之前一直在接触动态代理,但是对于一些概念还是不能很好得理解,知道模板怎么用,但是换一种方式,我就懵逼了。
为什么会有动态代理呢,先看下面得例子:
由来
1.首先定义一个接口Subject
package com.wx.proxy.jdkproxy;
public interface Subject {
void hello(String param);
void say();
}
2. 定义接口得实现类SubjectImpl
package com.wx.proxy.jdkproxy;
public class SubjectImpl implements Subject {
public void hello(String param) {
System.out.println("hello "+param);
}
public void say() {
System.out.println("增加一个方法");
}
}
3. 创建主类,调用say方法
package jdkproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject = new SubjectImpl();
subject.say();
}
}
运行结果:
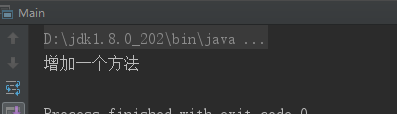
如果我想在这个方法前后打印日志,那么在不改动源码得基础上,创建一个代理类SubjectImplProxy,代码如下:
静态代理:
1.在原有基础上,创建SubjectImplProxy
package jdkproxy;
public class SubjectImplProxy implements Subject {
private Subject subject= null;
public SubjectImplProxy(Subject subject){
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public int hello(String param) {
System.out.println("开始执行hello方法");
subject.hello("world");
System.out.println("结束执行hello方法");
return 0;
}
@Override
public void say() {
System.out.println("开始执行say方法");
subject.say();
System.out.println("结束执行say方法");
}
}
2. 测试Main类修改为:
package jdkproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject = new SubjectImpl();
SubjectImplProxy subjectProxy = new SubjectImplProxy(subject);
subjectProxy.say();
}
}
测试结果
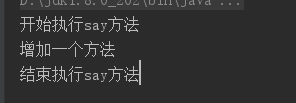
这里功能虽然实现,但是有一个问题就是,如果出现SubjectImpl2,或者其他类型得类需要代理,都需要创建一个新的代理类,这样就会很麻烦,为了解决这个问题,就出现了动态代理
JDK动态代理
1. 创建代理实现类SubjectProxy
在此类中。当代理对象执行方法时,会执行invoke方法。通过反射得到method对象,然后执行方法,返回执行方法后的返回值
package jdkproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class SubjectProxy implements InvocationHandler{
private Subject subject;
public SubjectProxy(Subject subject){
this.subject = subject;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("-----------------begin--------------------");
Object invoke = method.invoke(subject,args);
System.out.println("-----------------end----------------------");
return invoke;
}
}
2. 创建测试类
package jdkproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject = new SubjectImpl();
SubjectProxy subjectProxy = new SubjectProxy(subject);
Subject proxy = (Subject)Proxy.newProxyInstance(subjectProxy.getClass().getClassLoader(), subject.getClass().getInterfaces(), subjectProxy);
proxy.say();
}
}
测试结果:
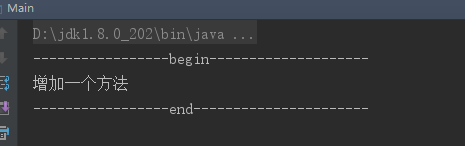
无需创建代理对象类,通过匿名内部类创建
修改后的Main类:
在此类中,通过匿名内部类创建代理对象,然后判断不同得执行方法,执行不同代码
package jdkproxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject subject = new SubjectImpl();
SubjectProxy subjectProxy = new SubjectProxy(subject);
Subject proxy = (Subject)Proxy.newProxyInstance(subject.getClass().getClassLoader(), subject.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if("say".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("=======开始=========");
Object object = method.invoke(subject,args);
System.out.println("=======结束=========");
return object;
}
if("hello".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("=============begin===============");
Object object = method.invoke(subject,args);
System.out.println("=============end=================");
return object;
}
return null;
}
});
proxy.hello("world");
proxy.say();
}
}
CGLIB动态代理
在jdk代理中,因为需要写实现类。为了直接对基本类进行代理,不要有实现接口,使用CGLIB动态代理。
1. 创建被代理类
package cglibProxy;
public class CGLIB {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("ceshi");
}
}
2. 创建代理类
创建代理类,实现MethodInterceptor接口
package cglibProxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class HelloInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("begin time -----> "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
Object o1 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("end time -----> "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
return o1;
}
}
3. 创建测试类
package cglibProxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(CGLIB.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new HelloInterceptor());
CGLIB cglib = (CGLIB) enhancer.create();
cglib.sayHello();
cglib.say();
}
}
4. 测试结果
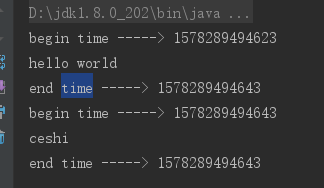
5. 另外一种方式测试
使用不需要实现MethodInterceptor接口得类,来代理普通类。使用method来判断,要对哪些方法进行代理。
package cglibProxy;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(CGLIB.class);
//enhancer.setCallback(new HelloInterceptor());
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
if("sayHello".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("begin time -----> "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
Object o1 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("end time -----> "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
return o1;
}else{
Object o2 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
return o2;
}
}
});
CGLIB cglib = (CGLIB) enhancer.create();
cglib.sayHello();
cglib.say();
}
}
6. 代理结果





















 585
585

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








