采用合并差分包的方式,不过要做一些处理,以下是一些分析
1、做出两个差分包
对比两个升级包可以看出,我们只需要处理system 和vendor部分,其他驱动文件原生处理为了整包升级,所以01-03 和 02-03 中是一样的
2、修改01-03升级包,
修改updater-scrypt,以以下格式处理脚本文件
if getprop("ro.build.date.utc") == "1562576172" then
01-03升级脚本
......
else
02-03升级脚本
......
endif;
修改01-03升级包中system vendor文件的名称
system01.transfer.list system01.new.dat system01.patch.dat
vendor01.transfer.list vendor01.new.dat vendor01.patch.dat
同时修改updater-scrypt 中01-03脚本中的system vendor的名称
3、将02-03中升级包的updater-scrypt中的内容直接复制到else 后的部分,这里不用做任何的更改,全部脚本复制
4、将02-03中system 和 vendor的相关文件放入到 之前处理的的升级包中
处理后的截图如下
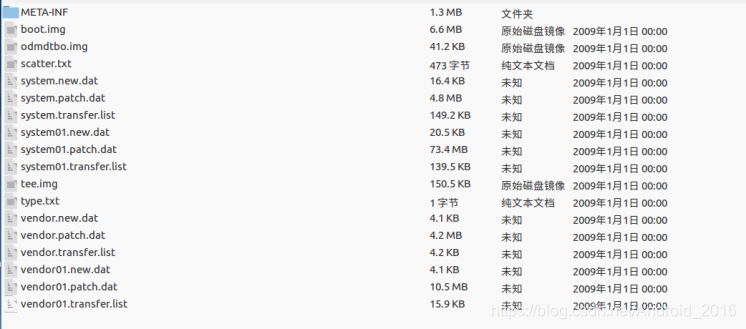
这样处理完后验证,发现刷01版本 可以正常升级到03 ,但是刷机到02 却无法升级到03,报错patch失败
recovery的log如下,看错误确实走进了else方法,因为02-03的cache判断是25841664 needed
[ 6.998341] SELinux: Loaded file_contexts [ 6.998551] Source: LEAGOO/Z10/Z10:8.1.0/O11019/1553496128:user/release-keys [ 6.998579] Target: LEAGOO/Z10/Z10:8.1.0/O11019/1565838105:user/release-keys [ 6.998732] Verifying current system... [ 6.998805] 108990464 bytes free on /cache (25841664 needed) [ 19.534887] Verified system image... [ 20.454253] Verified vendor image... [ 20.454349] Patching system image after verification. [ 20.454449] performing update [ 20.462901] blockimg version is 4 [ 20.462951] maximum stash entries 0 [ 20.465919] creating stash /cache/recovery/3a0104144fd74fc8745d8bb2737492c5611934b0/ [ 20.466837] 108986368 bytes free on /cache (25841664 needed) [ 20.466929] erasing 68874 blocks [ 20.592881] stashing 284 overlapping blocks to a7201da77719855292aa705ec24e88804b4c1a68 [ 20.592944] 108986368 bytes free on /cache (1163264 needed) [ 20.593019] writing 284 blocks to /cache/recovery/3a0104144fd74fc8745d8bb2737492c5611934b0/a7201da77719855292aa705ec24e88804b4c1a68 [ 20.667376] patching 284 blocks to 284 [ 20.667434] Not a bsdiff patch. [ 20.667448] bspatch failed, result: 2 [ 20.667460] Patch may be corrupted, offset: 0, SHA1: 03110be20c1d315bc6814caa3e1086b042f907ae [ 20.667475] Failed to apply bsdiff patch. [ 20.667488] failed to execute command [bsdiff 0 210 a7201da77719855292aa705ec24e88804b4c1a68 a819a07d4258d79f6fa909984c0933983f211e9b 2,189705,189989 284 2,189705,189989] [ 20.669709] script aborted: E1001: Failed to update system image. [ 20.669829] Patch application failed, retry update.
