查看本机ip命令: ipconfig
端口号中0~1024已被占用,常见的网络程序端口号:
tomcat:8080
mysql:3306
oracle:1521
sqlserver:1433
InetAddress类操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException { //获取本机InetAddress对象 InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); System.out.println(localHost);//输出本机主机名和ip: //DESKTOP-M2GP14P/192.168.199.185 //根据主机名获取本机InetAddress对象 InetAddress byName = InetAddress.getByName("DESKTOP-M2GP14P"); System.out.println(byName);//DESKTOP-M2GP14P/192.168.199.185 //根据域名返回InetAddress对象 InetAddress bd = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); System.out.println(bd);//www.baidu.com/110.242.68.4 //通过InetAddress对象获取对应的地址 String hostAddress = localHost.getHostAddress(); System.out.println(hostAddress); //获取主机名域名 String hostName = bd.getHostName(); System.out.println(hostName); }
案例:Java的socket是一个全双工套接字,任何的输入流或输出流的close()都会造成Socket关闭。
//客户端code public class Socket01tcpClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.连接服务端(ip,port)案例中连接的是本机,所以是getLocalHost Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999); System.out.println("客户端"); // 连接上后,生成socket,通过socket.getOutputStream()获取和 // socket对象相关联的输出流对象 OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); // 通过输出流将数据写入数据通道 outputStream.write("hello,server".getBytes()); // 设置输出结束标记 socket.shutdownOutput(); // 获取和socket相关的InputStream,读取数据(字节),并显示 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int read; while((read = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0 , read) + read); } //关闭流对象和socket,socket连接数量是有限的,不关闭会占用连接数 outputStream.close(); inputStream.close(); socket.close(); System.out.println("客户端退出。。。"); } }//服务器端code public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 思路 // 1.在本机的9999端口号监听,等待连接 // 细节:要求本机中无其他程序监听该9999端口 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999); System.out.println("服务器在9999端口监听,等待连接。。。"); // 2.当没有客户端连接,程序阻塞,等待连接 // 如果有客户端连接,则会返回socket对象,程序继续 //如果有多个客户端连接,则该serverSocket可以通过accept方法返回多个socket对象。 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println(socket.getClass()); // 3.通过socket.getInputStream()读取客户端写入到数据通道的数据,显示 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int read; while((read = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read) + read); } OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write("hello, client".getBytes()); // 设置输出结束标记 socket.shutdownOutput(); //关闭流和socket outputStream.close(); inputStream.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("服务器退出"); }
//服务器端 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //监听本机9998端口 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9998); System.out.println("监听9998。。。"); //等待连接 Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); String content = null; InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); content = br.readLine(); System.out.println(content); //发送端write可以使用bw.newline()作输入结束,但是必须在接收端使用br.readLine()接收 //如果使用循环读取,会出现客户端的newline结束失效的情况 //建议在发送端使用socket.shutdownOutput()作结束标志 // while((content = br.readLine()) != null) { // System.out.println(content); // } OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream(); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os)); bw.write("hello, client"); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); bw.close(); br.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("服务器退出"); }//客户端code public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9998); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream)); bw.write("hello ,server"); bw.newLine();//另一种输出结束标识,如果使用该方式,在服务器输入的时候要使用readLine方法读入 bw.flush();//使用字符流需要手动flush,否则数据不会写入到数据通道 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); String content = null; while((content = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(content.getClass()); System.out.println(content); } br.close(); bw.close(); socket.close(); System.out.println("退出客户端"); }
