一,含有嵌套的表达式求值
题目:给你一个字符串类型的表达式,例如:3 + (3 - 2 * 4 * (1 + 1) ),请问答案是多少。
由简单到复杂,先看没有括号的情况下如何解决。
无括号
思路:
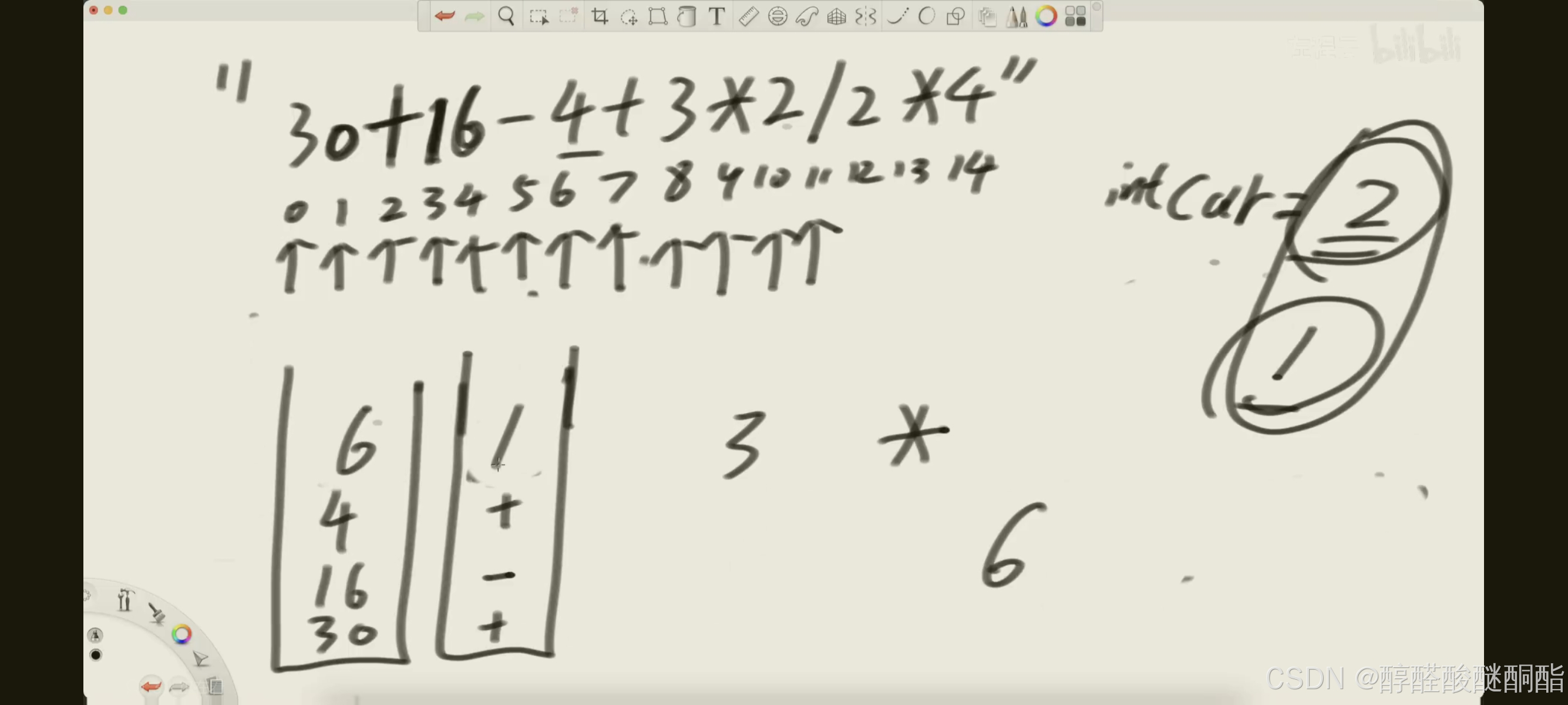
准备两个栈,让数字和运算符一一对应,通过指针或者迭代器来遍历识别数字和符号,如果符号栈顶已经是乘除,遇到数字。先弹出数字栈顶的数字与之运算,得到的结果又添加进数字栈中从而处理特殊运算符和优先级。
我的思路不一样,遇到符号就检查符号栈顶是不是乘除号,如果是就进行一次乘除运算。同时结束遍历后,还要检查一次。这些操作都是确保最后只有加减等最低级运算符。
上述过程中还要涉及翻转栈。
class NestedExpression
{
private:
int ans;
string str;
void calculate();
int getNum(string::iterator&);
public:
NestedExpression(string input);
int getAns();
};void NestedExpression::calculate()
{
auto current = str.begin();
int num = 0;
std::stack<int> num_stack;
std::stack<char> ope_stack;
// 辅助函数,用于执行一次乘除运算
auto performMulDiv = [&]() {
char op = ope_stack.top();
ope_stack.pop();
int right = num_stack.top();
num_stack.pop();
int left = num_stack.top();
num_stack.pop();
if (op == '*') {
num_stack.push(left * right);
} else if (op == '/') {
num_stack.push(left / right);
}
};
while (current != str.end())
{
if (isdigit(*current))
{
// 解析数字
num = getNum(current);
num_stack.push(num);
}
else if (*current == '+' || *current == '-' || *current == '*' || *current == '/')
{
// 只要遇到运算符,就检查栈顶,处理掉乘除符号,保证栈里面的优先级一样。
if(!ope_stack.empty() && (ope_stack.top() == '*' || ope_stack.top() == '/'))
{
performMulDiv();
}
// 将当前运算符压入栈
ope_stack.push(*current);
current++;
}
else
{
// 忽略空格或其他无效字符
current++;
}
}
// 处理栈中剩余的乘除法
while (!ope_stack.empty() && (ope_stack.top() == '*' || ope_stack.top() == '/'))
{
performMulDiv();
}
// 反转栈,以便正确处理加减法
std::stack<int> num_stack_reversed;
std::stack<char> ope_stack_reversed;
while (!num_stack.empty())
{
num_stack_reversed.push(num_stack.top());
num_stack.pop();
}
while (!ope_stack.empty())
{
ope_stack_reversed.push(ope_stack.top());
ope_stack.pop();
}
// 处理加减法
int result = num_stack_reversed.top();
num_stack_reversed.pop();
while (!ope_stack_reversed.empty())
{
char op = ope_stack_reversed.top();
ope_stack_reversed.pop();
int next = num_stack_reversed.top();
num_stack_reversed.pop();
if (op == '+')
{
result += next;
}
else if (op == '-')
{
result -= next;
}
}
// 最终结果
ans = result;
}
int NestedExpression::getNum(string::iterator& current)
{
int num = 0;
while (current != str.end() && isdigit(*current)) // 读取数字
{
