前言 本文为原创,可能会存在一些知识点或理解上的问题,欢迎切磋和交流 ^_^
1. 为什么要用kprobe调试工具
定位和复现内核挂死问题,如果要分析内核vfs层代码,需要在函数接口中添加一些调试日志,如果只是单纯的使用printk、pr_info或dout这些打印函数来打印相关参数值,需要重编内核,从时间成本、定位根因上考虑,该方法不利于快速定位问题。
Kprobe作为一种内核热补丁调试工具,能够大大提高添加调试日志效率,加快内核问题定位。Kprobe技术提供了三种探测手段:kprobe、jprobe和kretprobe。其中,kprobe可以在函数任意的位置进行探测,jprobe探测工具只能对函数入参进行探测捕获,kretprobe针对函数返回值进行探测。
1.1 获取kprobe工程文件
Linux 4.1以后的内核源码包都已合入kprobe探测工程文件,从我们公司gerrit上下载的kernel-4.14内核项目工程也都有,具体如下图1-1所示。

图1-1 kprobe工程文件1
打开kprobe工程目录,如下图1-2所示。

图1-2 kprobe工程文件2
2. jprobe使用实例分析
下面通过一个实例,说明如何通过jprobe探测工具的使用,分析操作文件系统引用计数mnt_count的调试日志。
2.1.分析操作mnt_count引用计数的函数
通过cat /proc/kallsys命令获取当前函数是否支持kprobe工具探测
通过分析,对文件系统mnt_count引用计数操作的函数有如下函数:
static inline void mnt_add_count(struct mount *mnt, int n)
unsigned int mnt_get_count(struct mount *mnt)
void mntput(struct vfsmount *mnt)
struct vfsmount *mntget(struct vfsmount *mnt)所有对mnt_count引用计数操作最后都是通过mnt_add_count()进行加减操作,因为对该函数进行热探测捕获,需要重编内核包,故本实例只对mntput()进行热探测。
void mntput(struct vfsmount *mnt)函数如下:
void mntput(struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
if (mnt) {
struct mount *m = real_mount(mnt);
/* avoid cacheline pingpong, hope gcc doesn't get "smart" */
if (unlikely(m->mnt_expiry_mark))
m->mnt_expiry_mark = 0;
mntput_no_expire(m);
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mntput);2.2.编写探测函数
打开jprobe_example.c文件,编写mntput()的探测函数,通过入参打印出mnt_count引用计数值的变化,对探测函数编写要求如下:
修改jprobe_example.c文件内容如下:
(1)探测函数编写
要求:
函数入参和函数返回值要求与被探测函数一致
函数体最后不要忘记执行jprobe_return();
38 void j_mntput(struct vfsmount *mnt)
39 {
40
41 pr_info("__TEST_func[%s],LINE[%d].",__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);
42 jprobe_return();
43 }
(2)修改my_jprobe结构体内容
将.entry赋值内容修改为探测函数j_mntput
.symbol_name赋值内容修改为被探测函数
45 static struct jprobe my_jprobe = {
46 .entry = j_mntput,
47 .kp = {
48 .symbol_name = "mntput",
49 },
50 };
(3)添加相应头文件
16 #include <linux/module.h>
2.3.修改Makefile文件并编译调试ko
修改Makefile文件如下图所示
1 # builds the kprobes example kernel modules;
2 # then to use one (as root): insmod <module_name.ko>
3
4 #obj-$(CONFIG_SAMPLE_KPROBES) += kprobe_example.o jprobe_example.o
5 #obj-$(CONFIG_SAMPLE_KRETPROBES) += kretprobe_example.o
6 obj-m += jprobe_example.o
7 obj-m += kretprobe_down_write.o
8 #kprobe-y := probe.o
9 KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
10
11 all:
12 make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
13 clean:
14 rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o .*.cmd *.symvers modul* *.mod.c *.rc
执行make进行编译,编译通过后,会生成相应ko文件,如下图所示。
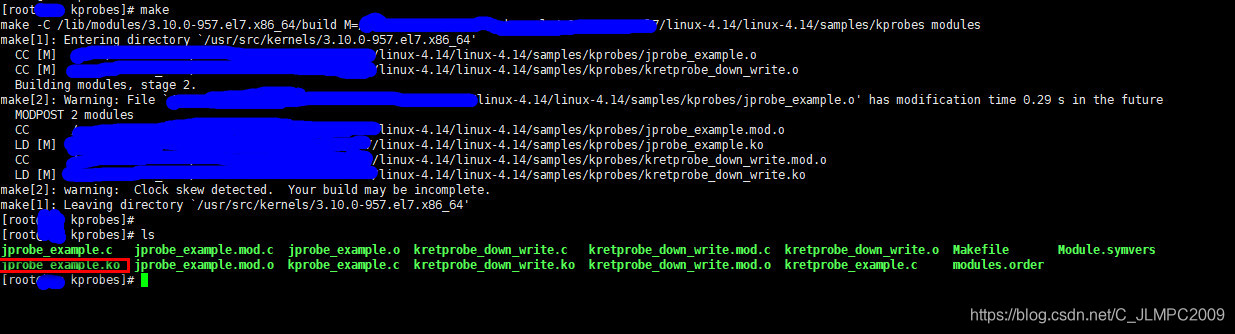
2.4.加载调试ko
执行如下命令即可进行加载,如下图所示。
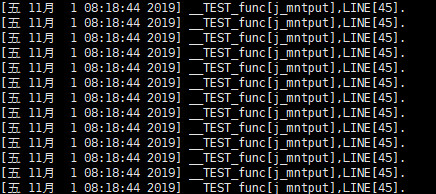
insmod jprobe_example.ko2.5通过调试信息分析操作mnt_count引用计数流程
通过dmesg命令可查看内核调试打印,如下图所示(未打出引用计数变化,只输出函数打印做演示)。
3. kretprobe使用案例分析
3.1.什么情况下使用kretprobe调试工具
死锁是内核问题中较常见的一种,我在定位一个版本在线升级问题时,就遇到过一个死锁问题,通过/proc/PID/stack文件,可以看到死锁堆栈信息。通过堆栈,发生死锁的函数如下图所示。
