spark学习笔记—核心算子(一)
HashPartitioner的决定分区的逻辑
核心方法
def getPartition(key: Any): Int = key match {
case null => 0
case _ => Utils.nonNegativeMod(key.hashCode, numPartitions)
}
/* Calculates 'x' modulo 'mod', takes to consideration sign of x,
* i.e. if 'x' is negative, than 'x' % 'mod' is negative too
* so function return (x % mod) + mod in that case.
*/
def nonNegativeMod(x: Int, mod: Int): Int = {
val rawMod = x % mod
rawMod + (if (rawMod < 0) mod else 0)
}
这里的HashPartitioner是进行groupByKey的过程中根据结果进行shuffleWrite的过程中决定写入文件的哪一个位置(文件+索引的结构)
RDD object中的隐式转换将RDD转化为PairRDDFunctions,里面包含着对于(K,V)对偶类型RDD的转换操作,比如aggregateByKey,foldByKey等
object RDD {
private[spark] val CHECKPOINT_ALL_MARKED_ANCESTORS =
"spark.checkpoint.checkpointAllMarkedAncestors"
// The following implicit functions were in SparkContext before 1.3 and users had to
// `import SparkContext._` to enable them. Now we move them here to make the compiler find
// them automatically. However, we still keep the old functions in SparkContext for backward
// compatibility and forward to the following functions directly.
implicit def rddToPairRDDFunctions[K, V](rdd: RDD[(K, V)])
(implicit kt: ClassTag[K], vt: ClassTag[V], ord: Ordering[K] = null): PairRDDFunctions[K, V] = {
new PairRDDFunctions(rdd)
}
//RDD object中的其他代码
...
}
groupByKey
/**
* Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Hash-partitions the
* resulting RDD with the existing partitioner/parallelism level. The ordering of elements
* within each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ each time the resulting RDD is
* evaluated.
*
* @note This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an
* aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using `PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey`
* or `PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey` will provide much better performance.
*/
def groupByKey(): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
groupByKey(defaultPartitioner(self))
}
/**
* Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Allows controlling the