这里报错是patch文件不对,起初怀疑是不是用错了02的包,但是实际测试02-03原始升级包是可以升级成功的
目前针对这个错误判断是我们拷贝后的dat文件损坏了,但是对比跟02-03原包是一样,所以基本上是卡这儿了,只能填坑了
5、生成差分包dat文件处理
既然我们这样手动放入或者用zip命令不行,只能看最初的生成差分包时,是怎么把dat文件放入到升级包中
ota_from_target_file.py
def WriteBlockIncrementalOTAPackage(target_zip, source_zip, output_zip):
......
......
system_diff.WriteScript(script, output_zip,
progress=0.8 if vendor_diff else 0.9)
if vendor_diff:
vendor_diff.WriteScript(script, output_zip, progress=0.1)
common.py
WriteScript方法
def WriteScript(self, script, output_zip, progress=None):
if not self.src:
# write the output unconditionally
script.Print("Patching %s image unconditionally..." % (self.partition,))
else:
script.Print("Patching %s image after verification." % (self.partition,))
if progress:
script.ShowProgress(progress, 0)
self._WriteUpdate(script, output_zip)
if OPTIONS.verify:
self._WritePostInstallVerifyScript(script)
self._WriteUpdate(script, output_zip)
看到我们想要的代码了 ,处理new.dat 和 patch.dat部分
def _WriteUpdate(self, script, output_zip):
ZipWrite(output_zip,
'{}.transfer.list'.format(self.path),
'{}.transfer.list'.format(self.partition))
# For full OTA, compress the new.dat with brotli with quality 6 to reduce its size. Quailty 9
# almost triples the compression time but doesn't further reduce the size too much.
# For a typical 1.8G system.new.dat
# zip | brotli(quality 6) | brotli(quality 9)
# compressed_size: 942M | 869M (~8% reduced) | 854M
# compression_time: 75s | 265s | 719s
# decompression_time: 15s | 25s | 25s
if not self.src:
bro_cmd = ['bro', '--quality', '6',
'--input', '{}.new.dat'.format(self.path),
'--output', '{}.new.dat.br'.format(self.path)]
print("Compressing {}.new.dat with brotli".format(self.partition))
p = Run(bro_cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
p.communicate()
assert p.returncode == 0,\
'compression of {}.new.dat failed'.format(self.partition)
new_data_name = '{}.new.dat.br'.format(self.partition)
ZipWrite(output_zip,
'{}.new.dat.br'.format(self.path),
new_data_name,
compress_type=zipfile.ZIP_STORED)
else:
new_data_name = '{}.new.dat'.format(self.partition)
ZipWrite(output_zip, '{}.new.dat'.format(self.path), new_data_name)
ZipWrite(output_zip,
'{}.patch.dat'.format(self.path),
'{}.patch.dat'.format(self.partition),
compress_type=zipfile.ZIP_STORED)
ZipWrite方法
#
def ZipWrite(zip_file, filename, arcname=None, perms=0o644,
compress_type=None):
import datetime
# http://b/18015246
# Python 2.7's zipfile implementation wrongly thinks that zip64 is required
# for files larger than 2GiB. We can work around this by adjusting their
# limit. Note that `zipfile.writestr()` will not work for strings larger than
# 2GiB. The Python interpreter sometimes rejects strings that large (though
# it isn't clear to me exactly what circumstances cause this).
# `zipfile.write()` must be used directly to work around this.
#
# This mess can be avoided if we port to python3.
saved_zip64_limit = zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT
zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT = (1 << 32) - 1
=================
<zipfile.ZipFile object at 0x7fd94260b0d0>
/tmp/tmpBmzgWk/system.patch.dat
system.patch.dat
0
=================
print("=================")
print(zip_file)
print(filename)
print(arcname)
print(compress_type)
print("=================")
if compress_type is None:
compress_type = zip_file.compression
if arcname is None:
arcname = filename
saved_stat = os.stat(filename)
try:
# `zipfile.write()` doesn't allow us to pass ZipInfo, so just modify the
# file to be zipped and reset it when we're done.
os.chmod(filename, perms)