num = num * 10 + (*current - '0');
current++;
}
return num;
}
NestedExpression::NestedExpression(string input) : str(input),ans(0)
{
}
int NestedExpression::getAns()
{
calculate();
return ans;
}
后面继续拓展,如果表达式里有括号怎么办?
有括号
首先,我们需要知道左括号只会出现在运算符号的后面,实际上括号所包裹的就相当于一个数字。就等同于每次压入数字栈的数字。当我们遇到左括号时,就进入递归,函数返回的值就是那个num。递归函数遇到右括号就停止。
使用类的成员变量来充当记录访问字符串位置的索引。
class NestedExpressionWithBracket
{
private:
int index;
string str;
int recursion();
public:
int getAns();
NestedExpressionWithBracket(string str);
};int NestedExpressionWithBracket::recursion()
{
int result = 0;
int cur = 0;
std::stack<int> nums;
std::stack<char> opes;
while (index != str.length() && str[index] != ')')
{
if (isdigit(str[index]))
{
cur = cur * 10 + (str[index] - '0'); // 处理多位数
}
else if (str[index] == ' ')
{
// 忽略空格
}
else if (str[index] == '(')
{
// 遇到左括号,递归计算括号内的表达式
index++;
cur = recursion();
}
else
{
// 处理当前数字
nums.push(cur);
cur = 0;
// 处理栈顶的乘法和除法
while (!opes.empty() && (opes.top() == '*' || opes.top() == '/'))
{
int right = nums.top();
nums.pop();
int left = nums.top();
nums.pop();
char ope = opes.top();
opes.pop();
if (ope == '*') nums.push(left * right);
else nums.push(left / right);
}
// 将当前运算符压入栈
opes.push(str[index]);
}
index++;
}
// 处理最后一个数字
nums.push(cur);
// 处理栈中剩余的乘法和除法
while (!opes.empty() && (opes.top() == '*' || opes.top() == '/'))
{
int right = nums.top();
nums.pop();
int left = nums.top();
nums.pop();
char ope = opes.top();
opes.pop();
if (ope == '*') nums.push(left * right);
else nums.push(left / right);
}
// 处理栈中剩余的加法和减法
result = nums.top();
nums.pop();
while (!opes.empty())
{
char ope = opes.top();
opes.pop();
int last = nums.top();
nums.pop();
if (ope == '+') result += last;
else if (ope == '-') result = last - result;
}
return result;
}
int NestedExpressionWithBracket::getAns()
{
return recursion();
}
NestedExpressionWithBracket::NestedExpressionWithBracket(string str) : str(str),index(0)
{
}
二,含有嵌套的字符串解码
题目
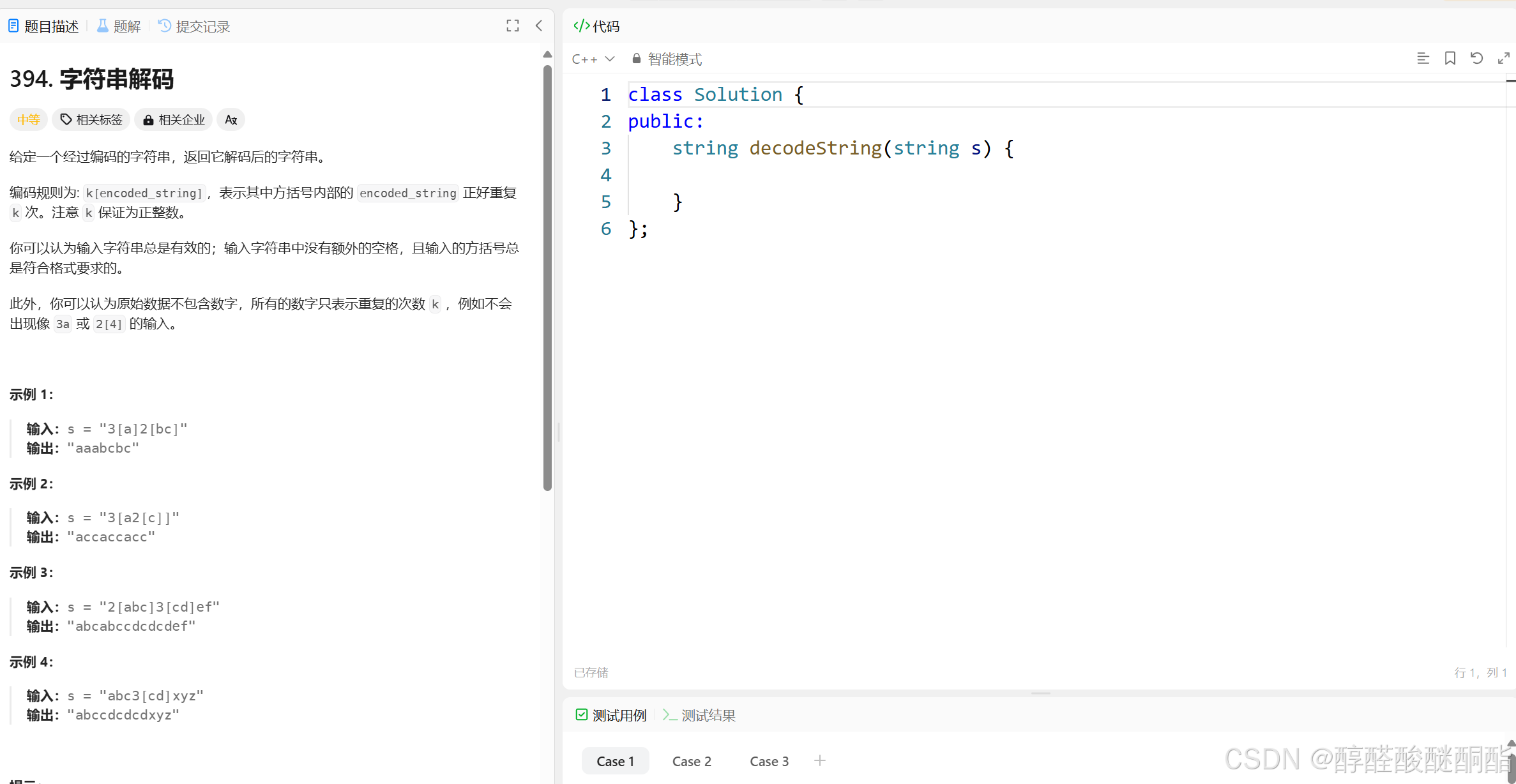
链接:394. 字符串解码
还是由简单到复杂,如果没有嵌套怎么处理
1,没有嵌套
class StringDecoding
{
private:
int index;
string str;
string decoded_str;
void append(int, string&, string);
void decode();
public:
StringDecoding(string& s);
string getAns();
};//StringDecoding
