insert
如果我们需要一次性往数据库表中插入多条记录,可以从以下三个方面进行优化。
insertinto tb_test values(1,'tom');
insertinto tb_test values(2,'cat');
insertinto tb_test values(3,'jerry');
.....
复制代码优化方案一:
批量插入数据
Insertinto tb_test values(1,'Tom'),(2,'Cat'),(3,'Jerry');
复制代码优化方案二
手动控制事务
start transaction;
insertinto tb_test values(1,'Tom'),(2,'Cat'),(3,'Jerry');
insertinto tb_test values(4,'Tom'),(5,'Cat'),(6,'Jerry');
insertinto tb_test values(7,'Tom'),(8,'Cat'),(9,'Jerry');
commit;
复制代码优化方案三
主键顺序插入,性能要高于乱序插入。
主键乱序插入 : 8192188241589573
主键顺序插入 : 1234578915218889复制代码大批量插入数据
如果一次性需要插入大批量数据(比如: 几百万的记录),使用insert语句插入性能较低,此时可以使用MySQL数据库提供的load指令进行插入。操作如下:
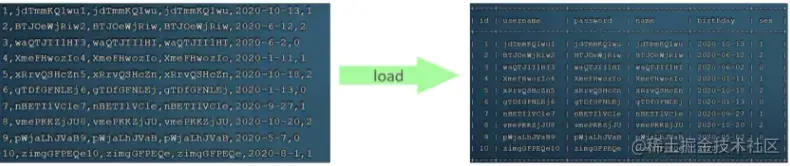
可以执行如下指令,将数据脚本文件中的数据加载到表结构中:
-- 客户端连接服务端时,加上参数 -–local-infile
mysql –-local-infile -u root -p
-- 设置全局参数local_infile为1,开启从本地加载文件导入数据的开关setglobal local_infile =1;
-- 执行load指令将准备好的数据,加载到表结构中
load data local infile '/root/sql1.log'intotable tb_user fields terminated by',' lines terminated by'\n' ;
复制代码主键顺序插入性能高于乱序插入
实例演示:
创建表结构
CREATETABLE `tb_user` (
`id` INT(11) NOTNULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` VARCHAR(50) NOTNULL,
`password` VARCHAR(50) NOTNULL,
`name` VARCHAR(20) NOTNULL,
`birthday` DATEDEFAULTNULL,
`sex` CHAR(1) DEFAULTNULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `unique_user_username` (`username`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ;
复制代码设置参数
-- 客户端连接服务端时,加上参数 -–local-infile
mysql –-local-infile -u root -p
-- 设置全局参数local_infile为1,开启从本地加载文件导入数据的开关setglobal local_infile =1;
复制代码load加载数据
load data local infile '/root/load_user_100w_sort.sql'intotable tb_user fields terminated by',' lines terminated by'\n' ;
复制代码mysql> load data local infile '/root/load_user_100w_sort.sql'intotable tb_user fields terminated by',' lines terminated by'\n' ;
Query OK, 1000000rows affected (15.47 sec)
Records: 1000000 Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql>selectcount(*) from tb_user;
+----------+|count(*) |+----------+|1000000|+----------+1rowinset (0.31 sec)
复制代码我们看到,插入100w的记录,15.47s就完成了,性能很好。
在load时,主键顺序插入性能高于乱序插入
主键优化
主键顺序插入的性能是要高于乱序插入的。我们来介绍一下具体的原因,然后再分析一下主键又该如何设计。
数据组织方式
