MyBatis
MyBatis入门
MyBatis 框架介绍
//框架是一款半成品,我们可以给予这个半成品软件继续开发,来完成我们个新华的需求
ORM(Object Relational Mapping):对象关系映射
指的是持久化数据和实体对象的映射模式,为了解决面向对象与关系型数据库存在的互不匹配的现象的技术。
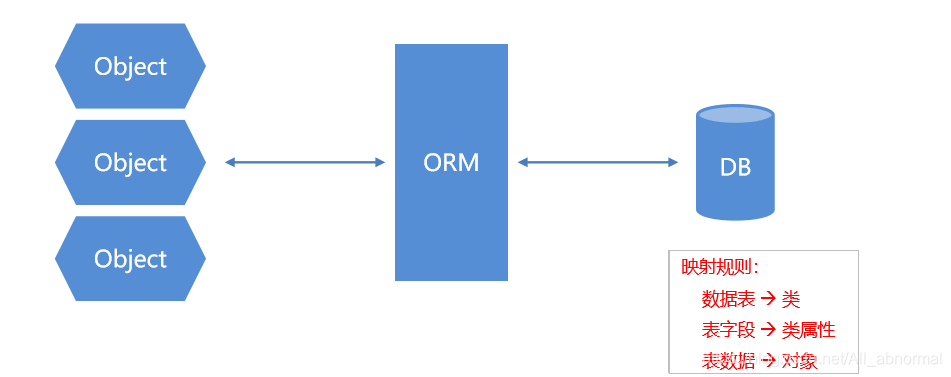
MyBatis 介绍
MyBatis 入门程序:查询数据库中的所有学生表中的数据
public class JDBCDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//① 导入jar包
// ② 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// ③ 获取数据库连接
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://192.168.23.129:3306/db14", "root", "root");
// ④ 获取执行者对象
Statement stat = con.createStatement();
// ⑤ 执行sql语句并返回结果
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student";
ResultSet re = stat.executeQuery(sql);
// ⑥ 处理结果1
while (re.next()) {
System.out.println(re.getInt("sid")
+ "\t" + re.getString("NAME")
+ "\t" + re.getString("age")
+ "\t" + re.getString("birthday"));
}
// ⑦ 释放资源
re.close();
stat.close();
con.close();
}
}
小结:
MyBatis 是一个优秀的基于 Java 的持久层框架,它内部封装了 JDBC,使开发者只需要关注 SQL 语句本身, 而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建执行者等复杂的操作。
MyBatis 通过 xml 或注解的方式将要执行的各种Statement 配置起来,并通过Java 对象和 Statement 中 SQL 的动态参数进行映射生成最终要执行的SQL 语句。
最后 MyBatis 框架执行完SQL 并将结果映射为 Java 对象并返回。采用ORM 思想解决了实体和数据库映射 的问题,对 JDBC 进行了封装,屏蔽了JDBC API 底层访问细节,使我们不用与JDBC API 打交道,就可以 完成对数据库的持久化操作。
MyBatis 相关API
public void selectAll() throws IOException {
//1 加载核心配置文件
//Resources加载配置文件为inputStream的工具类:加载资源的工具类
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2 获取SqlSession工厂对象------获取SqlSessionFactory 工厂对象的功能类
SqlSessionFactory sqlsessionfactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3 通过SqlSession工厂对象过去SqlSession对象-----获取SqlSession 构建者对象的工厂接口
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlsessionfactory.openSession();
//4 执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接受接过
List<Student> list = sqlSession.selectList("StudentMapper.selectAll");
//5 处理结果
for (Student student : list) {
System.out.println(student);
}
//6 释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
Resources: 加载资源的工具列,通过类加载器返回指定资源的字节输入流
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder: 获取SqlSessionFactory 工厂对象的功能类, 通过指定资源字节输入流获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory: 获取SqlSession 构建者对象的工厂接口, 获取SqlSession构建者对象,并开启手动提交事务,如果参数为true,则开启 自动提交事务
SqlSession:构建者对象接口。用于执行SQL、管理事务、接口代理,方法**如图所示:
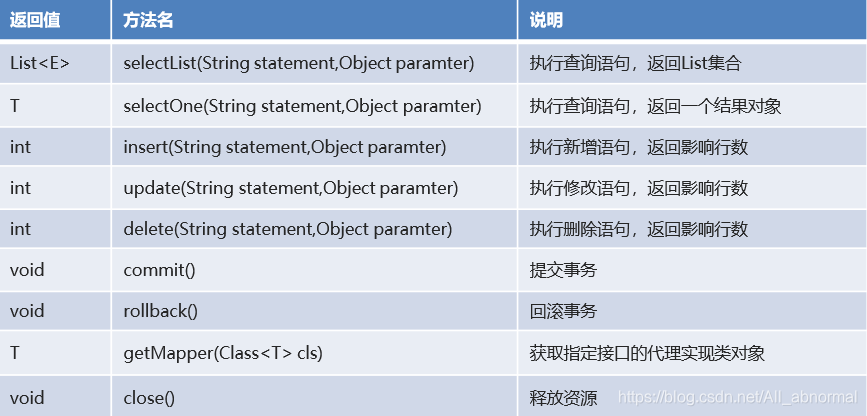 ## 映射配置文件介绍
## 映射配置文件介绍
<mapper namespace="itheima001_1.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!--
select:查询功能的标签
id属性:唯一标识
resultType属性:指定结果映射对象类型
parameterType属性:指定参数映射对象类型
-->
<!--查询所有-->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="student">
SELECT * FROM student
</select>
<!--查询一个 resultType:返回值 parameterType:参数-->
<select id="selectById" resultType="student" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
SELECT * FROM student WHERE sid = #{sid}
</select>
<!--添加一个-->
<insert id="insert" parameterType="student">
</insert>
<!--修改一个-->
<update id="update" parameterType="student">
UPDATE student SET name = #{name},age = #{age} WHERE sid =#{sid}
</update>
<!--删除一个-->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="student">
DELETE FROM student WHERE sid = #{sid}
</delete>
</mapper>
核心配置文件介
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!--MyBatis的DTD约束-->
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration 核心根标签 -->
<configuration>
<!--引入数据库连接的配置文件-->
<properties resource="JDK.properties"></properties>
<!--配置LOG4-->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/>