void StringDecoding::append(int times, string& src, string add)
{
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
src += add;
}
}
void StringDecoding::decode()
{
int num = 0;
string temp;
while (index != str.length())
{
if (isdigit(str[index]))
{
num = num * 10 + (str[index] - '0');
}
else
{
while (index != str.length()&&!isdigit(str[index]))
{
temp += str[index++];
}
append(num, decoded_str, temp);
num = 0;
temp.clear();
continue;
}
index++;
}
}
StringDecoding::StringDecoding(string& s) : str(s) ,index(0),decoded_str("")
{
}
string StringDecoding::getAns()
{
decode();
return decoded_str;
}2,有嵌套的
我们把括号内的也当作一个字符,遇到左括号就调用递归,让重复的字符串等于递归结果
class StringDecoding
{
private:
int index;
string str;
string decoded_str;
void append(int, string&, string);
void decode();
string decodeWithBracket();
public:
StringDecoding(string& s);
string getAns();
string getAnsWithBracket();
};string StringDecoding::decodeWithBracket()
{
int num = 0;
string result = "";
string temp = "";
while (index != str.length())
{
if (isdigit(str[index]))
{
num = num * 10 + (str[index++] - '0');
}
else if (str[index] == ')')
{
append(num, result, temp);
index++;
break;
}
else
{
if (str[index] == '(')
{
index++;
temp += decodeWithBracket();
}
else
{
while (index != str.length()&&!isdigit(str[index]))
{
if (str[index] == ')') break;
temp += str[index++];
}
}
if (num == 0) append(1, result, temp);
else append(num, result, temp);
num = 0;
temp.clear();
}
}
return result;
}
string StringDecoding::getAnsWithBracket()
{
decoded_str = decodeWithBracket();
return decoded_str;
}需要注意的一点是
while (index != str.length()&&!isdigit(str[index]))
{
if (str[index] == ')') break;
temp += str[index++];
}在解析获取需要重复的字符串时,特殊处理右括号。
3,带注释的代码
AI修改后的
// 定义一个名为StringDecoding的类,用于字符串解码操作
class StringDecoding {
private:
string str; // 待解码的原始字符串
int index; // 当前处理到的字符位置索引
string decoded_str; // 解码后的字符串结果
// 辅助函数:将字符串add追加到src中times次
void append(int times, string& src, string add) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
src += add; // 每次循环将add追加到src的末尾
}
}
public:
// 构造函数:初始化原始字符串str、索引index和解码结果字符串decoded_str
StringDecoding(string& s) : str(s), index(0), decoded_str("") {}
// 主解码函数:不处理带括号的情况
void decode() {
int num = 0; // 用于存储当前解析到的数字倍数