# Use a fixed timestamp so the output is repeatable.
epoch = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(0)
timestamp = (datetime.datetime(2009, 1, 1) - epoch).total_seconds()
os.utime(filename, (timestamp, timestamp))
zip_file.write(filename, arcname=arcname, compress_type=compress_type)
finally:
os.chmod(filename, saved_stat.st_mode)
os.utime(filename, (saved_stat.st_atime, saved_stat.st_mtime))
zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT = saved_zip64_limit
通过打印我们知道了进入ZipWrite的参数,同时我看到了compress_type=zipfile.ZIP_STORED这样一个参数,对于patch.dat,查询后发现这是zipfile模块的一个参数
zipfile.ZIP_STORED
表示非压缩的常量。
那现在就比较明了了,对于dat文件,虽然是放进升级包,但是不做任何压缩的处理,而我们不管是怎么手动放,都对dat进行了压缩,所以我们现在要用zipfile模块写一个脚本去处理dat文件的拷贝
6、形成脚本处理升级包
import os
import os.path
import re
import subprocess
import sys
import shlex
import shutil
import tempfile
import threading
import time
import zipfile
import datetime
def ZipWrite(input_zip, filename, arcname=None, perms=0o644):
# http://b/18015246
# Python 2.7's zipfile implementation wrongly thinks that zip64 is required
# for files larger than 2GiB. We can work around this by adjusting their
# limit. Note that `zipfile.writestr()` will not work for strings larger than
# 2GiB. The Python interpreter sometimes rejects strings that large (though
# it isn't clear to me exactly what circumstances cause this).
# `zipfile.write()` must be used directly to work around this.
#
# This mess can be avoided if we port to python3.
saved_zip64_limit = zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT
zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT = (1 << 32) - 1
saved_stat = os.stat(filename)
try:
# `zipfile.write()` doesn't allow us to pass ZipInfo, so just modify the
# file to be zipped and reset it when we're done.
os.chmod(filename, perms)
# Use a fixed timestamp so the output is repeatable.
# 处理文件的时间戳
epoch = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(0)
timestamp = (datetime.datetime(2009, 1, 1) - epoch).total_seconds()
os.utime(filename, (timestamp, timestamp))
#将传入的文件生成为zipfile对象,传入参数a 代表可以追加文件
zip_file = zipfile.ZipFile(input_zip, "a")
#如果我们要追加的文件不在zip_file 文件列表中,执行追加
if arcname not in zip_file.namelist():
#使用write方法追加文件,并给到参数zipfile.ZIP_STORED
zip_file.write(filename, arcname, zipfile.ZIP_STORED)
else:
print >> sys.stderr, "%s is already exist,do nothing..." % (arcname)
finally:
os.chmod(filename, saved_stat.st_mode)
os.utime(filename, (saved_stat.st_atime, saved_stat.st_mtime))
zipfile.ZIP64_LIMIT = saved_zip64_limit
#处理好后关闭
zip_file.close()
return True
def main(argv):
if len(argv) != 3:
print(__doc__)
sys.exit(1)
input_zip = argv[0]
filename = argv[1]
arcname = argv[2]
#传入的三个参数,1、升级包 2、需要放入的文件 3、放入后文件的名称
if not ZipWrite(input_zip, filename, arcname):
print >> sys.stderr, "error: failed to zip %s to %s" % (arcname,zip_file)
exit(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv[1:])
执行脚本:
./build/tools/releasetools/adups_zipfile_for_dat.py update.zip '/home/adups/FOTA/2019090901/02/target_files-package02/update002/vendor.transfer.list' vendor.transfer.list
使用重新生成的差分包测试01-03 和 02-03 均验证OK,问题解决





 本文详细解析了差分包升级失败的问题,通过分析发现dat文件处理不当导致升级失败,最终通过正确处理dat文件解决了问题。
本文详细解析了差分包升级失败的问题,通过分析发现dat文件处理不当导致升级失败,最终通过正确处理dat文件解决了问题。
















 1365
1365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








