A. Food for Animals

样例输入:
7
1 1 4 2 3
0 0 0 0 0
5 5 0 4 6
1 1 1 1 1
50000000 50000000 100000000 100000000 100000000
0 0 0 100000000 100000000
1 3 2 2 5
样例输出:
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
题意:给你a袋狗粮,b袋猫粮,c袋万能粮(万能粮可以作为猫粮也可以作为狗粮),x条狗,y只猫,问能否满足每个动物都有一袋适合自己的粮食。
分析:首先先判断所有的粮食数够不够没人一袋,再看一下把万能粮全部变为猫粮够不够猫分以及把万能粮全部变为狗粮够不够狗分,如果都满足的话就可以给每只动物分一袋,否则就不行。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int a,b,c,x,y;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&x,&y);
bool flag=true;
if(a+b+c<x+y) flag=false;
if(a+c<x) flag=false;
if(b+c<y) flag=false;
if(flag) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
} B. Make It Increasing

样例输入:
7
3
3 6 5
4
5 3 2 1
5
1 2 3 4 5
1
1000000000
4
2 8 7 5
5
8 26 5 21 10
2
5 14
样例输出:
2
-1
0
0
4
11
0
题意:给定一个长度为n的数组,每次操作可以把一个位置上的数变为原来的数的一半下取整,问至少需要多少次可以把原数组变为严格递增数组。
分析:首先我们可以发现每一个数只能减少不能增加,所以肯定最后一个位置上的数的值不能发生变化,我们直接从倒数第二个数开始操作,直至倒数第二个数小于倒数第一个数为止,依次往前操作,其他位置也是同理,如果某一时刻出现了某数变为0还不能满足题意就直接输出-1即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int ans=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
while(a[i]>=a[i+1])
{
if(!a[i])
{
ans=-1;
break;
}
a[i]/=2,ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}C. Detective Task

样例输入:
8
0
1
1110000
?????
1?1??0?0
0?0???
??11
??0??
样例输出:
1
1
2
5
4
1
1
3
题意:有个人,他有一幅画,把这幅画放在一个房间里,让他的朋友一个一个进房间来看这幅画。所有人看完后画不见了。他问其朋友是否在房间中看到这幅画,如果看见就输出1,没有看见就输出0,不确定就输出?只有小偷会骗人。此时你需要判断小偷可能是哪几个人,输出这个人数。
分析:首先我们知道,0的后面是不可能有1的,因为最多只有一个小偷,所以0只可能位于1的后面,那么小偷一定位于最后一个1和第一个0之间,这个很简单,因为如果最后一个1不是,那么他说的是真话,那么画肯定没有在他之前被偷,而且0如果不是小偷,那么在他之前画就被偷了,小偷也不可能在其之后,所以只能是位于两者之间,而且这两个人都有可能是小偷。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
char s[N];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
scanf("%s",s+1);
int n=strlen(s+1);
int mx=1,mn=n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(s[i]=='1') mx=i;
else if(s[i]=='0'&&mn==n) mn=i;
printf("%d\n",mn-mx+1);
}
return 0;
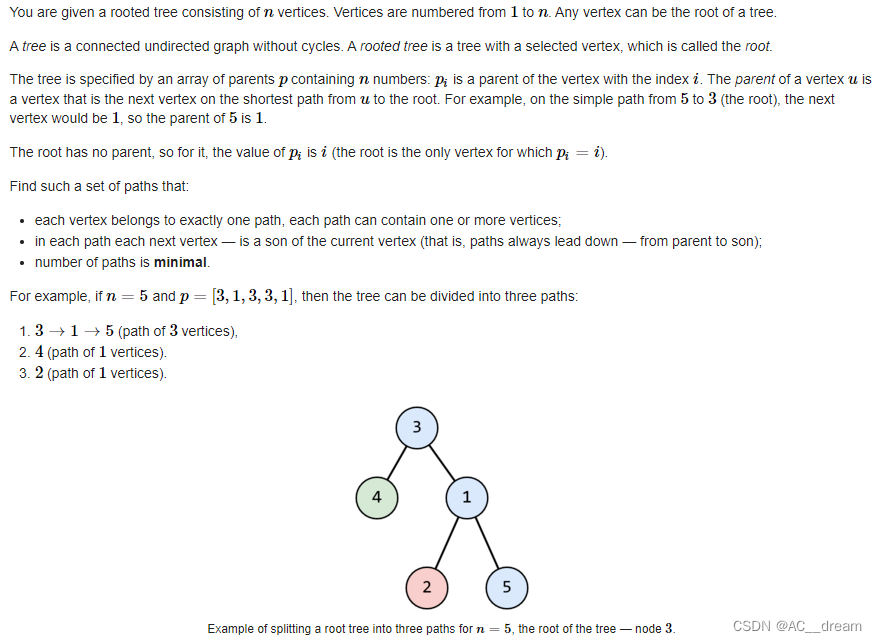
}D. Vertical Paths
样例输入:
6
5
3 1 3 3 1
4
1 1 4 1
7
1 1 2 3 4 5 6
1
1
6
4 4 4 4 1 2
4
2 2 2 2
样例输出:
3
3
3 1 5
1
2
1
4
2
2
1 2
2
4 3
1
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1
1
1
3
3
4 1 5
2
2 6
1
3
3
2
2 1
1
3
1
4
题意:给定一棵有根树,然我们求出最小的路径数,使得每个点至少在一个路径中,而且路径不能包含一个结点的两个或多个儿子结点。
分析:显然一个叶子结点就对应一条路径,我们直接从叶子结点向上找直至有一个点已经被计算过,然后直接把这个路径输出即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
int fu[N],cnt[N],vis[N];
int st[N],tt;
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n,root;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cnt[i]=0,vis[i]=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&fu[i]);
cnt[fu[i]]++;
if(i==fu[i]) root=i;
}
if(n==1)
{
puts("1");
puts("1");
puts("1");
continue;
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!cnt[i]) ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!cnt[i])
{
int j=i;
while(!vis[j])
{
st[++tt]=j;
vis[j]=true;
j=fu[j];
}
printf("%d\n",tt);
while(tt) printf("%d ",st[tt--]);
puts("");
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}E. Replace With the Previous, Minimize