string temp; // 用于临时存储当前解析到的字符串片段
while (index != str.length()) { // 当索引未到达字符串末尾时,继续解析
if (isdigit(str[index])) { // 如果当前字符是数字
num = num * 10 + (str[index] - '0'); // 更新num为当前解析到的数字倍数
index++; // 移动到下一个字符
} else { // 如果当前字符不是数字
while (index != str.length() && !isdigit(str[index])) { // 继续读取直到遇到数字或字符串结束
temp += str[index++]; // 将当前字符加入temp
}
append(num, decoded_str, temp); // 将temp追加到decoded_str中num次
num = 0; // 重置num为0,以便处理下一个数字倍数
temp.clear(); // 清空temp,以便解析下一个字符串片段
}
}
}
// 解码函数:处理带括号的情况
string decodeWithBracket() {
int num = 0; // 用于存储当前解析到的数字倍数
string result = ""; // 用于存储当前括号内的解码结果
string temp = ""; // 用于临时存储当前解析到的字符串片段
while (index != str.length()) { // 当索引未到达字符串末尾时,继续解析
if (isdigit(str[index])) { // 如果当前字符是数字
num = num * 10 + (str[index++] - '0'); // 更新num为当前解析到的数字倍数
} else if (str[index] == ')') { // 如果当前字符是右括号
append(num, result, temp); // 将temp追加到result中num次
index++; // 移动到下一个字符
break; // 遇到右括号,结束当前括号内的解析
} else { // 如果当前字符不是数字且不是右括号
if (str[index] == '(') { // 如果当前字符是左括号
index++; // 移动到下一个字符(即括号内的第一个字符)
temp += decodeWithBracket(); // 递归调用decodeWithBracket解析括号内的内容,并将结果加入temp
} else { // 如果当前字符是普通字符
while (index != str.length() && !isdigit(str[index]) && str[index] != ')') { // 继续读取直到遇到数字、右括号或字符串结束
temp += str[index++]; // 将当前字符加入temp
}
}
if (num == 0) append(1, result, temp); // 如果num为0,说明没有倍数要求,直接将temp追加到result一次
else append(num, result, temp); // 否则,将temp追加到result中num次
num = 0; // 重置num为0,以便处理下一个数字倍数
temp.clear(); // 清空temp,以便解析下一个字符串片段
}
}
return result; // 返回括号内的解码结果
}
// 获取解码后的字符串结果(不处理带括号的情况)
string getAns() {
decode(); // 调用decode函数进行解码
return decoded_str; // 返回解码后的字符串
}
// 获取解码后的字符串结果(处理带括号的情况)
string getAnsWithBracket() {
decoded_str = decodeWithBracket(); // 调用decodeWithBracket函数进行解码
return decoded_str; // 返回解码后的字符串
}
};4,leetcode上测试结果
三,计算原子个数
题目

跟上面的类似,遇到括号就调用递归函数,计算括号内的表达式,只不过上面返回的是字符串,这道题是以哈希表的形式存储的括号内的结果,没有采用全局变量,使用了引用传递来收集数据。
思路
还是从简单到复杂,先思考没有括号的情况,再在其基础上进行添加遇到括号怎么处理。
代码
//头文件
class CountOfAtoms
{
private:
int index;
string str;
std::unordered_map<string, int> map;
std::unordered_map<string, int> temp;
void recursion();
void recursionWithBracket(std::unordered_map<string,int>&);
public:
CountOfAtoms();
CountOfAtoms(string& s);
