认识双向链表
单项链表:
只能从头遍历到尾或者从尾部遍历到头(一般从头到尾)
也就是链表相连的过程是单向的,实现的原理是上一个链表中有一个指向下一个的引用
单向链表的缺点:
我们可以轻松的到达下一个节点,但是回到前一个节点很难。但是,在实际开发中,经常会遇到需要回到上一个节点的情况
双向链表:
每次在插入或删除的时候某个节点,需要处理四个节点的引用,而不是两个,也就是实现起来比较困难一点
并且相当于单项链表,必然占用内存空间更大一些
但是这些缺点和我们使用起来的方便程度相比,是微不足道的
双向链接的图解
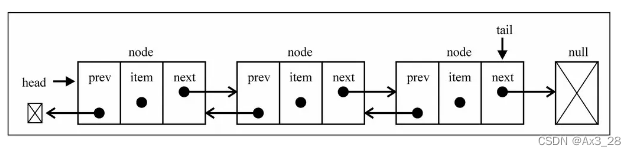
双向链表的创建
我们来创建一个双向链表的类
// 创建双向链表的构造函数
function DoublyLinkedList() {
// 创建节点构造函数
function Node(element) {
this.element = element
this.next = null
this.prev = null // 新添加的
}
// 定义属性
this.length = 0
this.head = null
this.tail = null // 新添加的
// 定义相关操作方法
}
操作双向链表
尾部追加数据
// 在尾部追加数据
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.append = function (element) {
// 1.根据元素创建节点
var newNode = new Node(element)
// 2.判断列表是否为空列表
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = newNode
}
// 3.length+1
this.length++
}
代码解析:
代码1部分不用多讲, 还是通过元素创建新的节点.
代码2部分相比之前有一些复杂, 但是还是两种情况.
情况一: 链表原来为空
链表中原来如果没有数据, 那么直接让head和tail指向这个新的节点即可.
情况二: 链表中已经存在数据
因为我们是要将数据默认追加到尾部, 所以这个变得也很简单.
首先tail中的next之前指向的是null. 现在应该指向新的节点newNode: this.tail.next = newNode
因为是双向链表, 新节点的next/tail目前都是null. 但是作为最后一个节点, 需要有一个指向前一个节点的引用. 所以这里我们需要newNode.prev = this.tail
因为目前newNod已经变成了最后的节点, 所以this.tail属性的引用应该指向最后: this.tail = newNode即可
代码3部分不用多做解析, length需要+1
正向反向遍历
forwardString: 正向遍历转成字符串的方法
reverseString: 反向遍历转成字符串的方法
toString: 正向遍历转成字符串的方法
方法的相关实现
// 正向遍历的方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.forwardString = function () {
var current = this.head
var forwardStr = ""
while (current) {
forwardStr += "," + current.element
current = current.next
}
return forwardStr.slice(1)
}
// 反向遍历的方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.reverseString = function () {
var current = this.tail
var reverseStr = ""
while (current) {
reverseStr += "," + current.element
current = current.prev
}
return reverseStr.slice(1)
}
// 实现toString方法
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
return this.forwardString()
}
完成上面的代码后,测试 append方法
// 1.创建双向链表对象
var list = new DoublyLinkedList()
// 2.追加元素
list.append("abc")
list.append("cba")
list.append("nba")
list.append("mba")
// 3.获取所有的遍历结果
alert(list.forwardString()) // abc,cba,nba,mba
alert(list.reverseString()) // mba,nba,cba,abc
alert(list) // abc,cba,nba,mba
任意位置插入
// 在任意位置插入数据
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, element) {
// 1.判断越界的问题
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return false
// 2.创建新的节点
var newNode = new Node(element)
// 3.判断插入的位置
if (position === 0) { // 在第一个位置插入数据
// 判断链表是否为空
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode
this.tail = newNode
} else {
this.head.prev = newNode
newNode.next = this.head
this.head = newNode
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 插入到最后的情况
// 思考: 这种情况是否需要判断链表为空的情况呢? 答案是不需要, 为什么?
this.tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = this.tail
this.tail = newNode
} else { // 在中间位置插入数据
// 定义属性
var index = 0
var current = this.head
var previous = null
// 查找正确的位置
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 交换节点的指向顺序
newNode.next = current
newNode.prev = previous
current.prev = newNode
previous.next = newNode
}
// 4.length+1
this.length++
return true
}
测试该方法
// 4.insert方法测试
list.insert(0, "100")
list.insert(2, "200")
list.insert(6, "300")
alert(list) // 100,abc,200,cba,nba,mba,300
位置移除数据
// 根据位置删除对应的元素
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.判断越界的问题
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.判断移除的位置
var current = this.head
if (position === 0) {
if (this.length == 1) {
this.head = null
this.tail = null
} else {
this.head = this.head.next
this.head.prev = null
}
} else if (position === this.length -1) {
current = this.tail
this.tail = this.tail.prev
this.tail.next = null
} else {
var index = 0
var previous = null
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
current.next.prev = previous
}
// 3.length-1
this.length--
return current.element
}
获取元素位置
// 根据元素获取在链表中的位置
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (element) {
// 1.定义变量保存信息
var current = this.head
var index = 0
// 2.查找正确的信息
while (current) {
if (current.element === element) {
return index
}
index++
current = current.next
}
// 3.来到这个位置, 说明没有找到, 则返回-1
return -1
}




















 1161
1161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








