概述
Vue.js 中的 v-for 指令用于基于源数据多次渲染一个元素或组件,是 Vue 中最常用的指令之一。它提供了强大的列表渲染功能,支持数组、对象和范围值的遍历。
基本用法
数组遍历
const items = ref([{ message: 'Foo' }, { message: 'Bar' }])
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ item.message }}
</li>
带索引的遍历
const parentMessage = ref('Parent')
const items = ref([{ message: 'Foo' }, { message: 'Bar' }])
<li v-for="(item, index) in items">
{{ parentMessage }} - {{ index }} - {{ item.message }}
</li>
输出结果:
-
Parent - 0 - Foo
-
Parent - 1 - Bar
作用域说明
v-for 的作用域类似于 JavaScript 的 forEach 方法:
const parentMessage = 'Parent'
const items = [
/* ... */
]
items.forEach((item, index) => {
// 可以访问外层的 parentMessage
// item 和 index 只在这个作用域可用
console.log(parentMessage, item.message, index)
})
使用解构
<li v-for="{ message } in items">
{{ message }}
</li>
<!-- 有索引时 -->
<li v-for="({ message }, index) in items">
{{ message }} {{ index }}
</li>
多层嵌套
<li v-for="item in items">
<span v-for="childItem in item.children">
{{ item.message }} {{ childItem }}
</span>
</li>
使用 of 分隔符
<div v-for="item of items"></div>
对象遍历
基本对象遍历
const myObject = reactive({
title: 'How to do lists in Vue',
author: 'Jane Doe',
publishedAt: '2016-04-10'
})
<ul>
<li v-for="value in myObject">
{{ value }}
</li>
</ul>
带键名的遍历
<li v-for="(value, key) in myObject">
{{ key }}: {{ value }}
</li>
带索引的对象遍历
<li v-for="(value, key, index) in myObject">
{{ index }}. {{ key }}: {{ value }}
</li>
使用范围值
v-for 可以接受整数值,基于 1...n 的范围重复渲染:
<span v-for="n in 10">{{ n }}</span>
注意:n 的初值是从 1 开始而非 0。
在 <template> 上使用 v-for
可以在 <template> 标签上使用 v-for 渲染多个元素:
<ul>
<template v-for="item in items">
<li>{{ item.msg }}</li>
<li class="divider" role="presentation"></li>
</template>
</ul>
v-for 与 v-if
优先级问题
v-if 比 v-for 优先级更高,因此不能在同一元素上同时使用:
<!-- 错误示例 -->
<li v-for="todo in todos" v-if="!todo.isComplete">
{{ todo.name }}
</li>
解决方案
使用 <template> 标签包装:
<template v-for="todo in todos">
<li v-if="!todo.isComplete">
{{ todo.name }}
</li>
</template>
最佳实践
-
过滤列表:使用计算属性返回过滤后的列表
-
条件渲染列表:将 v-if 移至容器元素
通过 key 管理状态