* partitioning of the resulting key-value pair RDD by passing a Partitioner.
* The ordering of elements within each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ
* each time the resulting RDD is evaluated.
*
* @note This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an
* aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using `PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey`
* or `PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey` will provide much better performance.
*
* @note As currently implemented, groupByKey must be able to hold all the key-value pairs for any
* key in memory. If a key has too many values, it can result in an `OutOfMemoryError`.
*/
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
// 上面的注释说明了groupByKey不会进行分区内的预聚合的功能
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}
groupBy底层使用的也是groupByKey,其通过map之后安装传入的函数生成key,原来的元素作为value,然后调用了groupByKey
def groupBy[K](f: T => K, p: Partitioner)(implicit kt: ClassTag[K], ord: Ordering[K] = null)
: RDD[(K, Iterable[T])] = withScope {
val cleanF = sc.clean(f)
this.map(t => (cleanF(t), t)).groupByKey(p)
}
groupByKey按照key对RDD中的value进行分组,从而生成单一的序列。groupByKey也可以通过传递分区器的方式,对结果键-值对RDD中的分区进行控制。默认情况下使用的时HashPartitioner,但也可使用用户分区器作为给定参数。每个分组的元素顺序是不能保证的,在每次执行结果RDD计算时可能都不相同。
下面是groupByKey的示意图,针对每个分区比如一号分区中的(HuBei,1)并不会进行分区内的聚合,实际执行任务的过程中就会存在大量的shuffle操作。
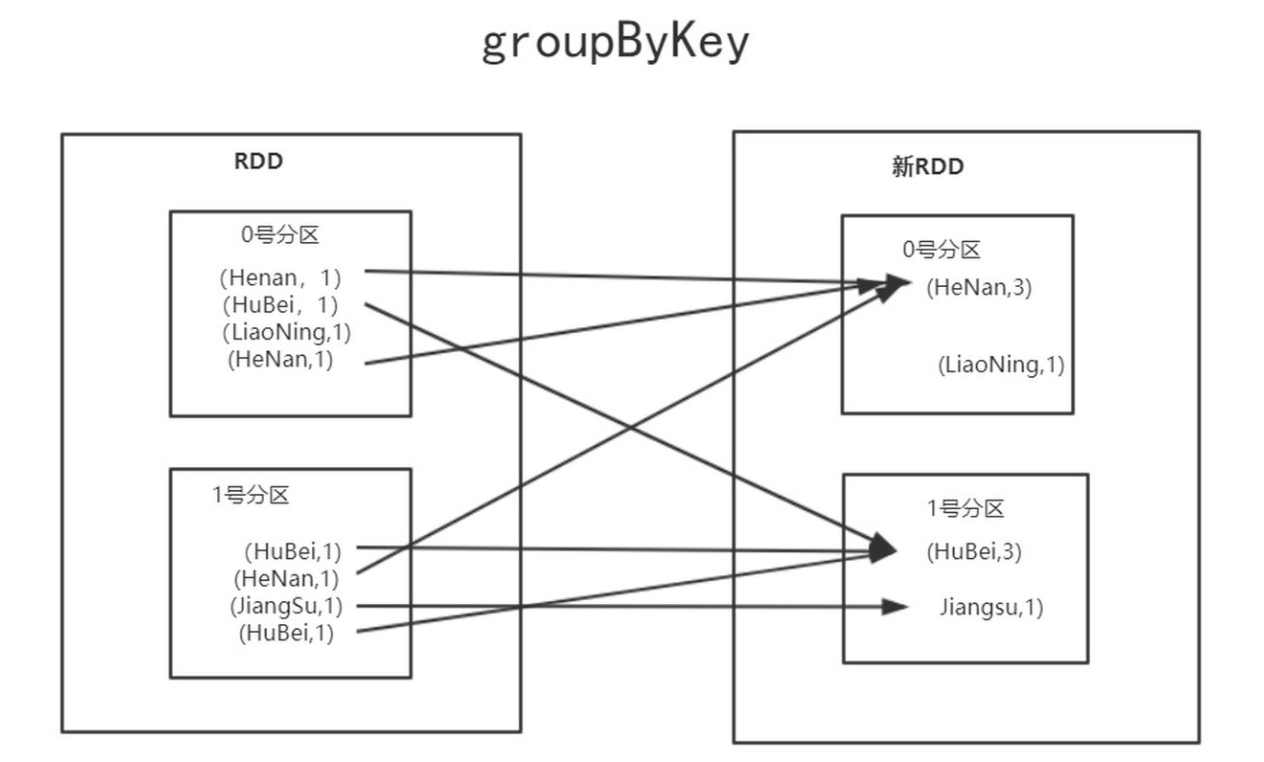
一旦使用,groupByKey需要将所有的key对应的键值对存储在内存中,如果一个key由太多value,则可能导致OOM(内存溢出错误)。
reduceByKey算子
reduceByKey底层使用的是combineByKeyWithClassTag,其中主要需要传入三个参数,分别是
// 对首个元素进行处理的逻辑
* - `createCombiner`, which turns a V into a C (e.g., creates a one-element list)
// 分区内处理逻辑
* - `mergeValue`, to merge a V into a C (e.g., adds it to the end of a list)
// 分区间处理逻辑
* - `mergeCombiners`, to combine two C's into a single one.
因为reduceByKey中分区内和分区间的处理逻辑是相同的,所以combineByKeyWithClassTag中的第二个参数和第三个参数是相同的,第一个参数就是单纯返回首个元素。
/**
* Merge the values for each key using an associative and commutative reduce function. This will
* also perform the merging locally on each mapper before sending results to a reducer, similarly
* to a "combiner" in MapReduce.
