Service 简介
Kubernetes Service是为了管理具有相同功能的一组Pod而定义的一种对象,Service具体的作用和场景如下:
- 通过
Pod的Label Selector访问Pod组。 Service的IP保持不变(Headless Servcie除外),保证了访问接口的稳定性,屏蔽了Pod的IP地址变化带来的影响,进而实现解耦合。虽然这样,还是建议使用ServiceName进行访问。Service通过kube-proxy借助iptables/ipvs提供负载均衡的能力,实现反向代理,将请求转发到合适的Pod上。
Service 使用场景:
- 当客户端想要访问
K8s集群中的Pod时,需要知道Pod的Ip以及端口, 实现K8s中在不知道Pod的地址信息的情况下进行Pod服务的快速连接。 - 若某一
Node上的Pod发生故障,K8s最大的特点就是能够给感知和重启该Pod,但是Pod重启后ip会发生变化,实现客户端感知并保持对Pod的访问。 - 如果多个
Pod组合在一起形成Pod组,实现被访问时达到负载均衡的效果。
Service 工作机制
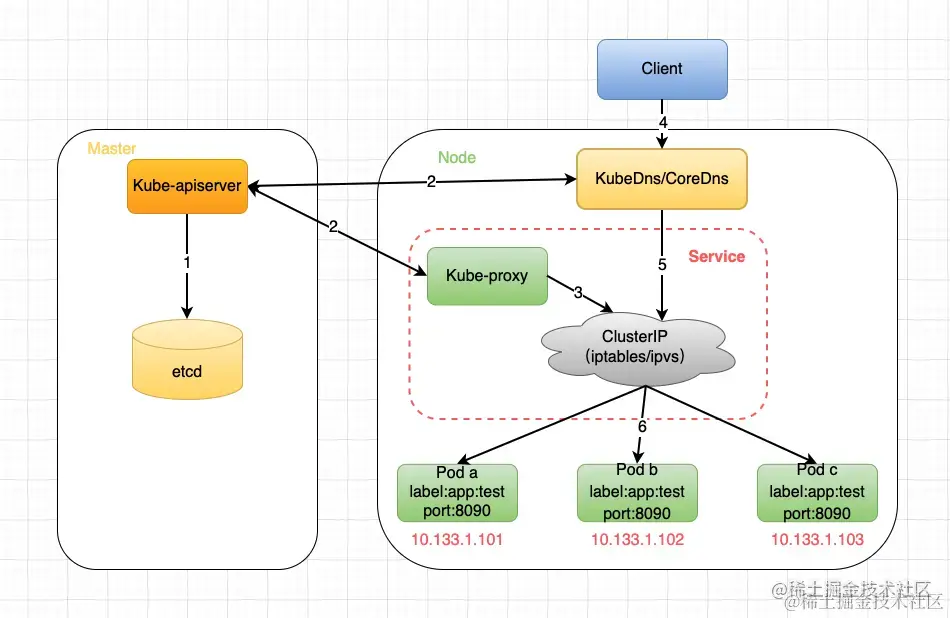
Service工作流程:
Master上的kube-apiserver会处理Service的创建,以及Service与通过label匹配与Pod绑定而产生的endpoints对象,并将这些元数据内容存储到etcd中。Node上的kube-proxy通过实时监听kube-apiserver上Service以及endpoints的变化情况来感知相关事件并更新本地的service和endpoint的映射关系;同时Node上的kubedns/coredns服务也会同时将service的域名信息与IP的对应关系存储起来供DNS解析之用。kube-proxy将从apiserver获取到的service和endpoint的映射关系保存在本地的iptables/ipvs中供后续查询使用client发起对服务的访问,首先kubedns/coredns将服务名称解析成一个虚拟IP(ClusterIP)- 然后使用这个
IP去iptables/ipvs中去找service和endpoint的映射关系。 - 找到映射关系后,通过
iptables/ipvs的负载均衡算法(典型也是最简单的就是roundrobin算法)匹配到一个合适的Pod进行访问即可。
Service 类型
K8s中Service分为四类,分别是ClusterIP,NodePort,LoadBalancer以及ExternalName。下面一张图描述了他们之间的关系以及服务类型:
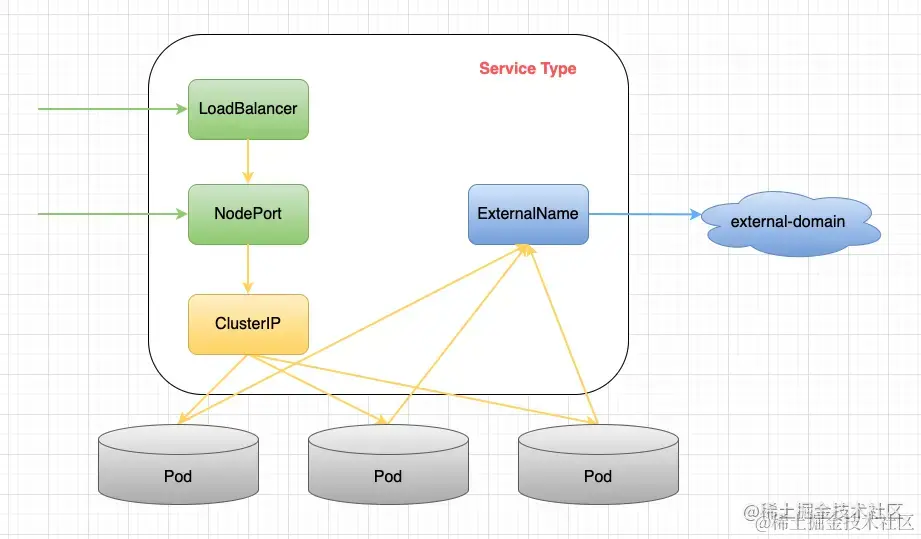
其中绿色的代表从外向内的访问模式;蓝色的代表从内向外的访问模式,黄色代表集群内部的访问模式。可以看到,除了ExternalName类型之外,其余三种类型都是逐层封装而来的。下面就分类讲一讲这四种类型:
ClusterIP(集群内部使用)
这是K8s默认的服务类型,只能在K8s中进行服务通信。在ClientIP中,K8s会在Service创建完毕后提供一个内部IP作为ClientIP属性,K8s内部服务可以通过ClientIP或者ServiceName来访问该服务。 创建该类型Service的yaml例子如下:
