前言
📅大四是整个大学期间最忙碌的时光,一边要忙着备考或实习为毕业后面临的就业升学做准备,一边要为毕业设计耗费大量精力。近几年各个学校要求的毕设项目越来越难,有不少课题是研究生级别难度的,对本科同学来说是充满挑战。为帮助大家顺利通过和节省时间与精力投入到更重要的就业和考试中去,学长分享优质的选题经验和毕设项目与技术思路。
🚀对毕设有任何疑问都可以问学长哦!
大家好,这里是海浪学长计算机毕设专题,本次分享的课题是
🎯基于深度学习的人脸五官分割算法
项目背景
人脸五官分割在计算机视觉和人机交互领域具有重要意义。准确地分割人脸图像中的五官(眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴等)是许多应用的基础,包括人脸识别、表情分析、虚拟化妆等。然而,由于人脸图像的复杂性和多样性,传统的分割方法往往难以达到高精度和鲁棒性。随着深度学习技术的快速发展,基于深度学习的人脸五官分割算法成为研究热点。通过深度学习模型的训练和优化,可以实现更准确、更稳定的人脸五官分割,为人机交互和人脸相关应用提供重要支持。
设计思路
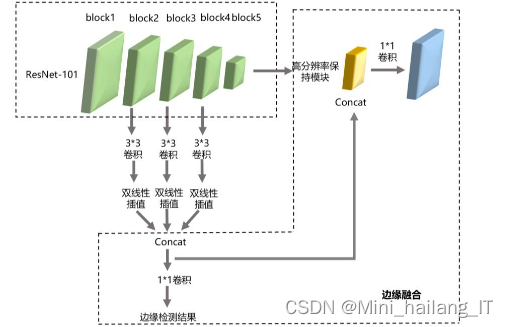
基于边缘融合的人脸分割算法通过三个关键模块实现高精度分割:1)受Sobel算子启发的边缘融合模块,增强边缘预测并提高准确率;通过应用Sobel算子或类似的边缘检测技术,该模块能够精确地标识出人脸的轮廓和各个特征部位(如眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴等)的边缘。2)上下文信息融合模块,结合了ResNet-101和PSPNet(金字塔场景解析网络)来处理和解决部件方向问题。ResNet-101是一种深度卷积神经网络,用于提取人脸图像的上下文信息;PSPNet则用于解析图像中的场景信息,进一步增强上下文感知能力。通过结合这两个网络,该模块能够更准确地识别和处理人脸各个部位的方向信息,从而提高分割精度。;3)高分辨率特征图保持模块,保护浅层特征并改善边缘分割效果,保持高分辨率特征图,同时防止在训练过程中出现分辨率下降的问题。。这些模块的有机组合形成了最终的网络结构,实现了人脸的高质量分割。
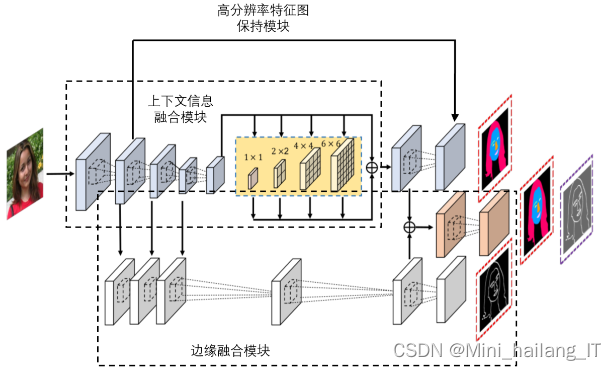
边缘融合部分的网络结构通过结合边缘检测、上下文融合和高分辨率特征保持模块,增强了语义特征中的边缘信息。边缘检测部分融合多层次的特征,形成富含边缘信息的特征图;高分辨率特征保持模块则提供包含语义信息的特征。为加强边缘效果,将两者通过双线性插值和1*1卷积进行融合,得到最终的分割结果。网络的训练则依赖于与真实分割标签比较计算的损失值。
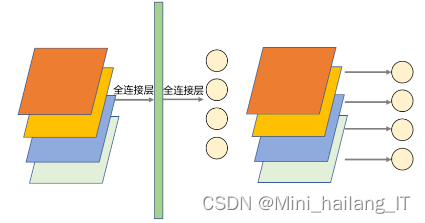
全局平均池化在卷积神经网络中的作用不可忽视。它不仅在位置上与全连接层相呼应,而且在功能上提供了一种更有效的方式来处理上下文信息。相比于全连接层全局平均池化通过提供一种简单而有效的方式来处理上下文信息,显著增强了卷积神经网络的能力。
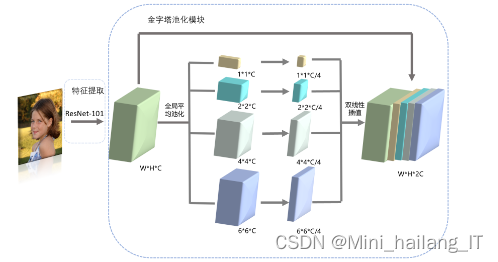
在复杂的分割任务中,PSPNet引入了金字塔池化模块以弥补全局平均池化在捕捉多尺度上下文信息方面的不足。该模块通过并行处理不同尺寸的全局平均池化操作,并将结果与原始特征融合,有效地区分了图像中的相似部件,如左右眼睛或眉毛。这种方法既保留了空间信息,又增强了特征的语义表示,从而提高了分割的准确性。
class PyramidPoolingModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, pool_type='avg'):
super(PyramidPoolingModule, self).__init__()
self.pool_type = pool_type
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(4),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
)
self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(8),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(4*out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
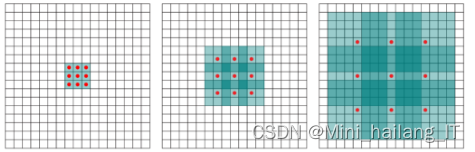
二维数据的空洞卷积通过在卷积核中引入“空洞”来增加感受野的尺寸,同时保持特征图的高分辨率。图3.8展示了不同空洞率(r)的卷积核结构,而图3.9则对比了卷积和空洞卷积在网络结构中的不同应用方式。传统的特征提取流程通常包括下采样、卷积、特征融合和上采样。而使用空洞卷积的方法则直接通过空洞卷积操作来扩大感受野并减少特征图尺寸的损失,无需降采样步骤。这种方法的优点在于不增加卷积核参数数量的情况下增加感受野尺寸,保持高分辨率特征图。
数据集
由于网络上缺乏现有的合适数据集,我决定自己进行数据集的制作。我收集了大量的人脸图像,并使用图像标注工具对每个图像进行五官的标记。通过手动标注,我能够准确地标记出人脸图像中的眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴等五官位置和边界。在数据收集过程中,我特别关注不同的人种、不同的表情和姿态,以保证数据集的多样性和适用性。这个自制的数据集将为基于深度学习的人脸五官分割算法的研究提供更准确、可靠的数据支持,并为该领域的发展做出积极贡献。