*/
def reduceByKey(partitioner: Partitioner, func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => v, func, func, partitioner)
}
下面使用shuffleRDD实现reduceByKey的功能
//wordAndOne.reduceByKey(_ + _)
//使用combineByKey实现reduceByKey的功能
val f1: Int => Int = (x: Int) => x
val f2: (Int, Int) => Int = (x: Int, y: Int) => x + y
val f3: (Int, Int) => Int = (x: Int, y: Int) => x + y
//使用shuffleRDD实现类似reduceByKey的功能
val shuffledRDD = new ShuffledRDD[String, Int, Int](
wordAndOne,
new HashPartitioner(wordAndOne.partitions.length)
)
//这里与之前的groupByKey不同,需要设置在分区内预聚合为true
shuffledRDD.setMapSideCombine(true)
shuffledRDD.setAggregator(new Aggregator[String, Int, Int](
f1, f2, f3
))
shuffledRDD.saveAsTextFile("shuffle-reduce")
reduced.saveAsTextFile("combine-out")
groupByKey中包含大量shuffle操作,而reduceByKey则更能提升性能,因为它不必发送pairRDD中的所有元素,会使用本地合并器先在本地完成基本的聚合操作,然后发送结果元素,这和groupByKey中的做法一样。可以极大降低传输的数据量,因为这样就不必发送所有数据。reducceByKey通过使用组合计算的reduce函数将每个key对应value进行合并。
reduceByKey工作时,会将分区所有的元素发送给基本分区器指定的分区,这样所有具有相同key的键值对都将被发送给同一个分区。但在shuffle之前,所有本地聚合操作也已完成,因此降低了需要执行shuffle操作的数据量。此后,最后分区中的聚合操作就很容易完成了。
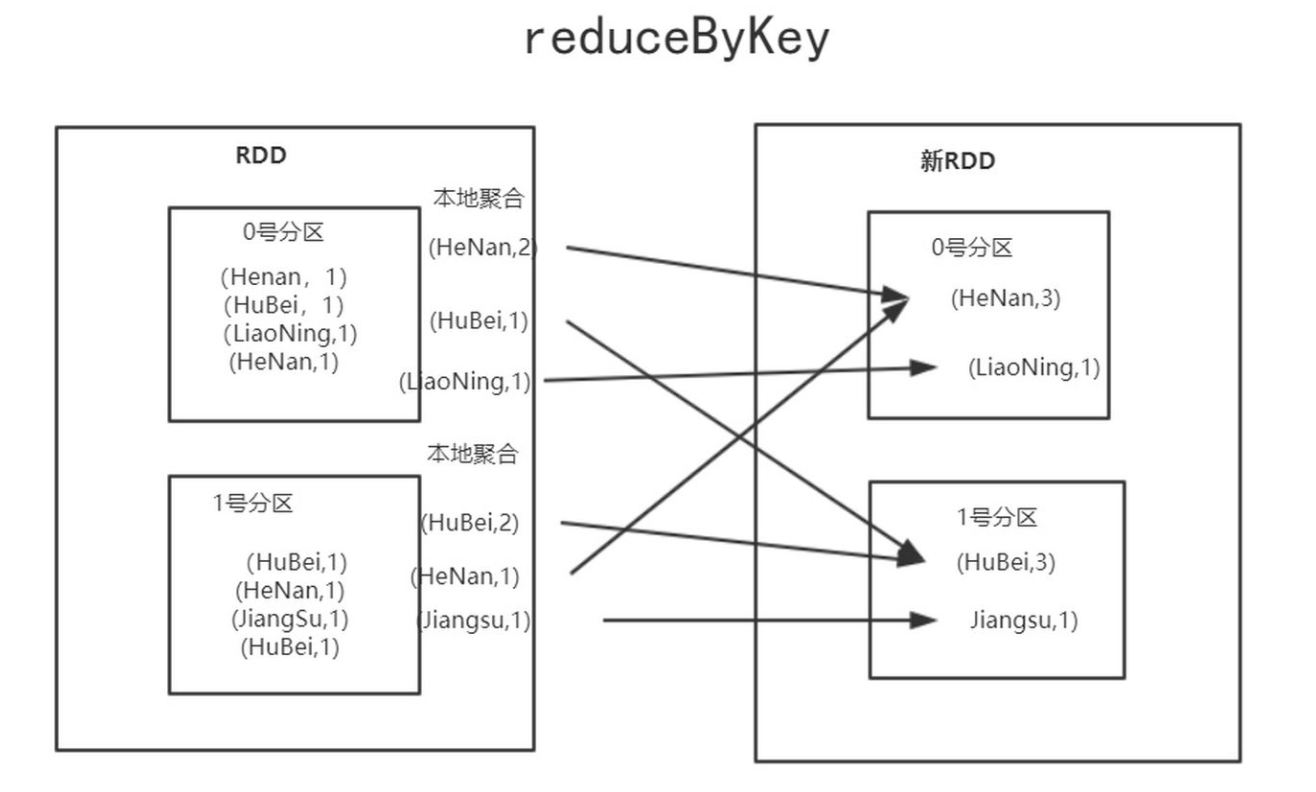
reduceByKey和groupByKey的区别
我们看一下两种计算word counts 的方法,一个使用reduceByKey,另一个使用 groupByKey:
val words = Array("one", "two", "two", "three", "three", "three")
val wordPairsRDD = sc.parallelize(words).map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCountsWithReduce = wordPairsRDD
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect()
val wordCountsWithGroup = wordPairsRDD
.groupByKey()
.map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum))
.collect()
而在groupByKey中,所有的key-value对被先shuffle到下游RDD分区中。这会导致很多不必要的网络数据传输。
在决定将一个key-value对shuffle到哪个机器上时,spark会key-value对中的key调用一个partitioning 函数,以决定分到的目标机器。在shuffle时,若是shuffle的数据(由于内存大小限制)无法全部放入到一个executor中,则Spark会将数据spill到disk。但是,在flush数据到disk时,一次只flush一个key(对应的key-value pairs 数据):所以如果单个key对应的key-value pairs 数据超出了executor可用的memory,则会抛出OOM异常。在较新版的Spark中会处理此异常并让job可以继续执行,但是仍需要尽量避免此类现象:当spark需要spill到磁盘时,spark性能会受到显著影响。
所以在非常大的数据集上计算时,对于reduceByKey与groupByKey来说,它们所需要传输的shuffle数据是有显著不同的。
而在小型数据集上进行测试时(仍使用word count的例子),从测试结果来看,groupByKey的表现要优于reduceByKey。抛开shuffle阶段来看,reduceByKey对内存率会更高于groupByKey,所以相对会报出更多内存不足的情况。若是需要使用reduceByKey,则需要给executor 更多内存在本地做计算。
相对于groupByKey,除了reduceByKey,下面的函数也会是更好的选择:
- combineByKey:可以用于combine元素,用于返回与输入类型不同类型的值
- foldByKey:初始化一个“zero value”,然后对每个Key的值做聚合操作
接下来详细介绍一下这两个函数。
combineByKey
我们先看一下combineByKey的定义:
def combineByKey[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners)(null)
}
可以看到此方法调用的是 combineByKeyWithClassTag:
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, defaultPartitioner(self))
}
继续查看下一层调用:
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true,
serializer: Serializer = null)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)]
查看reduceByKey代码,可以发现它最终调用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag 方法:
def reduceByKey(partitioner: Partitioner, func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => v, func, func, partitioner)
}
