console.log(res)
return 2
},
err => {}
)
.then(
res => {
console.log(res)
},
err => {}
)
我们首先要实现一个 Promise 的类,这个类的构造函数会传入一个函数作为参数,并且向该函数传入 resolve 和 reject 两个方法。
初始化 Promise 的状态为 pending。
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.executor = executor
this.value = null
this.status = ‘pending’
const resolve = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value // 调用 resolve 后记录 resolve 的值
this.status = ‘fulfilled’ // 调用 resolve 扭转 promise 状态
}
}
const reject = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value // 调用 reject 后记录 reject 的值
this.status = ‘rejected’ // 调用 reject 扭转 promise 状态
}
}
this.executor(resolve, reject)
}
(2)接下来要实现 promise 对象上的 then 方法,then 方法会传入两个函数作为参数,分别作为 promise 对象 resolve 和 reject 的处理函数。
这里要注意三点:
- then 函数需要返回一个新的 promise 对象
- 执行 then 函数的时候这个 promise 的状态可能还没有被扭转为 fulfilled 或 rejected
- 一个 promise 对象可以同时多次调用 then 函数
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.executor = executor
this.value = null
this.status = ‘pending’
this.onFulfilledFunctions = [] // 存放这个 promise 注册的 then 函数中传的第一个函数参数
this.onRejectedFunctions = [] // 存放这个 promise 注册的 then 函数中传的第二个函数参数
const resolve = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value
this.status = ‘fulfilled’
this.onFulfilledFunctions.forEach(onFulfilled => {
onFulfilled() // 将 onFulfilledFunctions 中的函数拿出来执行
})
}
}
const reject = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value
this.status = ‘rejected’
this.onRejectedFunctions.forEach(onRejected => {
onRejected() // 将 onRejectedFunctions 中的函数拿出来执行
})
}
}
this.executor(resolve, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const self = this
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
/**
- 当 promise 的状态仍然处于 ‘pending’ 状态时,需要将注册 onFulfilled、onRejected 方法放到 promise 的 onFulfilledFunctions、onRejectedFunctions 备用
*/
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.onFulfilledFunctions.push(() => {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
resolve(thenReturn)
})
this.onRejectedFunctions.push(() => {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
resolve(thenReturn)
})
})
} else if (this.status === ‘fulfilled’) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
resolve(thenReturn)
})
} else {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
resolve(thenReturn)
})
}
}
}
对于以上完成的 MyPromise 进行测试,测试代码如下
const p = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(1)
}, 1000)
})