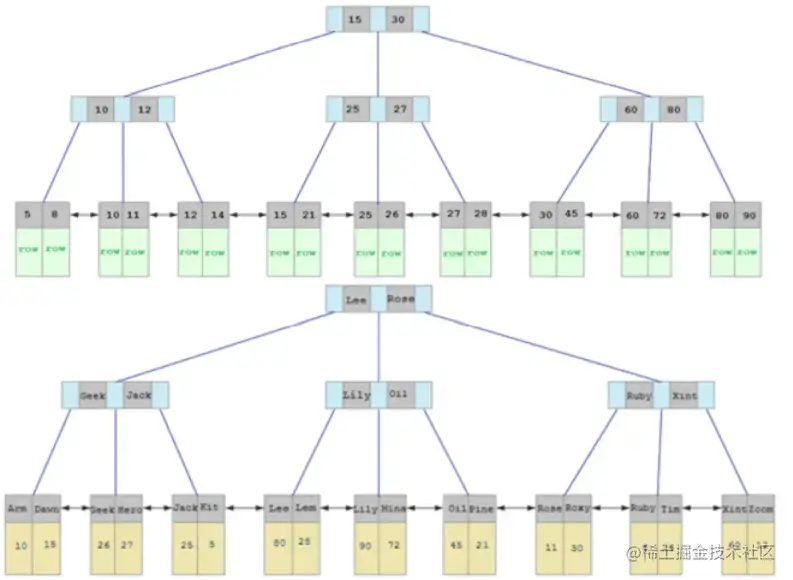
在InnoDB存储引擎中,表数据都是根据主键顺序组织存放的,这种存储方式的表称为索引组织表(index organized table IOT)。
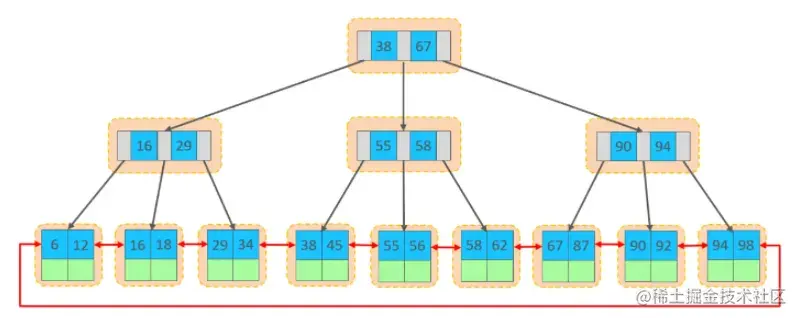
行数据,都是存储在聚集索引的叶子节点上的。而我们之前也讲解过InnoDB的逻辑结构图:
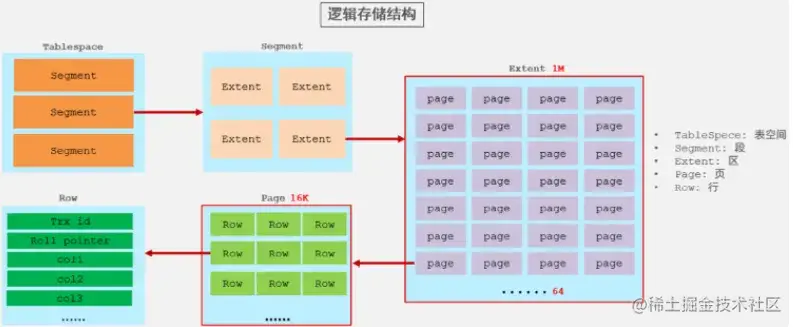
在InnoDB引擎中,数据行是记录在逻辑结构 page 页中的,而每一个页的大小是固定的,默认16K。那也就意味着, 一个页中所存储的行也是有限的,如果插入的数据行row在该页存储不小,将会存储到下一个页中,页与页之间会通过指针连接。
页分裂
页可以为空,也可以填充一半,也可以填充100%。每个页包含了2-N行数据(如果一行数据过大,会行溢出),根据主键排列。
主键顺序插入效果
从磁盘中申请页, 主键顺序插入
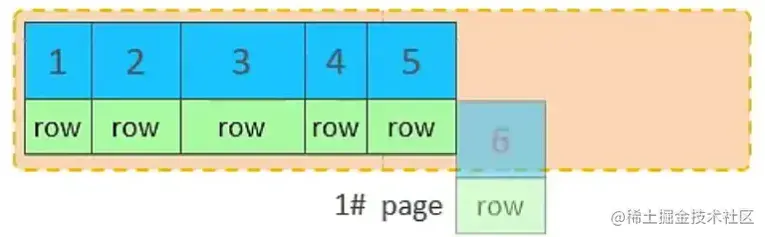
第一个页没有满,继续往第一页插入
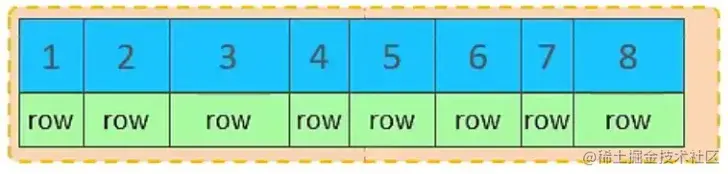
当第一个也写满之后,再写入第二个页,页与页之间会通过指针连接
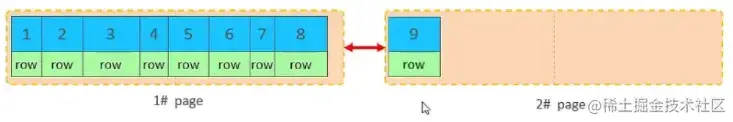
当第二页写满了,再往第三页写入
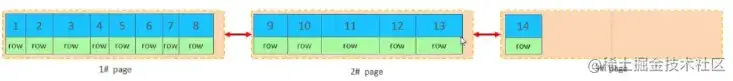
主键乱序插入效果
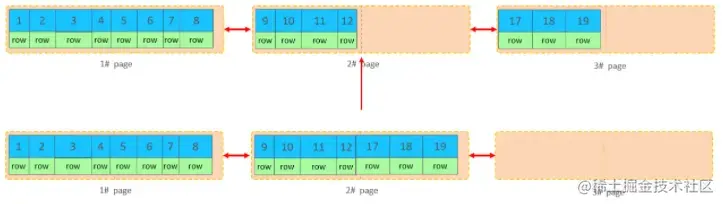
加入1#,2#页都已经写满了,存放了如图所示的数据
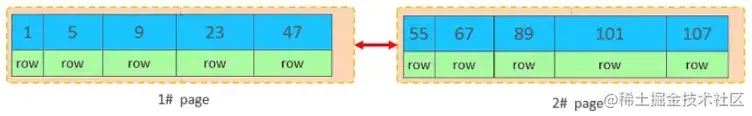
此时再插入id为50的记录,我们来看看会发生什么现象
会再次开启一个页,写入新的页中吗?
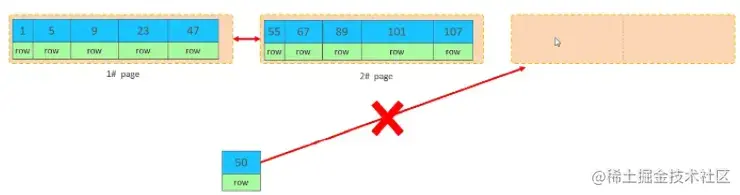
不会。因为,索引结构的叶子节点是有顺序的。按照顺序,应该存储在47之后。
复制代码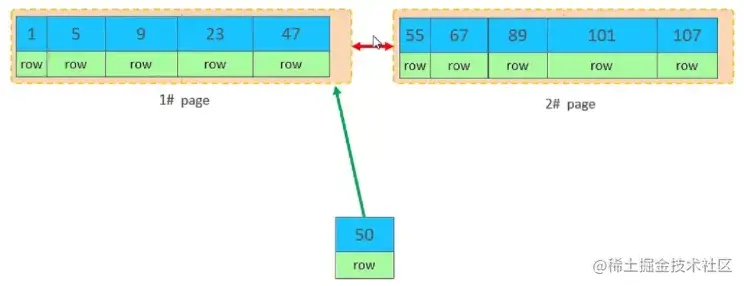
但是47所在的1#页,已经写满了,存储不了50对应的数据了。 那么此时会开辟一个新的页 3#。复制代码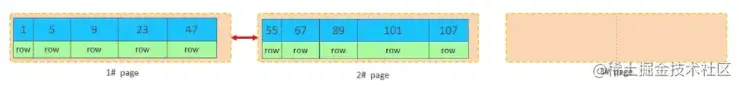
但是并不会直接将50存入3#页,而是会将1#页后一半的数据,移动到3#页,然后在3#页,插入50。复制代码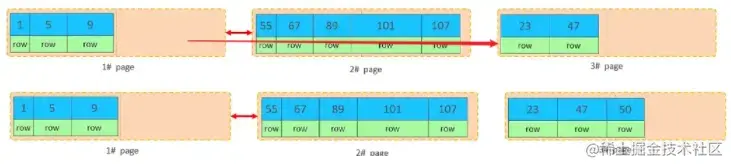
移动数据,并插入id为50的数据之后,那么此时,这三个页之间的数据顺序是有问题的。 1#的下一个 页,应该是3#, 3#的下一个页是2#。 所以,此时,需要重新设置链表指针。
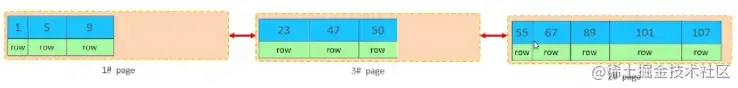
上述的这种现象,称之为 "页分裂",是比较耗费性能的操作。
复制代码页合并
目前表中已有数据的索引结构(叶子节点)如下:
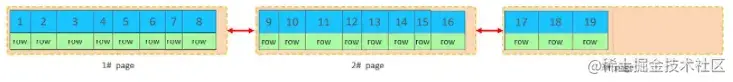
当我们对已有数据进行删除时,具体的效果如下:
当删除一行记录时,实际上记录并没有被物理删除,只是记录被标记(flaged)为删除并且它的空间变得允许被其他记录声明使用。
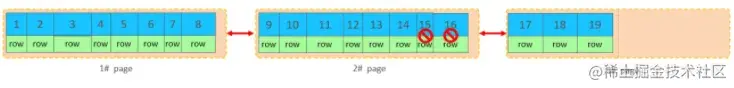
当我们继续删除2#的数据记录
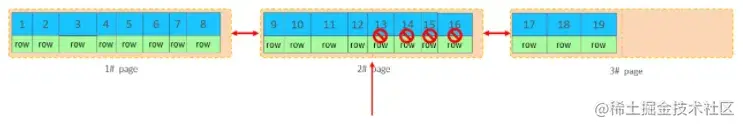
当页中删除的记录达到 MERGE_THRESHOLD(默认为页的50%),InnoDB会开始寻找最靠近的页(前 或后)看看是否可以将两个页合并以优化空间使用。
删除数据,并将页合并之后,再次插入新的数据21,则直接插入3#页
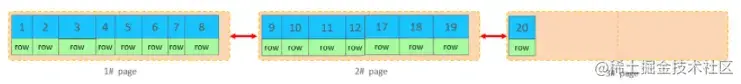
这个里面所发生的合并页的这个现象,就称之为 "页合并"。
知识小贴士:
MERGE_THRESHOLD:合并页的阈值,可以自己设置,在创建表或者创建索引时指定。
索引设计原则
满足业务需求的情况下,尽量降低主键的长度。
插入数据时,尽量选择顺序插入,选择使用AUTO_INCREMENT自增主键。
尽量不要使用UUID做主键或者是其他自然主键,如身份证号。
业务操作时,避免对主键的修改。
order by 优化
MySQL的排序,有两种方式:
Using filesort : 通过表的索引或全表扫描,读取满足条件的数据行,然后在排序缓冲区sort buffer中完成排序操作,所有不是通过索引直接返回排序结果的排序都叫 FileSort 排序。
Using index : 通过有序索引顺序扫描直接返回有序数据,这种情况即为 using index,不需要额外排序,操作效率高。
