核心容器
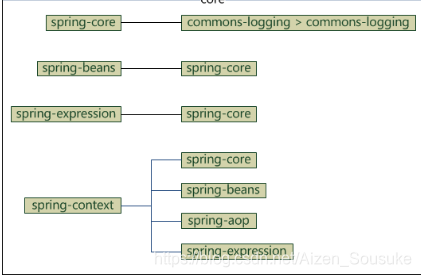
- spring-core:基本组成部分。包括IOC和DI
- spring-beans:提供BeanFactory
- spring-contex:在core和beans模块的基础上搭建。
- spring-expression:用于在运行时查询和操作对象图
数据访问/集成
- JDBC模块
- ORM模块:集成了流行的对象关系映射API,包括JPA、JDO和Hibernate等
- OXM模块:提供对OXM实现的支持,比如JAXB、Castor、XML Beans、JiBX、XStream等
- JMS模块:包含生产(produce)和消费(consume)消息的功能
- 事务模块:编程式事务需要自己写,声明式事务是通过注解或配置由spring自动处理
Web
- Web模块:比如多部分(multipart)文件上传功能、使用Servlet监听器初始化IoC容器等
- Web-MVC模块:提供了模型视图控制(MVC)和REST Web服务的实现
- Web-Socket模块:提供了客户端和服务器端之间通信的两种方式
- Web-Portlet模块:提供了用于Portlet环境的MVC实现,并反映了spring-webmvc模块的功能
其他重要的模块
- AOP
- Aspects
- Instrumentation
- Messaging
BeanFactory容器
主要功能是为依赖注入 提供支持
BeanFactory接口中最常用的是**XmlBeanFactory类 **,可以从配置文件中读取配置源数据
ApplicationContext容器
BeanFactory的子接口,是spring上下文
最常被使用的 ApplicationContext 接口实现:
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。需要提供给构造器 XML 文件的完整路径。
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 XML 文件中加载已被定义的 bean。需正确配置 CLASSPATH 环境变量
- WebXmlApplicationContext:会在一个 web 应用程序的范围内加载在 XML 文件中已被定义的 bean
Bean
bean对象由Spring IoC容器管理,是由用容器提供的配置元数据创建(如XML、注解、Java的配置):

Bean的作用域:定义bean时要声明作用域

Bean 生命周期
- 定义Bean时使用 init-method 或 destroy-method属性
-
init-method 属性指定一个方法,在实例化 bean 时,立即调用该方法。同样,destroy-method 指定一个方法,只有从容器中移除 bean 之后,才能调用该方法
Bean 后置处理器
- 允许在调用初始化方法前后对Bean进行二外的处理
- BeanPostProcessor接口定义回调方法
例子:创建类HelloWorld、InitHelloWorld 和 MainApp
HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message){
this.message = message;
}
public void getMessage(){
System.out.println("Your Message : " + message);
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Bean is going through init.");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Bean will destroy now.");
}
}
InitHelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
public class InitHelloWorld implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeforeInitialization : " + beanName);
return bean; // you can return any other object as well
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("AfterInitialization : " + beanName);
return bean; // you can return any other object as well
}
}
MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
//调用getMessage()方法前先调用的方法
//先调InitHelloWorld 的postProcessBeforeInitialization()--调用初始化方法 前 对 Bean 进行额外的处理
//再调用bean类的init方法
//再调InitHelloWorld 的postProcessAfterInitialization()--调用初始化方法 后 对 Bean 进行额外的处理
obj.getMessage();
//调用bean的destroy方法
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
init 和 destroy 方法需要的配置文件 Beans.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="message" value="Hello World!"/>
</bean>
<bean class="com.tutorialspoint.InitHelloWorld" />
</beans>
运行结果:
BeforeInitialization : helloWorld
Bean is going through init.
AfterInitialization : helloWorld
Your Message : Hello World!
Bean will destroy now.