p.then(res => {
console.log(‘first then’, res)
return res + 1
}).then(res => {
console.log(‘first then’, res)
})
p.then(res => {
console.log(second then, res)
return res + 1
}).then(res => {
console.log(second then, res)
})
/**
- 输出结果如下:
- first then 1
- first then 2
- second then 1
- second then 2
*/
(3)在 promise 相关的内容中,有一点常常被我们忽略,当 then 函数中返回的是一个 promise 应该如何处理?
考虑如下代码:
// 使用正确的 Promise
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
.then(res => {
console.log(‘外部 promise’)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(内部 promise)
})
})
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
/**
- 输出结果如下:
- 外部 promise
- 内部 promise
*/
通过以上的输出结果不难判断,当 then 函数返回的是一个 promise 时,promise 并不会直接将这个 promise 传递到下一个 then 函数,而是会等待该 promise resolve 后,将其 resolve 的值,传递给下一个 then 函数,找到我们实现的代码的 then 函数部分,做以下修改:
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const self = this
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.onFulfilledFunctions.push(() => {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
// 当返回值为 promise 时,等该内部的 promise 状态扭转时,同步扭转外部的 promise 状态
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
})
this.onRejectedFunctions.push(() => {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
// 当返回值为 promise 时,等该内部的 promise 状态扭转时,同步扭转外部的 promise 状态
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
})
})
} else if (this.status === ‘fulfilled’) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
// 当返回值为 promise 时,等该内部的 promise 状态扭转时,同步扭转外部的 promise 状态
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
})
} else {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
// 当返回值为 promise 时,等该内部的 promise 状态扭转时,同步扭转外部的 promise 状态
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
})
}
}
(4) 之前的 promise 实现代码仍然缺少很多细节逻辑,下面会提供一个相对完整的版本,注释部分是增加的代码,并提供了解释。
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.executor = executor
this.value = null
this.status = ‘pending’
this.onFulfilledFunctions = []
this.onRejectedFunctions = []
const resolve = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value
this.status = ‘fulfilled’
this.onFulfilledFunctions.forEach(onFulfilled => {
onFulfilled()
})
}
}
const reject = value => {
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
this.value = value
this.status = ‘rejected’
this.onRejectedFunctions.forEach(onRejected => {
onRejected()
})
}
}
this.executor(resolve, reject)
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const self = this
