Email:dev_as@163.com
OCAF Architecture Overview
OCAF provides you with an object-oriented Application-Document-Attribute model consisting of C++ class libraries.

这里涉及重要的4个概念:Application、Document、Attribute和Reference-key model
本文将重点描述Reference-key model机制:
-
Application
-
Application是一个抽象类,负责在工作期间处理documents
-
创建新的documents
-
存储documents
-
打开documents
-
初始化document的views
-
-
Document
-
"Application data"的容器
-
The document is the container for the application data.
-
The document is implemented by the concreate class : Document.
-
Documents offer access to the data framework and serve the following purposes
-
Manage the notification of changes 管理变更
-
Update external links 管理关联关系
-
Manage the saving and restoring of data 管理序列化和反序列化
-
Store the names of software extensions. 存储软件扩展
-
Manage command transactions. 管理命令事务
-
Manage Undo and Redo options.管理Undo和Redo
-
-
Each document is saved in a single flat ASCII file defined by its format and extension (a ready-to-use format is provided with OCAF)
-
除了作为应用程序数据容器的角色外,文档还可以相互引用;例如,文档 A 可以引用文档 B 中的特定标签。通过引用键可以实现此功能。
-
-
Attribute
-
“Application data” is described by Attributes, which are instances of classes derived from the Attribute abstract class.
-
The OCAF Data Framework references aggregations of attributes using persistent identifiers in a single hierarchy.
-
Attribute是一个抽象类
-
OCAF数据框架是一个引用属性的聚合aggregations
-
OCAF数据框架使用单个层次结构
-
OCAF数据框架使用持久化标识符
-
-
A wide range of attributes come with OCAF:
-
Standard attributes
-
operating with simple common data in the data framework (for example: integer, real, string, array kinds of data)
-
realize auxiliary functions (for example: tag sources attribute for the children of the label counter)
-
create dependencies (for example: reference, tree node)
-
-
Shape attributes
-
the geometry of the whole model or its elements including reference to the shapes and tracking of shape evolution;
-
整个模型或其元素的几何形状,包括对形状的引用和形状演化的跟踪
-
-
Other geometric attributes
-
Datums 基准 (points, axis and plane)
-
Constraints 约束 (tangent-to, at-a-given-distance, from-a-given-angle, concentric, etc.)(相切、在给定距离、从给定角度、同心等)
-
-
User attributes, that is, attributes typed by the application
-
Visualization attributes
-
Placing viewer information to the data framework
-
Visual representation of objects
-
Other auxiliary visual information,
-
Tips : which is needed for graphical data representation.
-
-
Function services
-
the purpose of these attributes is to rebuild objects after they have been modified (parameterization of models).
-
While the document manages the notification of changes, a function manages propagation of these changes.
-
The function mechanism provides links between functions and calls to various algorithms.
-
-
Custom Attributes
-
Application-specific data(custom data) can be added by defining new attribute classes;
-
This changes the standard file format.
-
The only functions that have to be implemented are :
-
Copy the attribute
-
Converting it from and persistent data storage
-
-
-
-
-
Reference-key model
-
几何建模现状:In most existing geometric modeling systems, the data are topology driven. They usually use a boundary representation (BRep), where geometric models are defined by a collection of faces, edges and vertices, to which application data are attached.
-
几何建模参数化带来的影响: When the geometric model is parameterized, that is, when you can change the value of parameters used to build the model (the radius of a blend, the thickness of a rib, etc.), the geometry is highly subject to change.
-
OCAF的目标: In order to maintain the attachment of application data, the geometry must be distinguished from other data.
-
OCAF的解决方案:
-
给与RKM一个唯一持久化标识 : In OCAF, the data are reference-key driven. It is a uniform model in which reference-keys are the persistent identification of data.
-
所有属性跟RKM绑定 : All accessible data, including the geometry, are implemented as attributes attached to reference-keys.
-
比如 : The geometry becomes the value of the Shape attribute, just as a number is the value of the Integer and Real attributes and a string that of the Name attribute.
-
-
RKM的核心就是聚合 : On a single reference-key, many attributes can be aggregated;
-
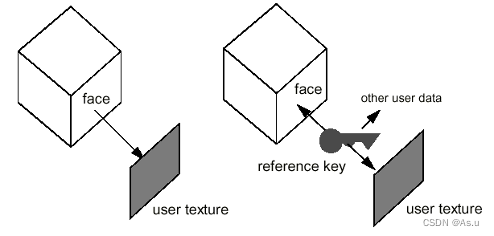
RKM的另一个核心就是RTTI : the application can ask at runtime which attributes are available. For example, to associate a texture to a face in a geometric model, both the face and the texture are attached to the same reference-key.