</settings>
<!--environments配置数据库环境,环境可以有多个。default属性指定使用的是哪个-->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--environment配置数据库环境 id属性唯一标识-->
<environment id="mysql">
<!-- transactionManager事务管理。 type属性,采用JDBC默认的事务-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- dataSource数据源信息 type属性 连接池-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- property获取数据库连接的配置信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- mappers引入映射配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<!-- mapper 引入指定的映射配置文件 resource属性指定映射配置文件的名称 -->
<mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
起别名
<!--起别名-->
<typeAliases><!--为全类名起别名的父标签。-->
<typeAlias type="itheima001_1.bean.Student" alias="student">
<!--type:指定全类名 alias:指定别名-->
</typeAlias><!--为全类名起别名的子标签。-->
</typeAliases>
Dao 层传统实现方式
分层思想:控制层(controller)→业务层(service)→持久层(dao)
调试流程如图所示:
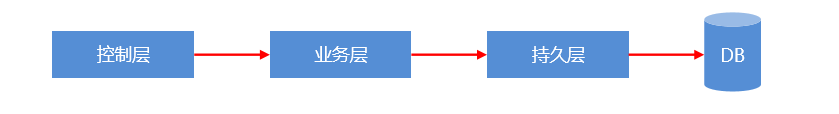 ### LOG4J
### LOG4J
在日常开发过程中,排查问题时难免需要输出MyBatis 真正执行的 SQL 语句、参数、结果等信息,我们就 可以借助 LOG4J 的功能来实现执行信息的输出。
使用步骤
- 导入 jar 包。
- 修改核心配置文件 添加如下代码。
<!--配置LOG4-->
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/>
</settings>
- 在 src 下编写 LOG4J 配置文件
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
接口代理方式-实现规则
-
删除 dao 层接口的实现类 只在写SQL语句。
-
修改映射配置文件填写成你dao文件的接口绝对路径。
<!-- mappers引入映射配置文件 -->
<mappers>
<package name="com.itheima.dao"/>
</mappers>
-
修改 service 层接口的实现类,采用接口代理方式实现功能。
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { StudentDao mapper; public StudentServiceImpl() { InputStream re = null; SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { re = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqls = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(re); sqlSession = sqls.openSession(true); mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public List<Student> findAll() { return mapper.findAll(); } @Override public Student findById(Integer sid) { return mapper.findById(sid); } @Override public Integer insert(Student student) { return null; } @Override public Integer update(Student student) { return mapper.update(student); } @Override public Integer delete(Integer sid) { return mapper.delete(sid); } }
实现规则
- 映射配置文件中的名称空间必须和Dao 层接口的全类名相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的id 属性必须和 Dao 层接口的方法名相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的parameterType 属性必须和 Dao 层接口方法的参数相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的resultType 属性必须和 Dao 层接口方法的返回值相同。
MyBatis 映射配置文件 - 动态 SQ
动态 SQL 介绍
1.MyBatis 映射配置文件中,前面我们的SQL 都是比较简单的,有些时候业务逻辑复杂时,我们的SQL 就是 动态变化的,此时在前面学习的SQL 就不能满足要求了
2.多条件查询
 ### < if>标签
### < if>标签
<select id="selectCondition" resultType="student" parameterType="student">
<include refid="select"/>
<where>
<if test="id != null">
id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null">
AND name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null">
AND age = #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
- < where>:条件标签。如果有动态条件,则使用该标签代替where 关键字。
- < if>:条件判断标签
< foreach>标签
< foreach>:循环遍历标签。适用于多个参数或者的关系
<!--id="selectByIds"bi表示为id为selectByIds
resultType="student"表示为引用数据类型
parameterType="list"表示为输出类型
-->
<select id="selectByIds" resultType="student" parameterType="list">
<include refid="select"/>
<where>
<foreach collection="list" open="id IN (" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
属性
- collection:参数容器类型,(list-集合,array-数组)。
- open:开始的 SQL 语句。
- close:结束的SQL 语句。