从combineByKeyWithClassTag方法定义来看,第一个参数是提供用户自定义的类型,用于将输入的<K,V> 中的 V 转化为用户指定类型,第二个参数用于merge V 的值到 C(用户定义类型),第三个参数用于将 C 的值 combine 为一个单值。这里可以看到默认是会在map端做combine,所以默认combineByKey与reduceByKey都是会在map端先做combine操作。
但是对于 groupByKey来说:
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}
可以看到,groupByKey虽然最终调用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag 方法,但是并不会在map端执行Combine操作(mapSideCombine为false)。
使用shuffleRDD实现groupByKeyRDD
从groupByKey的下面的源码中我们可以知道,其底层调用了shuffleRDD
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true,
serializer: Serializer = null)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
require(mergeCombiners != null, "mergeCombiners must be defined") // required as of Spark 0.9.0
if (keyClass.isArray) {
if (mapSideCombine) {
throw new SparkException("Cannot use map-side combining with array keys.")
}
if (partitioner.isInstanceOf[HashPartitioner]) {
throw new SparkException("HashPartitioner cannot partition array keys.")
}
}
val aggregator = new Aggregator[K, V, C](
self.context.clean(createCombiner),
self.context.clean(mergeValue),
self.context.clean(mergeCombiners))
if (self.partitioner == Some(partitioner)) {
self.mapPartitions(iter => {
val context = TaskContext.get()
new InterruptibleIterator(context, aggregator.combineValuesByKey(iter, context))
}, preservesPartitioning = true)
} else {
new ShuffledRDD[K, V, C](self, partitioner)
.setSerializer(serializer)
.setAggregator(aggregator)
.setMapSideCombine(mapSideCombine) //真正底层调用的是ShuffleRDD
}
}
object GroupByKeyDemo {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("WordCount").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val words: RDD[String] = sc.makeRDD(
List(
"spark", "hadoop", "hive", "spark",
"spark", "flink", "spark", "hbase",
"kafka", "kafka", "kafka", "kafka",
"hadoop", "flink", "hive", "flink"
), 4
)
val wordAndOne: RDD[(String, Int)] = words.map(((_: String), 1))
//使用groupByKey
//val grouped: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = wordAndOne.groupByKey()
//grouped.saveAsTextFile("group-out")
// 使用ShuffleRDD实现与groupByKey一样的功能
val shuffleRDD = new ShuffledRDD[String, Int, ArrayBuffer[Int]](
wordAndOne, new HashPartitioner(wordAndOne.partitions.length)
)
// 创建一个combiner:就是将每一个组内的第一个value方法应用到ArrayBuffer中
// 这里我们使用了可变集合ArrayBuffer,因为groupByKey源码中的CompactBuffer只用在spark包下才能使用
val createCombiner: Int => ArrayBuffer[Int] = (x: Int) => ArrayBuffer(x)
// 创建组内聚合的函数
val mergeValue = (ab: ArrayBuffer[Int], e: Int) => ab += e
// 创建分区间聚合的函数,全局合并执行
val mergeCombiners = (ab1: ArrayBuffer[Int], ab2: ArrayBuffer[Int]) => ab1 ++= ab2
shuffleRDD.setAggregator(new Aggregator[String, Int, ArrayBuffer[Int]](
createCombiner,
mergeValue,
mergeCombiners
))
// 分组不能在map side端进行预聚合
shuffleRDD.setMapSideCombine(false)
shuffleRDD.saveAsTextFile("shuffle-out")
//使用combineByKey实现reduceByKey的功能
val f1: Int => Int = (x: Int) => x
val f2: (Int, Int) => Int = (x: Int, y: Int) => x + y
val f3: (Int, Int) => Int = (x: Int, y: Int) => x + y
val reduced: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordAndOne.combineByKey(f1, f2, f3)
reduced.saveAsTextFile("combine-out")
//使用shuffleRDD实现类似reduceByKey的功能
val shuffledRDD = new ShuffledRDD[String, Int, Int](
