什么是BeanDefinition?
BeanDefinition是一个接口,描述bean实例,它具有属性值、构造函数参数值和具体实现提供的进一步信息,简单来说就是我们定义了一个bean之后,Spring通过这个BeanDefinition来存储被解析后的相关信息。
在一个bean中可能会有多个属性,BeanDefinition使用LinkHashMap来存储多条bean的属性,
在BeanDefinition的实现类RootBeanDefinition:
RootBeanDefinition 存储了关于Bean的所有必要信息,包括类名、构造函数参数、属性值、自动装配的模式等。
当存在多个Bean定义时(例如,来自不同的XML配置文件或注解),RootBeanDefinition 包含了合并这些定义的逻辑,以确保最终的Bean定义是一致的。
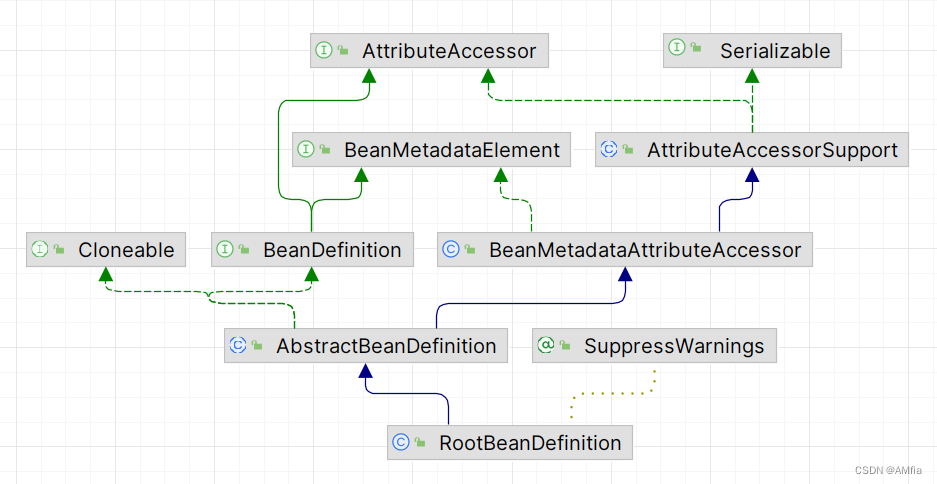
RootBeanDefinition最终实现了AttributeAccessor这个接口,它允许对属性的读写操作,通常用于Spring的Bean元数据。
public interface AttributeAccessor {
void setAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value);
@Nullable
Object getAttribute(String name);
default <T> T computeAttribute(String name, Function<String, T> computeFunction) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(computeFunction, "Compute function must not be null");
Object value = this.getAttribute(name);
if (value == null) {
value = computeFunction.apply(name);
Assert.state(value != null, () -> {
return String.format("Compute function must not return null for attribute named '%s'", name);
});
this.setAttribute(name, value);
}
return value;
}
@Nullable
Object removeAttribute(String name);
boolean hasAttribute(String name);
String[] attributeNames();
}
AttributeAccessorSupport实现了AttributeAccessor,可以看到使用了LinkedHashMap来接收bean中的数据。
public abstract class AttributeAccessorSupport implements AttributeAccessor, Serializable {
private final Map<String, Object> attributes = new LinkedHashMap();
public AttributeAccessorSupport() {
}
public void setAttribute(String name, @Nullable Object value) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
if (value != null) {
this.attributes.put(name, value);
} else {
this.removeAttribute(name);
}
}
@Nullable
public Object getAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.get(name);
}
public <T> T computeAttribute(String name, Function<String, T> computeFunction) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(computeFunction, "Compute function must not be null");
Object value = this.attributes.computeIfAbsent(name, computeFunction);
Assert.state(value != null, () -> {
return String.format("Compute function must not return null for attribute named '%s'", name);
});
return value;
}
@Nullable
public Object removeAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.remove(name);
}
public boolean hasAttribute(String name) {
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
return this.attributes.containsKey(name);
}
public String[] attributeNames() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.attributes.keySet());
}
protected void copyAttributesFrom(AttributeAccessor source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
String[] attributeNames = source.attributeNames();
String[] var3 = attributeNames;
int var4 = attributeNames.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String attributeName = var3[var5];
this.setAttribute(attributeName, source.getAttribute(attributeName));
}
}
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return this == other || other instanceof AttributeAccessorSupport && this.attributes.equals(((AttributeAccessorSupport)other).attributes);
}
public int hashCode() {
return this.attributes.hashCode();
}
}
并且在Spring中bean不会只有一个,BeanDefinition也不会只有一个,Spring需要管理这么多BeanDefinition,这个管理者就是BeanDefinitionRegistry,顾名思义注册接口,接口主要定义了一些对BeanDefinition管理的方法。
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry extends AliasRegistry {
//用这个注册中心注册一个新的bean定义。
void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException;
//删除给定名称的bean定义。
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//返回给定bean名称的bean定义。
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//检查此注册表是否包含具有给定名称的bean定义。
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
//返回在这个注册表中定义的所有bean的名称。
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
//返回注册表中定义的bean的数量。
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
//确定给定的bean名称是否已经在此注册中心中使用。
boolean isBeanNameInUse(String beanName);
}
实现类SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry,通过一个ConcurrentHashMap来存储所BeanDefinition。
public class SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
//bean定义对象的映射,以bean名称为键
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
后续IOC根据BeanDefinition中定义的bean来创建与销毁。




















 1351
1351