yaml
复制代码
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: service-clusterip spec: ports: - port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 # clusterIP: 10.233.3.127 # 可配可不配,不配的话系统会分配一个随机的IP并保持不变 selector: app: pod-clusterip type: ClusterIP # type可以不配,不配的话默认就是ClusterIP类型
NodePort(对外暴露应用)
NodePort则是Service type是Nodeport的实现,NodePort通过配置NodePort属性,外部用户可以通过NodeIP:NodePort的方式单独访问每个Node上的服务。 创建该类型Service的yaml例子如下:
yaml
复制代码
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: service-nodeport spec: ports: - port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 nodePort: 30080 #可配可不配,不配的话系统会分配一个随机的端口并保持不变 selector: app: pod-nodeport type: NodePort
LoadBalancer(对外暴露应用,适用于公有云)
LoadBalancer类型的service 是可以实现集群外部访问服务的另外一种解决方案。不过并不是所有的k8s集群都会支持,大多是在公有云托管集群中会支持该类型。负载均衡器是异步创建的,关于被提供的负载均衡器的信息将会通过Service的status.loadBalancer字段被发布出去。 创建该类型Service的yaml例子如下:
yaml
复制代码
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: service-loadbalancer spec: ports: - port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 nodePort: 30080 selector: run: pod-loadbalancer type: LoadBalancer
ExternalName
Service的ExternalName方式实现,即设置Service的type为ExternalName。这样做的好处就是内部服务访问外部服务的时候是通过别名来访问的,屏蔽了外部服务的真实信息,外部服务对内部服务透明,外部服务的修改基本上不会影响到内部服务的访问,做到了内部服务和外部服务解耦合。 创建该类型Service的yaml例子如下:
yaml
复制代码
kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: service-externalname spec: ports: - port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 type: ExternalName externalName: remote.server.url.com
K8s中的四种port
- NodePort:外部访问
K8s集群中service的端口,通过nodeIP: nodePort可以从外部访问到某个service。 - port:是
K8s集群内部访问service的端口,即通过clusterIP: port可以访问到某个service。 - targetPort:是
targetPort是Pod的端口,从Port和NodePort来的流量经过kube-proxy流入到后端Pod的targetPort上,最后进入容器。 - containerPort:
containerPort是Pod内部容器的端口,targetPort映射到containerPort。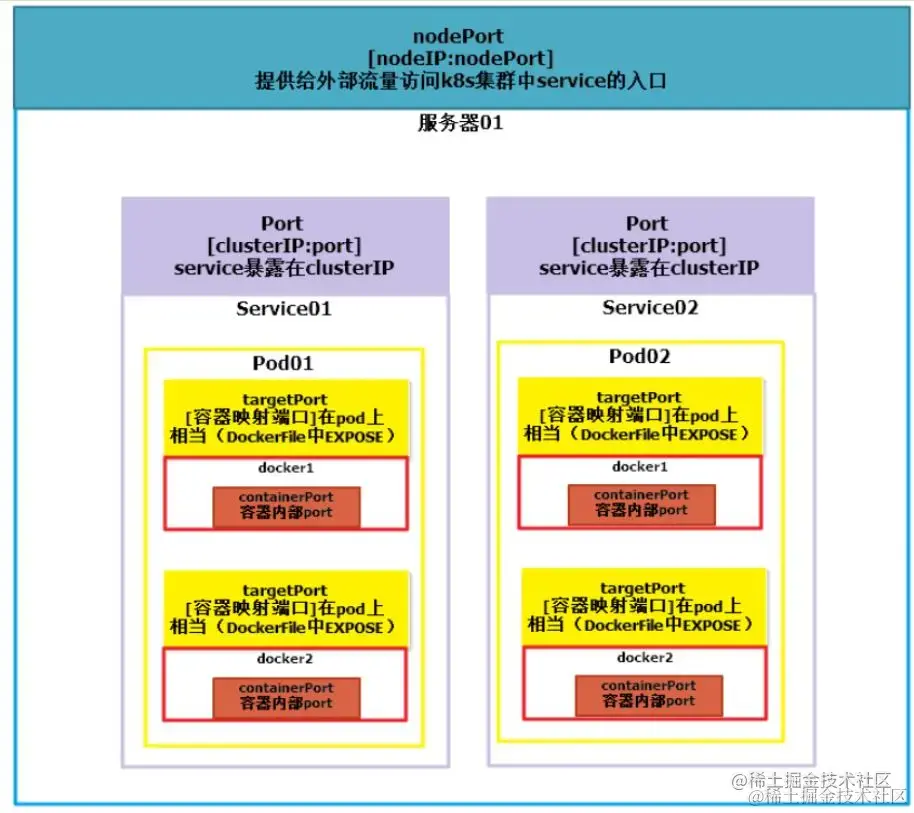
Endpoints
Endpoint是K8s集群中的一个资源对象,存储在etcd中,用来记录一个service对应的所有pod的访问地址。service配置selector endpoint controller才会自动创建对应的endpoint对象;否则,不会生成endpoint对象。
【例如】k8s集群中创建一个名为
hello的service,就会生成一个同名的Endpoint对象,Endpoint就是service关联的Pod的IP地址和端口。
工作流程
一个
Service由一组Pod组成。这些Pod通过Endpoints暴露出来。Service Selector将持续评估,结果被POST到一个名称为Service-hello的Endpoint对象上。 当Pod终止后,它会自动从Endpoint中移除,新的能够匹配上Service Selector的Pod将自动地被添加到Endpoint中。 检查该Endpoint,注意到IP地址与创建的Pod是相同的。现在,能够从集群中任意节点上使用curl命令请求hello Service。
示例
1、deployment-hello.yaml
yaml
复制代码
$ cat << EOF > deployment-hello.yaml apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: hello spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: run: hello template: metadata: labels: run: hello spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.17.1 EOF
2、service-hello.yaml
yaml
复制代码
