当多个事务同时操作同一数据时,如果没有良好的控制手段,则有可能同一数据被别的事务修改而造成混乱,此时可以利用数据库底层提供的锁机制对当前操作的数据进行锁定,以防止其他事务同时操作此数据;
悲观锁:
每次在操作数据时,总是悲观的认为会有别的事务也会操作同一数据,因此锁住该数据,直到自己操作完成后再解除锁,虽然安全但影响性能;
Hibernate的加锁模式有:
- LockMode.NONE :无锁机制。
- LockMode.WRITE :Hibernate在 Insert和 Update记录的时候会自动获取。
- LockMode.READ :Hibernate在读取记录的时候会自动获取。
- LockMode.UPGRADE :利用数据库的 for update 子句加锁。(select * from user2 where id=1 for update)
- LockMode. UPGRADE_NOWAIT : Oracle的特定实现,利用 Oracle的 for update nowait子句实现加锁。
加锁一般通过以下方法实现:
- Criteria.setLockMode
- Query.setLockMode
- Session.lock
注意,只有在查询开始之前(也就是 Hiberate生成 SQL之前)设定加锁,才会真正通过数据库的锁机制进行加锁处理,否则,数据已经通过不包含 for update子句的 Select SQL加载进来,所谓数据库加锁也就无从谈起。在Hibernate使用悲观锁十分容易,但实际应用中悲观锁是很少被使用的,因为它大大限制了并发性,并且利用数据库底层来维护锁,这样大大降低了应用程序的效率。
乐观锁:
相对于悲观锁而言,它通常认为多个事务同时操作同一数据的情况是很少的,因而不做数据库层次上的锁定,只是基于数据版本标识,实现应用程序级别上的锁定;
Hibernate为乐观锁提供了3中实现:
- 基于version
- 基于timestamp
- 为遗留项目添加添加乐观锁
version:
为数据增加一个版本标识,一般是通过数据库增加一个version字段实现。当读取数据时,连同版本号一起读出,之后更新此数据时版本号加1.在提交数据时将现有版本号与数据库对应的版本号进行对比,如果提交的版本号大于数据库表中的版本号,则允许更新数据,否则禁止更新数据。
![]()
在该表对应的实体类中,加@Version
private Integer version;@Column(name = "version")
@Version
public Integer getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(Integer version) {
this.version = version;
}@Test
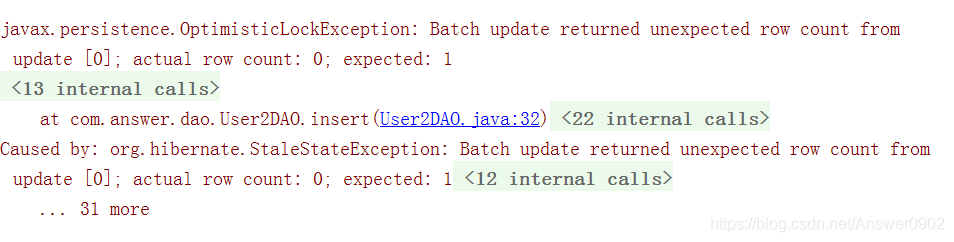
public void insert(){
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
Session session1=sessionFactory.openSession();
User2 user2=(User2) session.createQuery("from User2 where username='s1'").uniqueResult();
User2 user21=(User2) session1.createQuery("from User2 where username='s1'").uniqueResult();
System.out.println(user2.getVersion()+"----"+user21.getVersion());
Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction();
user2.setUsername("s2");
transaction.commit();
System.out.println(user2.getVersion()+"--"+user21.getVersion());
Transaction transaction1=session1.beginTransaction();
user21.setUsername("s3");
transaction1.commit();
}
缓存机制:
缓存是关于应用程序性能的优化,降低了应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能。
缓存对 Hibernate 来说也是重要的,它使用了如下解释的多级缓存方案:
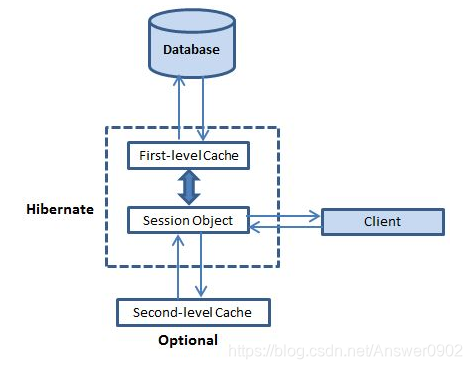
Hibernate中提供了两级缓存,一级缓存是Session级别的缓存,它属于事务范围的缓存,该级缓存由hibernate管理,应用程序无需干预;二级缓存是SessionFactory级别的缓存,该级缓存可以进行配置和更改,并且可以动态加载和卸载,hibernate还为查询结果提供了一个查询缓存,它依赖于二级缓存;
一级缓存:
第一级缓存是 Session 缓存并且是一种强制性的缓存,所有的要求都必须通过它。Session 对象在它自己的权利之下,在将它提交给数据库之前保存一个对象。如果你对一个对象发出多个更新,Hibernate 会尝试尽可能长地延迟更新来减少发出的 SQL 更新语句的数目。如果你关闭 session,所有缓存的对象丢失,或是存留,或是在数据库中被更新。
二级缓存:
第二级缓存是一种可选择的缓存并且第一级缓存在任何想要在第二级缓存中找到一个对象前将总是被询问。第二级缓存可以在每一个类和每一个集合的基础上被安装,并且它主要负责跨会话缓存对象。任何第三方缓存可以和 Hibernate 一起使用。org.hibernate.cache.CacheProvider 接口被提供,它必须实现来给 Hibernate 提供一个缓存实现的解决方法。
ehcache.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--Default Cache configuration. These will applied to caches programmatically created through
the CacheManager.