对于以上的两种排序方式,Using index的性能高,而Using filesort的性能低,我们在优化排序操作时,尽量要优化为 Using index。
接下来,我们来做一个测试:
数据准备
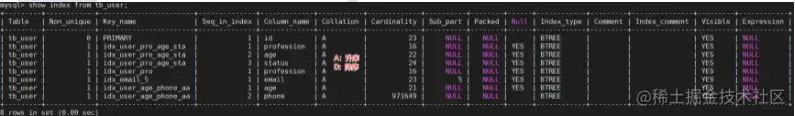
把之前测试时,为tb_user表所建立的部分索引直接删除掉
drop index idx_user_phone on tb_user;
drop index idx_user_phone_name on tb_user;
drop index idx_user_name on tb_user;
复制代码mysql>show index from tb_user;
+---------+------------+----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+|Table| Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name |Collation|Cardinality| Sub_part | Packed |Null| Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression |+---------+------------+----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+| tb_user |0|PRIMARY|1| id | A |23|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |0| idx_user_phone |1| phone | A |24|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |0| idx_user_phone_name |1| phone | A |935064|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |0| idx_user_phone_name |2| name | A |951995|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_user_name |1| name | A |24|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_user_pro_age_sta |1| profession | A |16|NULL|NULL| YES | BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_user_pro_age_sta |2| age | A |22|NULL|NULL| YES | BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_user_pro_age_sta |3| status | A |24|NULL|NULL| YES | BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_user_pro |1| profession | A |16|NULL|NULL| YES | BTREE ||| YES |NULL|| tb_user |1| idx_email_5 |1| email | A |23|5|NULL| YES | BTREE ||| YES |NULL|+---------+------------+----------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+10rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>drop index idx_user_phone on tb_user;
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.02 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql>drop index idx_user_phone_name on tb_user;
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql>drop index idx_user_name on tb_user;
Query OK, 0rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0复制代码执行排序SQL