$ cat << EOF > service-hello.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: service-hello labels: name: service-hello spec: type: NodePort # 这里代表是NodePort类型的,另外还有ingress,LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 protocol: TCP nodePort: 31111 # 所有的节点都会开放此端口30000--32767,此端口供外部调用。 selector: run: hello EOF
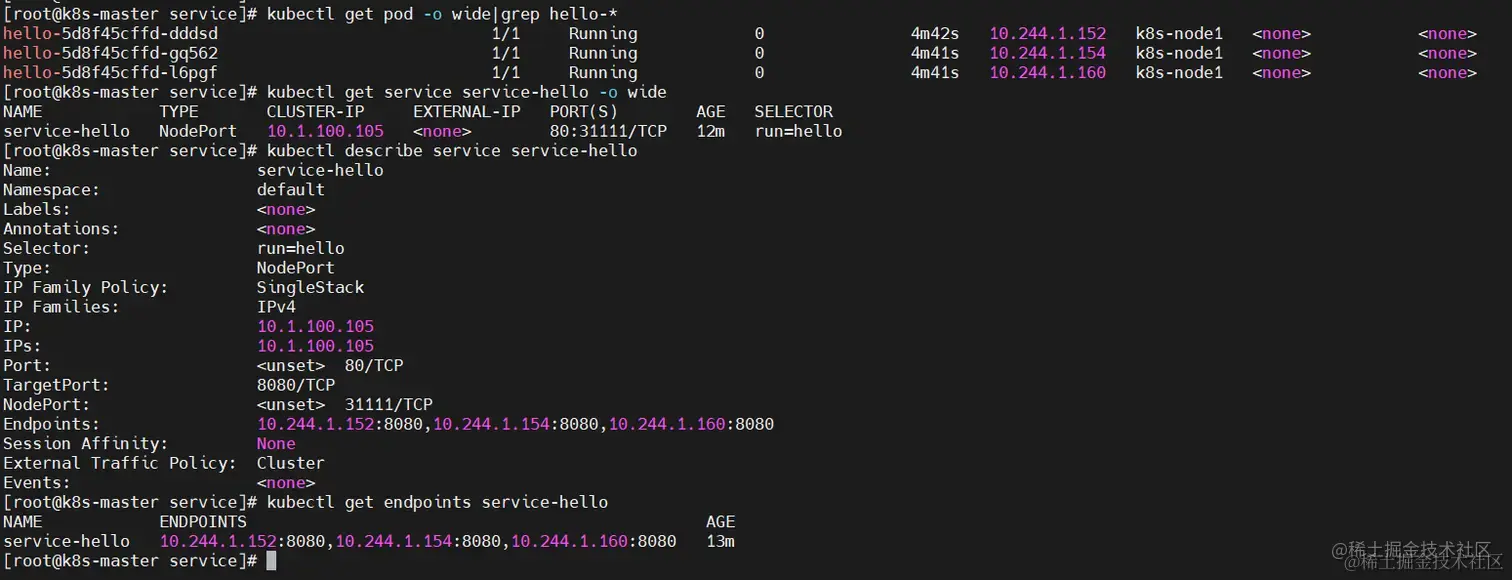
3、查看验证
yaml
复制代码
$ kubectl apply -f deployment-hello.yaml $ kubectl apply -f service-hello.yaml # 查看pod,如果本地没有镜像,可能等待的时候比较长,一定要等到所有pod都在运行中才行。 $ kubectl get pod -o wide|grep hello-* # 查看service $ kubectl get service service-hello -o wide # 查看service详情 $ kubectl describe service service-hello # 查看pointer $ kubectl get endpoints service-hello
Headless Service
Service的使用方法和实现逻辑,主要就是代理一组pod容器提供负载均衡以及反向代理服务。但是有时候我们不需要这种负载均衡,比如下面的两个场景:
K8s部署某个kafka集群,此时就不需要service来负载均衡,客户端需要的是一组Pod所有IP的列表。- 客户端自己处理负载均衡的逻辑,比如
K8s部署两个mysql,客户端自己处理负载请求,或者根本不处理这种负载,就要两套mysql然后手动控制读写请求。
基于上面的两个场景,K8s提供了Headless Serivce功能,字面意思是无头service,其实就是该service不显式的对外提供IP。 创建该类型Service的yaml例子如下:
yaml
复制代码
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: service-headless spec: ports: - port: 3000 protocol: TCP targetPort: 443 nodePort: 30080 clusterIP: None # 如此配置即开启了headless serivce selector: app: pod-headless type: NodePort
Headless Service一般结合StatefulSet来部署有状态的应用,比如大数据组件或者Nosql数据库等,这种分布式的系统需要Headless Service来获取所有节点IP的列表供业务场景使用。




















 6706
6706

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








