1:1 mapping between keys and columns
#> PROBEID SYMBOL
#> 1 16908472 LINC01494
#> 2 16962185 ALG3
#> 3 16920686 <NA>
#> 4 16965513 <NA>
#> 5 16819952 CBFB
3.2 Questions
How do you know what the central keys are? 如何知道谁是主键?
- If it’s a ChipDb, the central key are the manufacturer’s probe IDs
- It’s sometimes in the name - org.Hs.eg.db, where ‘eg’ means Entrez Gene ID
- You can see examples using e.g., head(keys(annopkg)), and infer from that
- But note that it’s never necessary to know the central key, as long as you specify the keytype
What keytypes or columns are available for a given annotation package? 如何了解注释包里面包含了哪些可以取用的特征信息?
使用keytypes()或columns()函数即可
keytypes(hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db)
#> [1] "ACCNUM" "ALIAS" "ENSEMBL" "ENSEMBLPROT"
#> [5] "ENSEMBLTRANS" "ENTREZID" "ENZYME" "EVIDENCE"
#> [9] "EVIDENCEALL" "GENENAME" "GO" "GOALL"
#> [13] "IPI" "MAP" "OMIM" "ONTOLOGY"
#> [17] "ONTOLOGYALL" "PATH" "PFAM" "PMID"
#> [21] "PROBEID" "PROSITE" "REFSEQ" "SYMBOL"
#> [25] "UCSCKG" "UNIGENE" "UNIPROT"
columns(hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db)
#> [1] "ACCNUM" "ALIAS" "ENSEMBL" "ENSEMBLPROT"
#> [5] "ENSEMBLTRANS" "ENTREZID" "ENZYME" "EVIDENCE"
#> [9] "EVIDENCEALL" "GENENAME" "GO" "GOALL"
#> [13] "IPI" "MAP" "OMIM" "ONTOLOGY"
#> [17] "ONTOLOGYALL" "PATH" "PFAM" "PMID"
#> [21] "PROBEID" "PROSITE" "REFSEQ" "SYMBOL"
#> [25] "UCSCKG" "UNIGENE" "UNIPROT"
select() 函数,也可以一次性选多列,但是这样可能会出现数据冗余的情况
ids <- c('16737401','16657436' ,'16678303')
select(hugene20sttranscriptcluster.db, ids, c("SYMBOL","MAP"))
#> PROBEID SYMBOL MAP
#> 1 16737401 TRAF6 11p12
#> 2 16657436 DDX11L1 1p36.33
#> 3 16657436 LOC102725121 1p36.33
#> 4 16657436 DDX11L2 2q14.1
#> 5 16657436 DDX11L9 15q26.3
#> 6 16657436 DDX11L10 16p13.3
#> 7 16657436 DDX11L5 9p24.3
#> 8 16657436 DDX11L16 Xq28
#> 9 16657436 DDX11L16 Yq12
#> 10 16678303 ARF1 1q42.13





















 975
975

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