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL|ALL|NULL|NULL|NULL|NULL|971649|100.00|Using filesort |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age, phone ;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age, phone;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL|ALL|NULL|NULL|NULL|NULL|971649|100.00|Using filesort |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码由于 age, phone 都没有索引,所以此时再排序时,出现Using filesort, 排序性能较低。
创建索引
-- 创建索引create index idx_user_age_phone_aa on tb_user(age,phone);
复制代码创建索引后,根据age, phone进行升序排序
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL| idx_user_age_phone_aa |48|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码建立索引之后,再次进行排序查询,就由原来的Using filesort, 变为了 Using index,性能就是比较高的了。
创建索引后,根据age, phone进行降序排序
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age desc , phone desc;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age desc , phone desc ;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL| idx_user_age_phone_aa |48|NULL|971649|100.00| Backward index scan; Using index |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+----------------------------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码也出现 Using index, 但是此时Extra中出现了 Backward index scan,这个代表反向扫描索引,因为在MySQL中我们创建的索引,默认索引的叶子节点是从小到大排序的,而此时我们查询排序时,是从大到小,所以,在扫描时,就是反向扫描,就会出现 Backward index scan。 在MySQL8版本中,支持降序索引,我们也可以创建降序索引。
根据phone,age进行升序排序,phone在前,age在后。
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby phone , age;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby phone , age;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL| idx_user_age_phone_aa |48|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index; Using filesor |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码排序时,也需要满足最左前缀法则,否则也会出现 filesort。因为在创建索引的时候, age是第一个字段,phone是第二个字段,所以排序时,也就该按照这个顺序来,否则就会出现 Usingfilesort。
根据age, phone进行降序一个升序,一个降序
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age asc , phone desc;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age asc , phone desc;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL| idx_user_age_phone_aa |48|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index; Using filesort |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+-----------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码因为创建索引时,如果未指定顺序,默认都是按照升序排序的,而查询时,一个升序,一个降序,此时就会出现Using filesort。