~CountOfAtoms() = default;
void printCount();
void printCountWithBracket();
};//具体函数实现
void CountOfAtoms::recursion()
{
string name = "";
int cnt = 1;
while (index != str.length())
{
if (str[index] >= 'a'&&str[index] <= 'z')
{
name += str[index++];
}
//遇到大写字母就开始处理(清算)之前记录在name中的字符。统计这个原子的个数。
else if (str[index] >= 'A' && str[index] <= 'Z')
{
if (map.find(name) == map.end()&&name != "")
{
map[name] = cnt;
}
else if(name != "") map[name] += cnt;
name.clear();
cnt = 1;
name += str[index++];
}
else if (isdigit(str[index]))
{
int num = 0;
while (index != str.length()&&isdigit(str[index]))
{
num = num * 10 + (str[index] - '0');
index++;
}
cnt = num;
if (map.find(name) == map.end()) map[name] = cnt;
else map[name] += cnt;
name.clear();
cnt = 1;
}
}
if (map.find(name) == map.end()&&name != "")
{
map[name] = cnt;
}
else if (name != "") map[name] += cnt;
return;
}
void CountOfAtoms::recursionWithBracket(std::unordered_map<string,int>& nested_map)
{
string name = "";
int cnt = 1;
while (index != str.length())
{
if (str[index] >= 'a'&&str[index] <= 'z')
{
name += str[index++];
}
//遇到大写字母就开始处理(清算)之前记录在name中的字符。统计这个原子的个数。
else if (str[index] >= 'A' && str[index] <= 'Z')
{
if (nested_map.find(name) == nested_map.end()&&name != "")
{
nested_map[name] = cnt;
}
else if(name != "") nested_map[name] += cnt;
name.clear();
cnt = 1;
name += str[index++];
}
else if (isdigit(str[index]))
{
int num = 0;
while (index != str.length()&&isdigit(str[index]))
{
num = num * 10 + (str[index] - '0');
index++;
}
cnt = num;
if (nested_map.find(name) == nested_map.end()) nested_map[name] = cnt;
else nested_map[name] += cnt;
name.clear();
cnt = 1;
}
else if (str[index] == '(')
{
//先处理前面的原子个数
if (name != "" && nested_map.find(name) == nested_map.end())
{
nested_map[name] = cnt;
}
else if (name != "") nested_map[name] += cnt;
cnt = 1;
name.clear();
// 遇到左括号,递归计算括号内的表达式
std::unordered_map<string,int> sub_map;
index++;
recursionWithBracket(sub_map);
int num = 0;
while (index != str.length()&&isdigit(str[index]))
{
num = num * 10 + (str[index] - '0');
index++;
}
for (const auto& it : sub_map)
{
if (nested_map.find(it.first) == nested_map.end()) nested_map[it.first] = it.second * num;
else nested_map[it.first] += it.second * num;