StreamUtils.java 文件包含两个函数,将流中的数据转换成字节数组,将流中的数据转换成字符串
public class StreanUtils { //将读入的字节流数据转成一整个字节数组 public static byte[] Streamtoarray(InputStream is ) throws IOException { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = is.read(bytes)) != -1) { bos.write(bytes, 0, len); } byte[] bytes1 = bos.toByteArray(); bos.close(); return bytes1; } // 将读取的字节流的数据转成字符串类型 public static String Streamtostring(InputStream is ) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is)); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); String line; while((line = br.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(line + "\rs\n"); } return sb.toString(); } }文件上传:
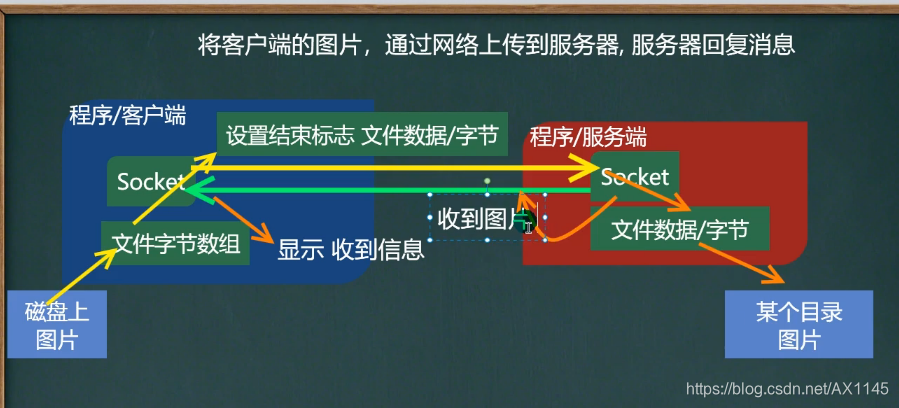
//TcpFileUploadClient public class TCPFileUploadClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888); //创建读取磁盘文件的输入流 String filepath = "e:/mg.png"; BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath)); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); byte[] bytes = StreanUtils.Streamtoarray(bis); bos.write(bytes); socket.shutdownOutput(); //接收服务器的回复 InputStream is = socket.getInputStream(); String s = StreanUtils.Streamtostring(is); System.out.println(s); bos.close(); bis.close(); socket.close(); System.out.println("推出客户端"); } }//TcpFileuploadServer package com.edu.upload; import java.io.*; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * @author mtl121 * @version 1.0 */ public class TCPFileUploadServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888); System.out.println("服务器在8888端口监听。。。"); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); byte[] bytes = StreanUtils.Streamtoarray(bis); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src/mg.png")); bos.write(bytes); bos.close(); //向客户端回复“收到图片” BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())); writer.write("收到图片 "); writer.flush();//讲内容刷新到数据通道 socket.shutdownOutput();//输出结束标识 writer.close(); bos.close(); bis.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("推出服务器"); } }
TCP网络通信编程
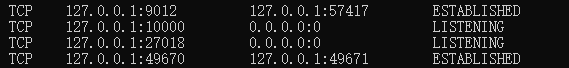
netstat 指令
四列表示的含义:
第一列是协议,第二列表示本地地址:0.0.0.0:或者127.0.0.1:表示本机地址
第三列表示外部链接地址,如果有外部的连接,则会显示出外部连接的地址,第四列表示状态,一个是LISTENING,表示处于监听状态,另一个是ESTABLISHED,表示正处于外部连接状态,有一个外部程序连接到了该端口
如果有一个外部程序(客户端)连接到该端口,就会显示一条连接信息
netstat -anb指令,查看是哪个程序连接到该端口,cmd需要管理员身份运行
假如在本地模拟运行客户端和服务器端,服务器端以8888端口监听,则通过netstat查看:60285就是客户端的接口
加入是两台主机分别担任客户端和服务器端,则在服务器端只会看到第一条,客户端只会看到第二条连接信息





 本文介绍了Java中InetAddress类的使用,包括获取本机IP和域名信息。接着讲解了Socket和ServerSocket在网络通信中的应用,展示了客户端和服务器端的代码示例,说明了全双工套接字的特点。此外,还讨论了文件上传的TCP实现,包括TCPFileUploadClient和TCPFileUploadServer的代码。最后提到了netstat命令在查看网络连接状态中的作用。
本文介绍了Java中InetAddress类的使用,包括获取本机IP和域名信息。接着讲解了Socket和ServerSocket在网络通信中的应用,展示了客户端和服务器端的代码示例,说明了全双工套接字的特点。此外,还讨论了文件上传的TCP实现,包括TCPFileUploadClient和TCPFileUploadServer的代码。最后提到了netstat命令在查看网络连接状态中的作用。























 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