The following attributes are required:
缓存最大数目
maxElementsInMemory - sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
缓存是否持久
eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the
element is never expired.
是否保存到磁盘,当系统当机时
overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
has reached the maxInMemory limit.
The following attributes are optional:
当缓存闲置n秒后销毁
timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires.
i.e. The maximum amount of time between accesses before an element expires
Is only used if the element is not eternal.
Optional attribute. A value of 0 means that an Element can idle for infinity.
The default value is 0.
当缓存存活n秒后销毁
timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires.
i.e. The maximum time between creation time and when an element expires.
Is only used if the element is not eternal.
Optional attribute. A value of 0 means that and Element can live for infinity.
The default value is 0.
指定缓存是否被持久化到硬盘中,保存路径由<diskStore>标签指定。
diskPersistent - Whether the disk store persists between restarts of the Virtual Machine.
The default value is false.
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds- The number of seconds between runs of the disk expiry thread. The default value
is 120 seconds.
-->
<ehcache>
<defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="3600"
timeToLiveSeconds="3600"
overflowToDisk="false">
</defaultCache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.internal.StandardQueryCache"
maxElementsInMemory="5" eternal="false" timeToLiveSeconds="120">
</cache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.spi.UpdateTimestampsCache"
maxElementsInMemory="5000" eternal="true">
</cache>
</ehcache>hibernate.cfg.xml:
<!-- 设置二级缓存插件EHCache的Provider类-->
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- 启用查询缓存,以缓存使用find(),list(),Iterator()等方法获得的查询结果集-->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_configuration_file_resource_path">classpath:ehcache.xml</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>进行查询:
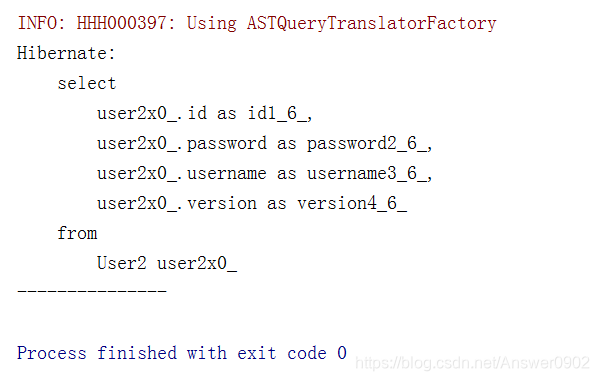
@Test
public void query(){//二级缓存
session=sessionFactory.openSession();
try{
Query<User2> query=session.createQuery("from User2 ");
query.setCacheable(true);
query.list();
System.out.println("---------------");
query.list();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
session.close();
}
}结果:只有一组Sql语句;
参考:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/an_2016/article/details/52088712
https://www.w3cschool.cn/hibernate/xrvi1iee.html





 本文深入探讨了Hibernate框架中的锁机制,包括悲观锁和乐观锁的工作原理及实现方式,以及版本控制和时间戳机制的运用。同时,详细解析了Hibernate的缓存机制,涵盖一级缓存和二级缓存的功能、配置与使用方法。
本文深入探讨了Hibernate框架中的锁机制,包括悲观锁和乐观锁的工作原理及实现方式,以及版本控制和时间戳机制的运用。同时,详细解析了Hibernate的缓存机制,涵盖一级缓存和二级缓存的功能、配置与使用方法。

















 328
328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