为了解决上述的问题,我们可以创建一个索引,这个联合索引中 age 升序排序,phone 倒序排序。
创建联合索引(age 升序排序,phone 倒序排序)
create index idx_phone_age_ad on tb_user(age asc,phone desc);
复制代码然后再次执行如下SQL
explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age asc,phone desc;
复制代码mysql> explain select id,age,phone from tb_user orderby age asc,phone desc;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL| idx_phone_age_ad |48|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+---------------+------------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
复制代码升序/降序联合索引结构图示:
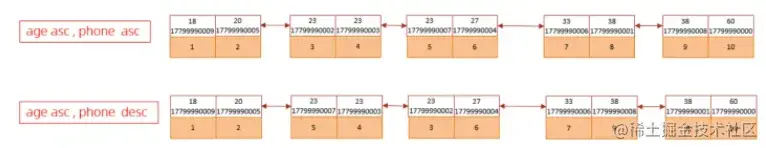
由上述的测试,我们得出order by优化原则:
根据排序字段建立合适的索引,多字段排序时,也遵循最左前缀法则。
尽量使用覆盖索引。
多字段排序, 一个升序一个降序,此时需要注意联合索引在创建时的规则(ASC/DESC)。
如果不可避免的出现filesort,大数据量排序时,可以适当增大排序缓冲区大小sort_buffer_size(默认256k)。
group by 优化
分组操作,我们主要来看看索引对于分组操作的影响。
首先我们先将 tb_user 表的索引全部删除掉 。
drop index idx_user_pro_age_sta on tb_user;
drop index idx_email_5 on tb_user;
drop index idx_user_age_phone_aa on tb_user;
drop index idx_user_age_phone_ad on tb_user;
复制代码mysql>show index from tb_user;
+---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+|Table| Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name |Collation|Cardinality| Sub_part | Packed |Null| Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression |+---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+| tb_user |0|PRIMARY|1| id | A |23|NULL|NULL|| BTREE ||| YES |NULL|+---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+1rowinset (0.00 sec)
复制代码接下来,在没有索引的情况下,执行如下SQL,查询执行计划:
explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user groupby profession;
复制代码mysql> explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user groupby profession ;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL|ALL|NULL|NULL|NULL|NULL|971649|100.00|Using temporary |+----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码然后,我们在针对于 profession , age, status 创建一个联合索引。
create index idx_pro_age_sta on tb_user(profession,age,status);