if (typeof onFulfilled !== ‘function’) {
// 兼容 onFulfilled 未传函数的情况
onFulfilled = function() {}
}
if (typeof onRejected !== ‘function’) {
// 兼容 onRejected 未传函数的情况
onRejected = function() {}
}
if (this.status === ‘pending’) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.onFulfilledFunctions.push(() => {
try {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
} catch (err) {
// catch 执行过程的错误
reject(err)
}
})
this.onRejectedFunctions.push(() => {
try {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
} catch (err) {
// catch 执行过程的错误
reject(err)
}
})
})
} else if (this.status === ‘fulfilled’) {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
const thenReturn = onFulfilled(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
} catch (err) {
// catch 执行过程的错误
reject(err)
}
})
} else {
return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
const thenReturn = onRejected(self.value)
if (thenReturn instanceof MyPromise) {
thenReturn.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(thenReturn)
}
} catch (err) {
// catch 执行过程的错误
reject(err)
}
})
}
}
}
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数同学面临毕业设计项目选题时,很多人都会感到无从下手,尤其是对于计算机专业的学生来说,选择一个合适的题目尤为重要。因为毕业设计不仅是我们在大学四年学习的一个总结,更是展示自己能力的重要机会。
因此收集整理了一份《2024年计算机毕业设计项目大全》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助提高效率,同时减轻大家的负担。
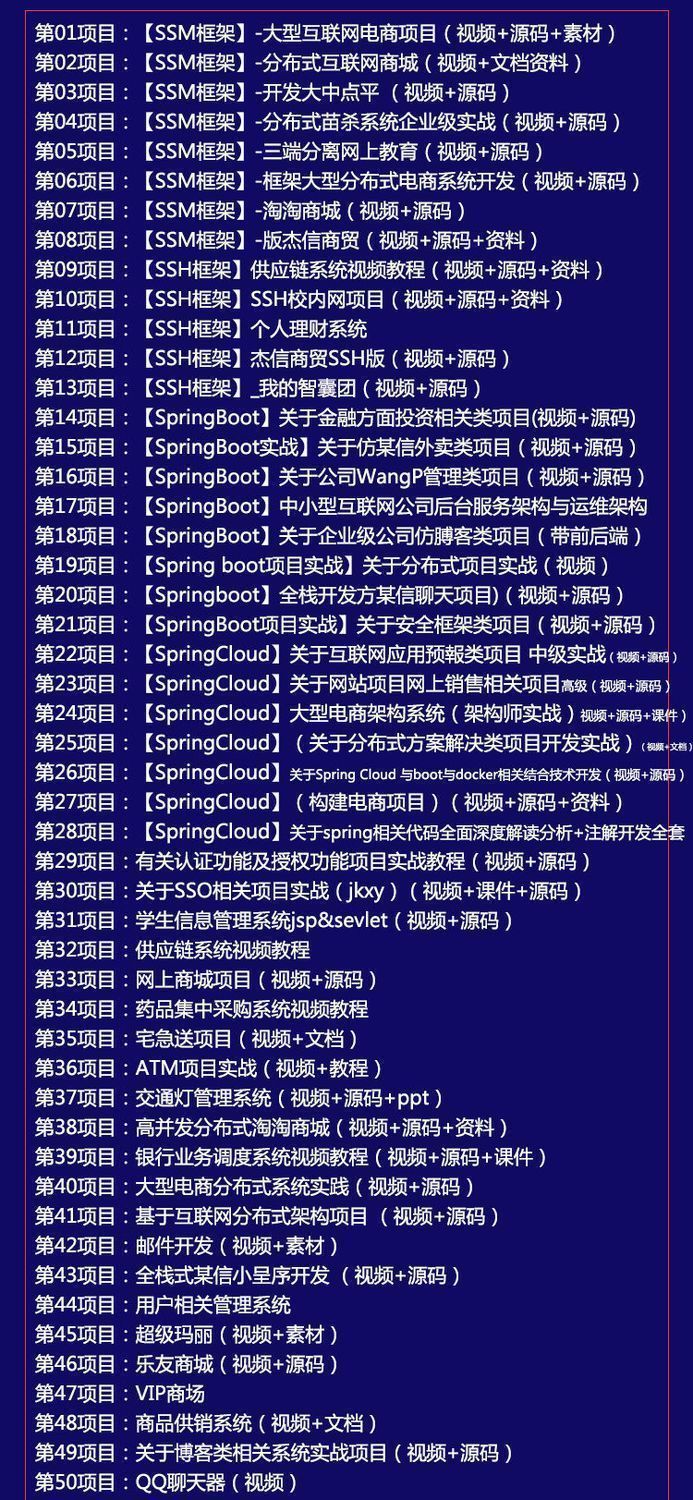
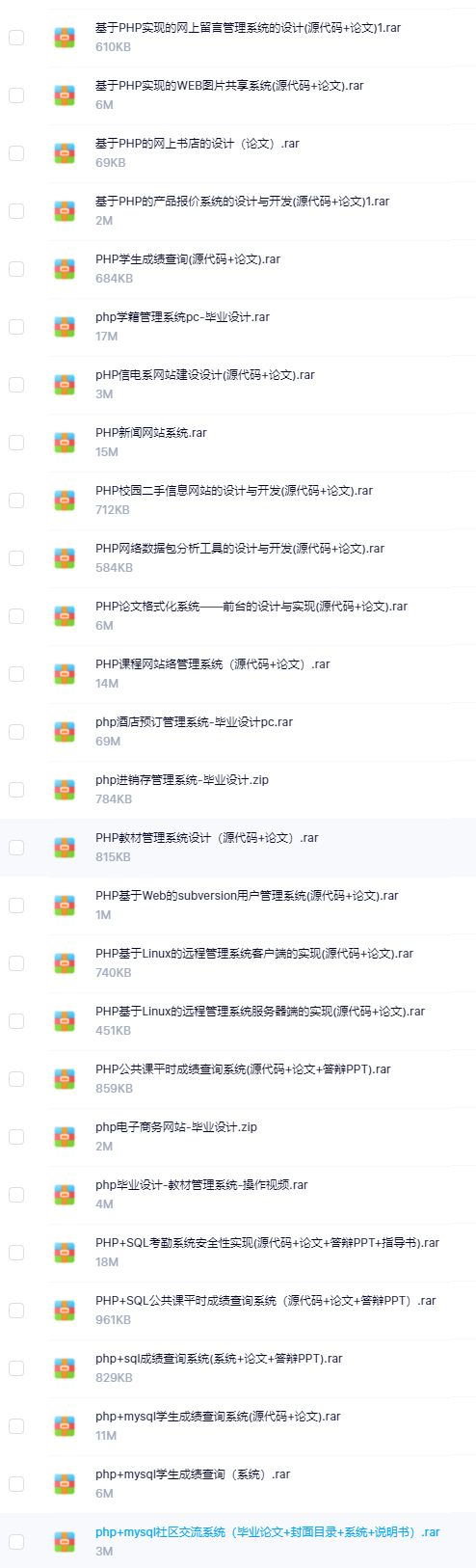
既有Java、Web、PHP、也有C、小程序、Python等项目供你选择,真正体系化!
由于项目比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含素材文档、项目源码、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加VX:vip1024c (备注项目大全获取)

[外链图片转存中…(img-5BsbzGCi-1712525814472)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-jfCvgEIX-1712525814473)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-io0zLEIr-1712525814473)]
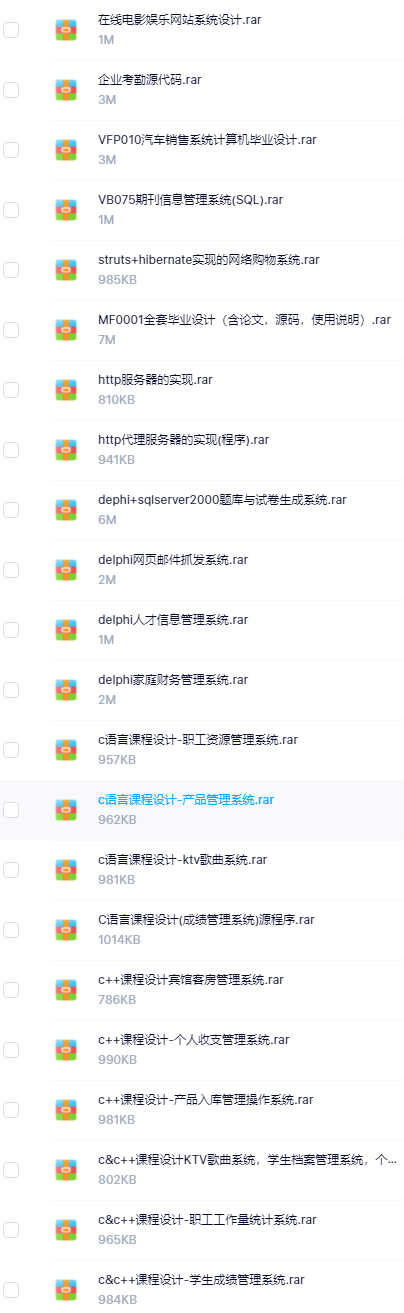
既有Java、Web、PHP、也有C、小程序、Python等项目供你选择,真正体系化!
由于项目比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含素材文档、项目源码、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加VX:vip1024c (备注项目大全获取)
[外链图片转存中…(img-iYzJmlgq-1712525814473)]





 本文详细描述了如何创建一个自定义Promise类,包括构造函数中接收的executor函数以及then方法的实现,强调了处理then函数返回的Promise时的同步策略。通过实例和测试代码展示了如何正确处理内部Promise的resolve和reject。
本文详细描述了如何创建一个自定义Promise类,包括构造函数中接收的executor函数以及then方法的实现,强调了处理then函数返回的Promise时的同步策略。通过实例和测试代码展示了如何正确处理内部Promise的resolve和reject。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