Bean定义继承
Bean 定义的继承与 Java 类的继承无关,但是继承的概念是一样的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
//<bean>中abstract="true"可以在定义Bean模板时使用,指定抽象属性
<!--
<bean id="beanTeamplate" abstract="true">
<property name="message1" value="Hello World!"/>
<property name="message2" value="Hello Second World!"/>
<property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/>
</bean>
-->
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld">
<property name="message1" value="Hello World!"/>
<property name="message2" value="Hello Second World!"/>
</bean>
<bean id="helloIndia" class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloIndia" parent="helloWorld">
<property name="message1" value="Hello India!"/>
<property name="message3" value="Namaste India!"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message1;
private String message2;
public void setMessage1(String message){
this.message1 = message;
}
public void setMessage2(String message){
this.message2 = message;
}
public void getMessage1(){
System.out.println("World Message1 : " + message1);
}
public void getMessage2(){
System.out.println("World Message2 : " + message2);
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class HelloIndia {
private String message1;
private String message2;
private String message3;
public void setMessage1(String message){
this.message1 = message;
}
public void setMessage2(String message){
this.message2 = message;
}
public void setMessage3(String message){
this.message3 = message;
}
public void getMessage1(){
System.out.println("India Message1 : " + message1);
}
public void getMessage2(){
System.out.println("India Message2 : " + message2);
}
public void getMessage3(){
System.out.println("India Message3 : " + message3);
}
}
创建 “helloIndia” bean 的同时并没有传递 message2,但是会继承“helloWorld”的message2
依赖注入
- 基于构造函数依赖注入
- 在Beans.xml中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- TextEditor类的构造函数参数spellChecker是SpellChecker类型的 -->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor">
<constructor-arg ref="spellChecker"/>
</bean>
<!-- 在这里指明spellChecker的类型 -->
<bean id="spellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean>
//根据构造函数参数类型注入
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg type="int" value="2001"/>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="Zara"/>
</bean>
//根据构造函数参数位置注入
<bean id="exampleBean" class="examples.ExampleBean">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="2001"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="Zara"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 根据set方法注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="john-classic" class="com.example.Person">
//value直接注入
<property name="name" value="John Doe"/>
//ref传递引用
<property name="spouse" ref="jane"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jane" class="com.example.Person">
<property name="name" value="John Doe"/>
</bean>
<!-- 缩写
<bean id="john-classic" class="com.example.Person"
p:name="John Doe"
p:spouse-ref="jane"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jane" class="com.example.Person"
p:name="John Doe"/>
</bean>
-->
<!-- results in a setAddressList(java.util.List) call -->
<property name="addressList">
<list>
<value>INDIA</value>
<value>Pakistan</value>
<value>USA</value>
<value>USA</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- results in a setAddressSet(java.util.Set) call -->
<property name="addressSet">
<set>
<value>INDIA</value>
<value>Pakistan</value>
<value>USA</value>
<value>USA</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- results in a setAddressMap(java.util.Map) call -->
<property name="addressMap">
<map>
<entry key="1" value="INDIA"/>
<entry key="2" value="Pakistan"/>
<entry key="3" value="USA"/>
<entry key="4" value="USA"/>
</map>
</property>
</beans>
Bean 自动装配
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- Definition for textEditor bean -->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor"
autowire="byName">
//java类中有名字为spellChecker的属性
//自动去找spellChecker的<bean>找不到会抛出异常
<property name="name" value="Generic Text Editor" />
</bean>
<!-- Definition for spellChecker bean -->
<bean id="spellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean>
<!-- Definition for textEditor bean -->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor"
autowire="byType">
//类中有SpellChecker类型的属性
//自动去找SpellChecker的<bean>
<property name="name" value="Generic Text Editor" />
</bean>
<!-- Definition for spellChecker bean -->
<bean id="SpellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean>