为了扩充数据集的规模和多样性,我采用了数据扩充的技术。通过对已有的人脸图像进行平移、旋转、缩放和仿射变换等操作,我生成了更多样化的训练样本。此外,我还利用图像增强方法对人脸图像进行处理,如亮度调整、对比度增强和噪声添加等,以增加数据集的多样性和泛化能力。通过数据扩充,我能够更全面地评估和改进基于深度学习的人脸五官分割算法的性能,并提高其在不同场景和条件下的鲁棒性和准确性。数据扩充为研究者提供了更丰富的数据资源,帮助他们更好地理解算法的行为和提出改进方法,从而推动人脸五官分割算法的发展。
for transform in transforms:
image = transform(image)
模型训练
人脸分割标注模块基于给定的106点关键点信息,生成人脸分割数据集。该模块由三部分组成:1)三分类分割,解决关键点中不包含头发和皮肤分界线区域的问题,对皮肤、头发和背景进行分类;2)关键点辅助生成五官分割部分,优化五官轮廓,确保正确拟合人脸部件形状;3)融合部分,将上述两个部分的结果进行整合,得到最终的人脸分割结果。

针对人脸分割中皮肤、头发和背景分割的重要性,但由于106点关键点缺乏前额和头发定义的问题,我们采用了三分类分割策略,并利用CHIP人体分割数据集进行训练。通过ROI区域提取优化数据,筛选出高质量人脸图片,最终使用PSPNet网络训练出效果良好的三分类人脸分割模型。
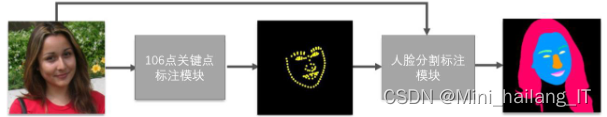
针对人脸五官分割,我们采用了基于106点关键点的方法。由于关键点分布相对稠密,我们采用多项式拟合方式对眉毛、眼睛和鼻子区域进行优化,生成更自然的分割结果。对于鼻子区域,我们将其分为6个部分进行处理,并采用二项式和多项式拟合方式来拟合鼻子的不同部分。嘴部区域分为上嘴唇、下嘴唇和嘴内区域,通过插值和二项式拟合方法生成闭合区域。最终,我们得到了效果自然的五官分割结果。
相关代码示例:
model = DeepLabV3Plus(num_classes=2, backbone='resnet')
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('pretrained_model.pth'))
model.eval()
image = Image.open('face_image.jpg')
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((520, 520)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
image = preprocess(image)
image = image.unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(image)
output = nn.functional.softmax(output, dim=1) # 对输出进行softmax归一化处理
output = output.squeeze(0) # 去除批处理维度和通道维度
output_predictions = torch.argmax(output, dim=0) # 获取每个像素的类别预测结果





 本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的面部五官分割算法,涉及边缘融合、上下文信息融合和高分辨率特征保持模块。作者分享了从项目背景、设计思路到数据集制作和模型训练的详细过程,以及关键代码示例,旨在帮助大学生高效完成毕业设计。
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的面部五官分割算法,涉及边缘融合、上下文信息融合和高分辨率特征保持模块。作者分享了从项目背景、设计思路到数据集制作和模型训练的详细过程,以及关键代码示例,旨在帮助大学生高效完成毕业设计。
















 218
218

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