/**
* grab_super - acquire an active reference
* @s: reference we are trying to make active
*
* Tries to acquire an active reference. grab_super() is used when we
* had just found a superblock in super_blocks or fs_type->fs_supers
* and want to turn it into a full-blown active reference. grab_super()
* is called with sb_lock held and drops it. Returns 1 in case of
* success, 0 if we had failed (superblock contents was already dead or
* dying when grab_super() had been called). Note that this is only
* called for superblocks not in rundown mode (== ones still on ->fs_supers
* of their type), so increment of ->s_count is OK here.
*/
static int grab_super(struct super_block *s) __releases(sb_lock)
{
s->s_count++;
spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
down_write(&s->s_umount);
if ((s->s_flags & SB_BORN) && atomic_inc_not_zero(&s->s_active)) {
put_super(s);
return 1;
}
up_write(&s->s_umount);
put_super(s);
return 0;
}那么问题来了,这把锁被谁持有,是否有什么方法可以捕获出来?
通过分析代码上下文,没有太多的思路,io路径上没有任何打印,继续看down_write()函数,如下图所示。
/*
* lock for writing
*/
void __sched down_write(struct rw_semaphore *sem)
{
might_sleep();
rwsem_acquire(&sem->dep_map, 0, 0, _RET_IP_);
LOCK_CONTENDED(sem, __down_write_trylock, __down_write);
rwsem_set_owner(sem);
}
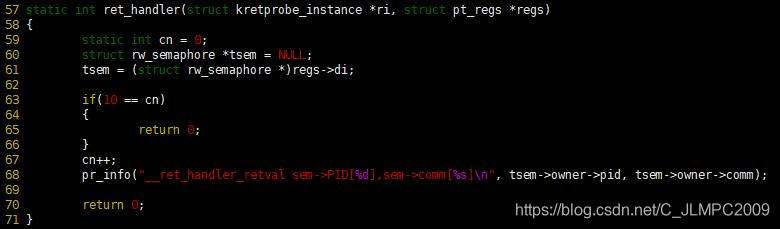
发现了红框起来的函数,通过进一步分析,如果能打印出sem结构体成员owner内容,即可知道持有该锁的进程pid和进程名。关系如下:
struct rw_semaphore *sem
|
struct task_struct *owner
|
pid_t pid
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN]故通过kretprobe调试工具即可获取。
3.2.struct pt_regs结构体
函数返回值被保存在struct pt_regs结构体的寄存器中,只要获取寄存器里的值,即可通过类型强转获取函数返回值。内核源码中,针对32位系统/64位系统分别定义了结构体,在此,只给出64位系统struct pt_regs结构体内容,如下图所示。
struct pt_regs {
/*
* C ABI says these regs are callee-preserved. They aren't saved on kernel entry
* unless syscall needs a complete, fully filled "struct pt_regs".
*/
unsigned long r15;
unsigned long r14;
unsigned long r13;
unsigned long r12;
unsigned long bp;
unsigned long bx;
/* These regs are callee-clobbered. Always saved on kernel entry. */
unsigned long r11;
unsigned long r10;
unsigned long r9; //第6个参数
unsigned long r8; //第5个参数
unsigned long ax; //返回值
unsigned long cx; //第4个参数
unsigned long dx; //第3个参数
unsigned long si; //第2个参数
unsigned long di; //第1个参数
/*
* On syscall entry, this is syscall#. On CPU exception, this is error code.
* On hw interrupt, it's IRQ number:
*/
unsigned long orig_ax;
/* Return frame for iretq */
unsigned long ip;
unsigned long cs;
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long sp;
unsigned long ss;
/* top of stack page */
};************************************************************************
注意:红框处寄存器表示函数返回值对应关系参照如下参考网址:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/already_skb/article/details/54558122
3.3.实现kretprobe调试ko
针对down_write()函数返回值进行kretprobe探测,文件所在目录如下图所示。