-
RKM有两种创建方式:
-
At programming time, by the application
-
At runtime, by the end-user of the application (providing that you include this capability in the application)
-
-
RKM定义一个立方柱:
-
As an application developer, you generate reference-keys in order to give semantics to the data. For example, a function building a prism may create three reference-keys: one for the base of the prism, a second for the lateral faces and a third for the top face. This makes up a semantic built-in the application's prism feature.
-
On the other hand, in a command allowing the end-user to set a texture to a face he/she selects, you must create a reference-key to the selected face if it has not previously been referenced in any feature (as in the case of one of the lateral faces of the prism).
-
-
OCAF实现RKM的实现方式——属性命名:When you create a reference-key to selected topological elements (faces, edges or vertices), OCAF attaches to the reference-key information defining the selected topology — the Naming attribute(类似拓扑命名).
-
属性命名举例:For example, it may be the faces to which a selected edge is common to(共同拥有). This information, as well as information about the evolution of the topology at each modeling step (the modified, updated and deleted faces), is used by the naming algorithm to maintain the topology attached to the reference-key.
-
RKM修改参数化部分对引用主体的影响程度:As such, on a parametrized model, after modifying the value of a parameter, the reference-keys still address the appropriate faces, even if their geometry has changed. Consequently, you change the size of the cube shown in the figure above, the user texture stay attached to the right face.
-
-
关于the Naming attribute 和 the Topological naming
-
Note : As Topological naming is based on "the reference-key" and "attributes" such as Naming (selection information) and Shape (topology evolution information), OCAF is not coupled to the underlying modeling libraries.
-
Naming : When you create a reference-key to selected topological elements (faces, edges or vertices), OCAF attaches to the reference-key information defining the selected topology — the Naming attribute.
-
Shape - topology evolution information : This information, as well as information about the evolution of the topology at each modeling step (the modified, updated and deleted faces), is used by the naming algorithm to maintain the topology attached to the reference-key.
-
Each algorithm must provide information about the evolution of the topology (the list of faces modified, updated and deleted by the algorithm)
-
Exploration of the geometric model must be available (a 3D model is made of faces bounded by close wires, themselves composed by a sequence of edges connected by their vertices)
-
-
关于数据结构
-
推荐聚合,拒绝继承:To design an OCAF-based data model, the application developer is encouraged to aggregate ready-to-use attributes instead of defining new attributes by inheriting from an abstract root class.
-
对于聚合的两个建议:
-
As you don't implement data by defining new classes, the format of saved data provided with OCAF doesn't change; so you don't have to write the Save and Open functions,由于没有使用继承,OCAF提供的保存数据的格式不会改变,这样就不必编写Save和Open函数
-
The application can query the data at runtime if a particular attribute is available,RTTI和QueryInterface
-
-
-
-
Conclusion
-
OCAF is based on a uniform reference-key model in which:
-
持久化:Reference-keys provide persistent identification of data;
-
数据引用和RKM的关联:Data, including geometry, are implemented as attributes attached to reference-keys;
-
参数化增删改查机制-拓扑命名:Topological naming maintains the selected geometry attached to reference-keys in parametrized models;
-
-
In many applications, the data format provided with OCAF doesn't need to be extended;
-
OCAF is not coupled to the underlying modeling libraries.
-








 OCAF(Open CASCADE Technology Application Framework)提供了一个面向对象的模型,由C++类库构成,包括Application、Document、Attribute和Reference-key模型。本文重点讨论Reference-key模型,它为数据提供了持久化标识,使得在几何模型参数化后仍能维持应用数据的关联。OCAF通过属性和引用键来管理数据,即使几何形状变化,仍能保持数据的正确引用。
OCAF(Open CASCADE Technology Application Framework)提供了一个面向对象的模型,由C++类库构成,包括Application、Document、Attribute和Reference-key模型。本文重点讨论Reference-key模型,它为数据提供了持久化标识,使得在几何模型参数化后仍能维持应用数据的关联。OCAF通过属性和引用键来管理数据,即使几何形状变化,仍能保持数据的正确引用。

















 1400
1400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