</beans>
注解
启用注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- bean definitions go here -->
</beans>
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Required | 用于 bean 属性的 setter 方法。 |
| @Autowired | 可以应用到 bean 属性的 setter 方法,非 setter 方法,构造函数和属性。 |
| JSR-250 Annotations | 支持 JSR-250 的基础的注解,其中包括了 @Resource,@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解 |
| @Configuration | 表示这个类可以使用 Spring IoC 容器作为 bean 定义的来源 |
| @Bean | 返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册为在 Spring 应用程序上下文中的 bean |
事件处理
ApplicationContext,它负责管理 beans 的完整生命周期。当加载 beans 时,ApplicationContext 发布某些类型的事件。
例如,当上下文启动时,ContextStartedEvent 发布,当上下文停止时,ContextStoppedEvent 发布。
一个 bean 实现 ApplicationListener(例如实现接口 implements ApplicationListener <-ContextStartedEvent->),那么每次 ApplicationEvent 被发布到 ApplicationContext 上,那个 bean 会被通知。

为了监听上下文事件,一个 bean 应该实现只有一个方法 onApplicationEvent() 的 ApplicationListener 接口
AOP
| 项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Aspect | 切面,简单来说就是把一个类当做一个面,去监听里边的每个方法 |
| Join point | 连接点,就是spring允许通知(Advice)的地方。和方法有关的前后都是连接点 |
| Advice | 通知,想要的功能,比如事务、日志、安全等 |
| Pointcut | 切入点,假如一个类中有十几个方法就有十几个连接点,不想所有方法都是用通知,只想让其中几个使用,用切点来筛选连接点,选中想要操作的几个方法 |
| Introduction | 引入,向现有的类添加新方法属性,也就是把切面用到目标类中 |
| target | 被通知对象,也就是真正的业务逻辑,可以被一个或多个方面通知 |
| Weaving | 把方面连接到其它的应用程序类型或者对象上,并创建一个被通知的对象 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
<!-- 自动扫描包配置 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="要扫描的包">
<!-- bean definition & AOP specific configuration -->
<!-- 配置Bean -->
<bean id="arithmeticCalculator" class="com.hk.spring.aop.xml.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl"> </bean>
<!-- 配置切面的Bean -->
<bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.hk.spring.aop.xml.LoggingAspect"> </bean>
//配置aop
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.hk.spring.aop.xml.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int,int))" id="pointcut"/>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="loggingAspect" order="2" >
<!-- 通知 -->
<aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pointcut" throwing="ex"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pointcut" returning="result" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
事务管理
| 事务传播行为类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。这是最常见的选择。 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NESTED | 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。 |
隔离级别
| 事务的隔离级别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| read uncommited | 是最低的事务隔离级别,它允许另外一个事务可以看到这个事务未提交的数据。 |
| read commited | 保证一个事物提交后才能被另外一个事务读取。另外一个事务不能读取该事物未提交的数据。 |
| repeatable read | 这种事务隔离级别可以防止脏读,不可重复读。但是可能会出现幻象读。它除了保证一个事务不能被另外一个事务读取未提交的数据之外还避免了以下情况产生(不可重复读)。 |
| serializable | 这是花费最高代价但最可靠的事务隔离级别。事务被处理为顺序执行。除了防止脏读,不可重复读之外,还避免了幻象 |
基于 TransactionProxyFactoryBean的声明式事务管理
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="myTracnsactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务代理工厂 -->
<!-- 生成事务代理对象 -->
<bean id="serviceProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="myTracnsactionManager"></property>
<property name="transactionAttributes">
<props>
<!-- 主要 key 是方法
ISOLATION_DEFAULT 事务的隔离级别
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 传播行为
-->
<prop key="add*">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>
<!-- -Exception 表示发生指定异常回滚,+Exception 表示发生指定异常提交 -->
<prop key="buyStock">ISOLATION_DEFAULT,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,-Exception</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
基于 @Transactional 的声明式事务管理
指定方法增加注解
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,rollbackFor=异常类.class)
spring.xml
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="myTracnsactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 启用事务注解 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="myTracnsactionManager"/>
基于Aspectj AOP配置事务
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="myTracnsactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="myTracnsactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 为连接点指定事务属性 -->
<tx:method name="add*" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="buyStock" isolation="DEFAULT" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="切点抛异常类型"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点配置 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))" id="point"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:config>






















 174万+
174万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