修改实现步骤如下:
- 修改探测函数名称
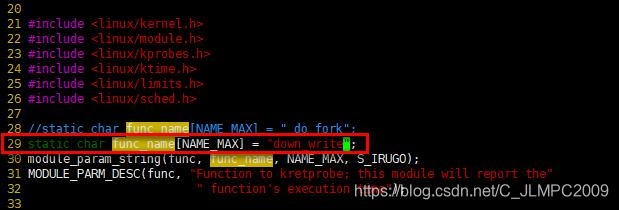
- 修改ret_handler函数
- 修改Makefile文件如下
- make编译后生成文件如下

- 加载ko
![]()
- 打印日志如下图
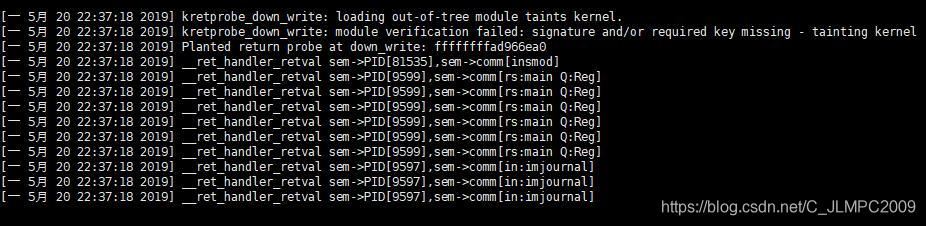
4. 参考网址
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/already_skb/article/details/54558122





 本文介绍Kprobe、jprobe和kretprobe三种内核热补丁调试工具的使用方法,通过实例展示如何分析文件系统mnt_count引用计数和解决内核死锁问题。
本文介绍Kprobe、jprobe和kretprobe三种内核热补丁调试工具的使用方法,通过实例展示如何分析文件系统mnt_count引用计数和解决内核死锁问题。
















 1130
1130

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