- item:参数变量名。 separator:分隔符
MyBatis 核心配置文件 – 分页插件
分页插件介绍
- 分页可以将很多条结果进行分页显示。
- 如果当前在第一页,则没有上一页。如果当前在最后一页,则没有下一页。
- 需要明确当前是第几页,这一页中显示多少条结果。
- 在企业级开发中,分页也是一种常见的技术。而目前使用的MyBatis 是不带分页功能的,如果想实现分页的 功能,需要我们手动编写LIMIT 语句。但是不同的数据库实现分页的SQL 语句也是不同的,所以手写分页 成本较高。这个时候就可以借助分页插件来帮助我们实现分页功能。
- PageHelper:第三方分页助手。将复杂的分页操作进行封装,从而让分页功能变得非常简单。
分页插件实现步骤
<!--1.导入 jar 包-->
<!--2.在核心配置文件中实现 集成分页助手插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
//3.通过分页助手来实现分页功能
// 第一页:显示3条数据
//PageHelper.startPage(1,3);
// 第二页:显示3条数据
//PageHelper.startPage(2,3);
// 第三页:显示3条数据
PageHelper.startPage(3,3);
分页插件相关参数
- PageInfo:封装分页相关参数的功能类。
- 核心方法如图所示:
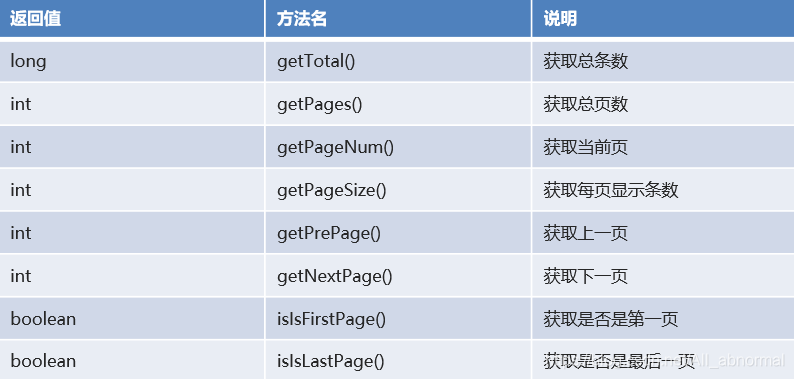 ## MyBatis 注解开发
## MyBatis 注解开发
常用注解介绍
- 我们除了可以使用映射配置文件来操作以外,还可以使用注解形式来操作。
- 常用注解
- @Select(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行查询操作注解
- @Insert(“新增的 SQL 语句”):执行新增操作注解
- @Update(“修改的 SQL 语句”):执行修改操作注解
- @Delete(“删除的SQL 语句”):执行删除操作注解
public interface StudentMapper {
//查询所有
@Select("SELECT * FROM student")
public abstract List<Student> selectAll();
//添加一个学生
@Insert("INSERT INTO student VALUES (#{id},#{name},#{age}")
public abstract Integer insert(Student student);
//修改操作
@Update("UPDATE student SET name=#{name},age=#{age} WHERE id=#{id}")
public abstract Integer update(Student stu);
//删除操作
@Delete("DELETE FROM student WHERE id=#{id}")
public abstract Integer delete(Integer id);
//---------------------------测试类------------------------------------------
public class Testmedo {
//查询所有
@Test
public void selectAll() throws IOException {
InputStream re = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory build = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(re);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession(true);
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectAll();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
sqlSession.close();
re.close();
}
//添加一个学生
@Test
public void insert() throws IOException {
InputStream re = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory build = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(re);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession(true);
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student(5, "迷魂汤", 80);
Integer insert = mapper.insert(student);
System.out.println(insert);
sqlSession.close();
re.close();
}
//修改操作
@Test
public void update() throws Exception {
//1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果
Student stu = new Student(4, "赵六", 36);
Integer result = mapper.update(stu);
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(result);
//7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
//删除操作
@Test
public void delete() throws Exception {
//1.加载核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");
//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
//4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//5.调用实现类对象中的方法,接收结果
Integer result = mapper.delete(4);
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(result);
//7.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
}
-
注解可以简化开发操作,省略映射配置文件的编写。
-
常用注解如下:
- @Select(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行查询操作注解
- @Insert(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行新增操作注解
- @Update(“查询的 SQL 语句”):执行修改操作注解
- @Delete(“查询的SQL 语句”):执行删除操作注解
-
配置映射关系
< mappers> < package name=“接口所在包”/>
</mappers





















 15万+
15万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