复制代码紧接着,再执行前面相同的SQL查看执行计划。
mysql> explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user groupby profession;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index | idx_pro_age_sta | idx_pro_age_sta |54|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码再执行如下的分组查询SQL,查看执行计划:
mysql> explain select profession , count(*) from tb_user groupby profession,age;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index | idx_pro_age_sta | idx_pro_age_sta |54|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select age , count(*) from tb_user groupby age;
+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+|1| SIMPLE | tb_user |NULL| index | idx_pro_age_sta | idx_pro_age_sta |54|NULL|971649|100.00|Using index; Using temporary |+----+-------------+---------+------------+-------+-----------------+-----------------+---------+------+--------+----------+------------------------------+1rowinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码我们发现,如果仅仅根据age分组,就会出现 Using temporary ;而如果是 根据profession,age两个字段同时分组,则不会出现 Using temporary。原因是因为对于分组操作,在联合索引中,也是符合最左前缀法则的。
所以,在分组操作中,我们需要通过以下两点进行优化,以提升性能:
在分组操作时,可以通过索引来提高效率。
分组操作时,索引的使用也是满足最左前缀法则的。
limit 优化
在数据量比较大时,如果进行limit分页查询,在查询时,越往后,分页查询效率越低。
我们一起来看看执行limit分页查询耗时对比:
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 0,10;
10rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 100,10;
10rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 1000,10;
10rowsinset (0.00 sec)
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 50000,10;
10rowsinset (0.01 sec)
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 500000,10;
10rowsinset (0.16 sec)
mysql>select*from tb_user limit 900000,10;
10rowsinset (0.28 sec)
复制代码通过测试我们会看到,越往后,分页查询效率越低,这就是分页查询的问题所在。
因为,当在进行分页查询时,如果执行 limit 2000000,10 ,此时需要MySQL排序前2000010 记录,仅仅返回 2000000 - 2000010 的记录,其他记录丢弃,查询排序的代价非常大 。
优化思路: 一般分页查询时,通过创建 覆盖索引 能够比较好地提高性能,可以通过覆盖索引加子查询形式进行优化。
explain select u.*from tb_user u,(select id from tb_user orderby id limit 900000,10) a where u.id = a.id;