wordAndOne,
new HashPartitioner(wordAndOne.partitions.length)
)
shuffledRDD.setAggregator(new Aggregator[String, Int, Int](
f1, f2, f3
))
shuffledRDD.saveAsTextFile("shuffle-reduce")
sc.stop()
// Thread.sleep(1000000)
}
}
foldByKey算子
/**
* Merge the values for each key using an associative function and a neutral "zero value" which
* may be added to the result an arbitrary number of times, and must not change the result
* (e.g., Nil for list concatenation, 0 for addition, or 1 for multiplication.).
*/
def foldByKey(
zeroValue: V,
partitioner: Partitioner)(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
// Serialize the zero value to a byte array so that we can get a new clone of it on each key
val zeroBuffer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance().serialize(zeroValue)
val zeroArray = new Array[Byte](zeroBuffer.limit)
zeroBuffer.get(zeroArray)
// When deserializing, use a lazy val to create just one instance of the serializer per task
lazy val cachedSerializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance()
val createZero = () => cachedSerializer.deserialize[V](ByteBuffer.wrap(zeroArray))
val cleanedFunc = self.context.clean(func)
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => cleanedFunc(createZero(), v),
cleanedFunc, cleanedFunc, partitioner)
}
foldByKey底层使用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag,其需要传递一个初始值,这个初始值会在每个分区内聚合的过程中会用到,全局聚合的时候不会用到,如果一个分区内没有对应的数据,那么这个值也不会其在相应的分区内不会起作用。
aggregateByKey算子
aggregateByKey算子与foldByKey算子类似,只不过分区内和分区间的计算逻辑可以是不同的,其底层也是使用了combineByKeyWithClassTag
/**
* Aggregate the values of each key, using given combine functions and a neutral "zero value".
* This function can return a different result type, U, than the type of the values in this RDD,
* V. Thus, we need one operation for merging a V into a U and one operation for merging two U's,
* as in scala.TraversableOnce. The former operation is used for merging values within a
* partition, and the latter is used for merging values between partitions. To avoid memory
* allocation, both of these functions are allowed to modify and return their first argument
* instead of creating a new U.
*/
def aggregateByKey[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U, partitioner: Partitioner)(seqOp: (U, V) => U,
combOp: (U, U) => U): RDD[(K, U)] = self.withScope {
// Serialize the zero value to a byte array so that we can get a new clone of it on each key
val zeroBuffer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance().serialize(zeroValue)
val zeroArray = new Array[Byte](zeroBuffer.limit)
zeroBuffer.get(zeroArray)
lazy val cachedSerializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance()
val createZero = () => cachedSerializer.deserialize[U](ByteBuffer.wrap(zeroArray))
// We will clean the combiner closure later in `combineByKey`
val cleanedSeqOp = self.context.clean(seqOp)
combineByKeyWithClassTag[U]((v: V) => cleanedSeqOp(createZero(), v),
cleanedSeqOp, combOp, partitioner)
}























 1803
1803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