为什么需要 key
Vue 默认使用"就地更新"策略,为了跟踪节点标识,需要提供唯一的 key:
<div v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">
<!-- 内容 -->
</div>
在 <template> 上使用 key
<template v-for="todo in todos" :key="todo.name">
<li>{{ todo.name }}</li>
</template>
key 的注意事项
-
key 应该是基础类型值(字符串或数字)
-
不要使用对象作为 key
-
推荐始终提供 key,除非迭代内容非常简单
在组件上使用 v-for
基本用法
<MyComponent v-for="item in items" :key="item.id" />
传递数据给组件
需要显式传递 props:
<MyComponent
v-for="(item, index) in items"
:item="item"
:index="index"
:key="item.id"
/>
数组变化侦测
变更方法
Vue 能够侦听以下数组变更方法:
-
push()
-
pop()
-
shift()
-
unshift()
-
splice()
-
sort()
-
reverse()
替换数组
使用非变更方法时,需要替换整个数组:
// items 是一个数组的 ref
items.value = items.value.filter((item) => item.message.match(/Foo/))
Vue 会智能地重用 DOM 元素,保证高效更新。
展示过滤或排序后的结果
使用计算属性
const numbers = ref([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
const evenNumbers = computed(() => {
return numbers.value.filter((n) => n % 2 === 0)
})
<li v-for="n in evenNumbers">{{ n }}</li>
在嵌套 v-for 中使用方法
const sets = ref([
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
])
function even(numbers) {
return numbers.filter((number) => number % 2 === 0)
}
<ul v-for="numbers in sets">
<li v-for="n in even(numbers)">{{ n }}</li>
</ul>
注意 reverse() 和 sort()
这些方法会变更原始数组,应该先创建副本:
// 错误做法
return numbers.reverse()
// 正确做法
return [...numbers].reverse()
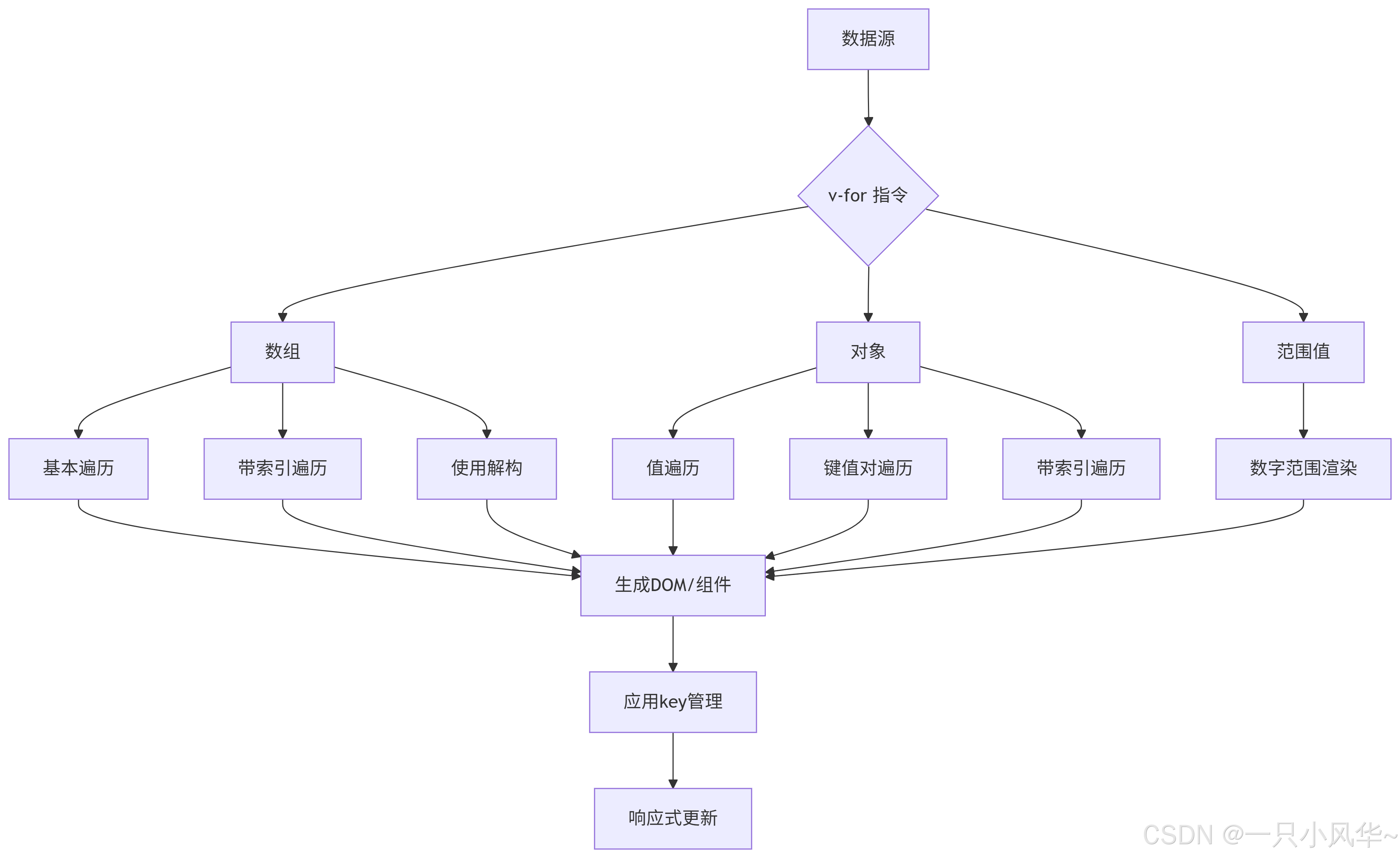
总结图表
v-for 用法总结
| 数据类型 | 语法示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 数组 | v-for="item in items" | 基本数组遍历 |
| 数组带索引 | v-for="(item, index) in items" | 带位置索引的遍历 |
| 对象 | v-for="value in object" | 遍历对象属性值 |
| 对象带键名 | v-for="(value, key) in object" | 带属性名的遍历 |
| 对象带索引 | v-for="(value, key, index) in object" | 带索引的对象遍历 |
| 范围值 | v-for="n in 10" | 基于1-n的范围渲染 |
v-for 工作流程
最佳实践总结
-
总是提供 key:为每个迭代项提供唯一的 key 属性
-
避免 v-if 和 v-for 一起使用:使用计算属性或包装元素替代
-
使用计算属性过滤/排序:避免在模板中处理复杂逻辑
-
注意数组变更方法:使用变更方法或正确替换数组
-
组件通信:在组件上使用 v-for 时要显式传递 props























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