复制代码mysql> explain select u.*from tb_user u,(select id from tb_user orderby id limit 900000,10) a where u.id = a.id;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+| id | select_type |table| partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len |ref|rows| filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+------------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+|1|PRIMARY|<derived2>|NULL|ALL|NULL|NULL|NULL|NULL|900010|100.00|NULL||1|PRIMARY| u |NULL| eq_ref |PRIMARY|PRIMARY|4| a.id |1|100.00|NULL||2| DERIVED | tb_user |NULL| index |NULL|PRIMARY|4|NULL|900010|100.00|Using index |+----+-------------+------------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+3rowsinset, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
复制代码count 优化
selectcount(*) from tb_user;
复制代码在之前的测试中,我们发现,如果数据量很大,在执行count操作时,是非常耗时的。
MyISAM 引擎把一个表的总行数存在了磁盘上,因此执行 count(*) 的时候会直接返回这个数,效率很高; 但是如果是带条件的count,MyISAM也慢。
InnoDB 引擎就麻烦了,它执行 count(*) 的时候,需要把数据一行一行地从引擎里面读出来,然后累积计数。
如果说要大幅度提升InnoDB表的count效率,主要的优化思路:自己计数(可以借助于redis这样的数据库进行,但是如果是带条件的count又比较麻烦了)。
count 用法
count() 是一个聚合函数,对于返回的结果集,一行行地判断,如果 count 函数的参数不是NULL,累计值就加 1,否则不加,最后返回累计值。
用法:count(*)、count(主键)、count(字段)、count(数字)
count 用法 | 含义 |
count(主键) | InnoDB 引擎会遍历整张表,把每一行的 主键id 值都取出来,返回给服务层。服务层拿到主键后,直接按行进行累加(主键不可能为null) |
count(字段) | 没有not null 约束 : InnoDB 引擎会遍历整张表把每一行的字段值都取出来,返回给服务层,服务层判断是否为null,不为null,计数累加。有not null 约束:InnoDB 引擎会遍历整张表把每一行的字段值都取出来,返回给服务层,直接按行进行累加。 |
count(数字) | InnoDB 引擎遍历整张表,但不取值。服务层对于返回的每一行,放一个数字“1”进去,直接按行进行累加。 |
count(*) | InnoDB引擎并不会把全部字段取出来,而是专门做了优化,不取值,服务层直接按行进行累加。 |
按照效率排序的话,count(字段) < count(主键 id) < count(1) ≈ count( ),所以尽量使用 count()。
update 优化
我们主要需要注意一下update语句执行时的注意事项。
update course set name ='javaEE'where id =1 ;
复制代码当我们在执行删除的SQL语句时,会锁定id为1这一行的数据,然后事务提交之后,行锁释放。
但是当我们在执行如下SQL时。
update course set name ='SpringBoot'where name ='PHP' ;
复制代码当我们开启多个事务,在执行上述的SQL时,我们发现行锁升级为了表锁。 导致该update语句的性能大大降低。
作者:博学谷_狂野架构师




 文章介绍了数据库操作中的多种优化方法,包括批量插入数据以提高插入性能,主键顺序插入优于乱序插入,以及如何通过索引优化排序和分组查询。还讨论了LIMIT分页查询的优化策略和COUNT函数的高效用法,以及UPDATE语句可能导致的行锁升级问题。
文章介绍了数据库操作中的多种优化方法,包括批量插入数据以提高插入性能,主键顺序插入优于乱序插入,以及如何通过索引优化排序和分组查询。还讨论了LIMIT分页查询的优化策略和COUNT函数的高效用法,以及UPDATE语句可能导致的行锁升级问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