样例输入:
4
3 2
cba
4 5
fgde
7 5
gndcafb
4 19
ekyv
样例输出:
aaa
agaa
bnbbabb
aapp
题意:给定一个由小写字母组成的字符串,然后我们可以进行k次操作,每次操作可以选定一个字符x,把字符串中所有的x都变为比x字典序小1的字符(这里默认a变为z),问k次操作后所能得到的字典序最小的字符串是什么?
分析:这道题直接贪心来想即可。我们记录一个vis[i],如果vis[i~j]=true代表ascall码位于i~j的字符可以随意变换。我们从前往后遍历,如果当前字母的ascall码不在可变范围内而且我们还可以进行操作,那么我们就扩大可变范围,如果在可变范围内,我们直接令其等于可变范围内最小的字符即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+10;
char s[N];
int a[N];
bool vis[30];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
scanf("%s",s+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=s[i]-'a'+1;
memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int t=a[i];
while(t!=1&&m)
{
while(t>1&&vis[t]) t--;
while(t>1&&(!vis[t])&&m)
m--,vis[t--]=true;
}
while(t>1&&vis[t]) t--;
a[i]=t;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%c",a[i]-1+'a');
puts("");
}
return 0;
}F. Vlad and Unfinished Business

样例输入:
3
3 1
1 3
2
1 3
1 2
6 4
3 5
1 6 2 1
1 3
3 4
3 5
5 6
5 2
6 2
3 2
5 3
1 3
3 4
3 5
5 6
5 2
样例输出:
3
7
2
题意:给定一棵树,每个结点有一个编号,我们需要从x走到y,每个结点可以经过多次,但是走到y之前我们必须先到达k个结点,问最短路径长度。
分析:通过简单模拟我们可以发现,最短路径就是x到y的距离加上k个结点中每个结点到x与y路径上的点的距离的最小值的2倍(重合路径需要去掉)。那么我们就可以用一个vis[i]=true表示从i点到达x与y路径上的贡献已经被计算,然后我们以x为根搜索一次求出所有结点的父节点,然后我们直接求出来每个结点到达x与y路径中的结点的距离最小值即可,方法是直接暴力往上跳,遇到一个vis[]=true就终止,说明往上的贡献已经被计算,直接计入当前点扩展的贡献即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
int h[N],ne[N],e[N],idx;
int d[N],t[N],vis[N],fu[N];
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[idx]=y;
ne[idx]=h[x];
h[x]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int x,int fa)
{
fu[x]=fa;
d[x]=d[fa]+1;
for(int i=h[x];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(j==fa) continue;
dfs(j,x);
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
int n,k;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
d[i]=0;
h[i]=-1;
vis[i]=false;
}
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
scanf("%d",&t[i]);
idx=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
add(u,v);add(v,u);
}
dfs(x,x);
vis[x]=true;
long long ans=0;
while(y!=x)
{
vis[y]=true;
y=fu[y];
ans++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
if(vis[t[i]]) continue;
int cnt=0;
while(!vis[t[i]])
{
vis[t[i]]=true;
cnt++;
t[i]=fu[t[i]];
}
ans+=2*cnt;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}




 本文精选了Codeforces平台上的A至F六道题目并提供详细解答,涵盖动物喂养问题、数组转换、侦探任务等典型算法挑战。每道题通过样例输入输出展示了问题背景与解决思路。
本文精选了Codeforces平台上的A至F六道题目并提供详细解答,涵盖动物喂养问题、数组转换、侦探任务等典型算法挑战。每道题通过样例输入输出展示了问题背景与解决思路。
















 348
348

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