}
}
else if (str[index] == ')')
{
index++;
if (name != "" && nested_map.find(name) == nested_map.end())
{
nested_map[name] = cnt;
}
else if (name != "") nested_map[name] += cnt;
return;
}
}
if (nested_map.find(name) == nested_map.end()&&name != "")
{
nested_map[name] = cnt;
}
else if (name != "") nested_map[name] += cnt;
return;
}
CountOfAtoms::CountOfAtoms() : index(0), str("")
{
}
CountOfAtoms::CountOfAtoms(string& s) : index(0),str(s)
{
}
void CountOfAtoms::printCount()
{
recursion();
for (const auto& it : map)
{
cout << "Atom " << it.first << " number " << it.second << endl;
}
return;
}
void CountOfAtoms::printCountWithBracket()
{
recursionWithBracket(map);
for (const auto& it : map)
{
cout << "Atom " << it.first << " number " << it.second << endl;
}
return;
}有点臃肿,其实很多重复部分可以单独封装成函数。
我让AI优化一下
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
std::string countOfAtoms(std::string formula) {
std::stack<std::unordered_map<std::string, int>> st;
st.push({});
int i = 0;
int n = formula.length();
while (i < n) {
if (std::isupper(formula[i])) {
std::string atom;
atom += formula[i++];
while (i < n && std::islower(formula[i])) {
atom += formula[i++];
}
int count = 0;
while (i < n && std::isdigit(formula[i])) {
count = count * 10 + (formula[i++] - '0');
}
if (count == 0) {
count = 1;
}
st.top()[atom] += count;
} else if (formula[i] == '(') {
st.push({});
i++;
} else if (formula[i] == ')') {
i++;
int count = 0;
while (i < n && std::isdigit(formula[i])) {
count = count * 10 + (formula[i++] - '0');
}
if (count == 0) {
count = 1;
}
auto subMap = st.top();
st.pop();
for (const auto& pair : subMap) {
st.top()[pair.first] += pair.second * count;
}
}
}
auto finalMap = st.top();
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> sortedAtoms(finalMap.begin(), finalMap.end());
std::sort(sortedAtoms.begin(), sortedAtoms.end(), [](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return a.first < b.first;
});
std::string result;
for (const auto& pair : sortedAtoms) {
result += pair.first;
if (pair.second > 1) {
result += std::to_string(pair.second);
}
}
return result;
}
};






















 2496
2496

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








