文章目录
栈是什么
栈是一种特殊的线性表只允许在一端进行插入和删除元素操作,进行元素的操作的一端是栈顶
存储方式:
先进后出(后进先出),当程序运行起来时,数据就会被压进栈,当被调用或使用时,数据就会被压出栈
举个例子:就相当于你坐电梯,先进去的人一般都是最后出来,也可以是先吃进去的食物最后吐出来
栈的实现
栈的实现可以用数组或链表,但我们这里
**优先选择数组**,因为数组在尾插入和删除数据都比较方便,链表需要你从头开始找尾,代价比较大
动态实现
对于栈的实现的接口函数,我们传一级指针就够了,我们通过结构体指针去访问结构体里的成员变量就可以了,并不需要通过指向结构体指针的指针去访问
自定义一个结构体栈
需要有数组的首元素地址,栈顶,和栈的容量
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;//数组首元素地址
STDataType top;
STDataType capacity;
}ST;
动态扩容
栈满了就要扩容,realloc出来的需要链接到栈的后面
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) //如果满了就要增容
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;//按倍数增容
STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);//数组的首元素
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail!");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
初始化栈和销毁栈
一定要断言
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;//top=0是指向栈顶的下一个,先给值后++,top=-1,先加加后给值
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
入栈(插入数据)
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//省略了扩容
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//栈为空,就不要再删了
ps->top--;
}
栈的大小和返回栈顶元素
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;//top是指向top的下一个,所以top就是size
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//栈为空,防止越界
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//同理
}
判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;//逻辑真假;如果栈顶为空就返回true,否则返回false
}
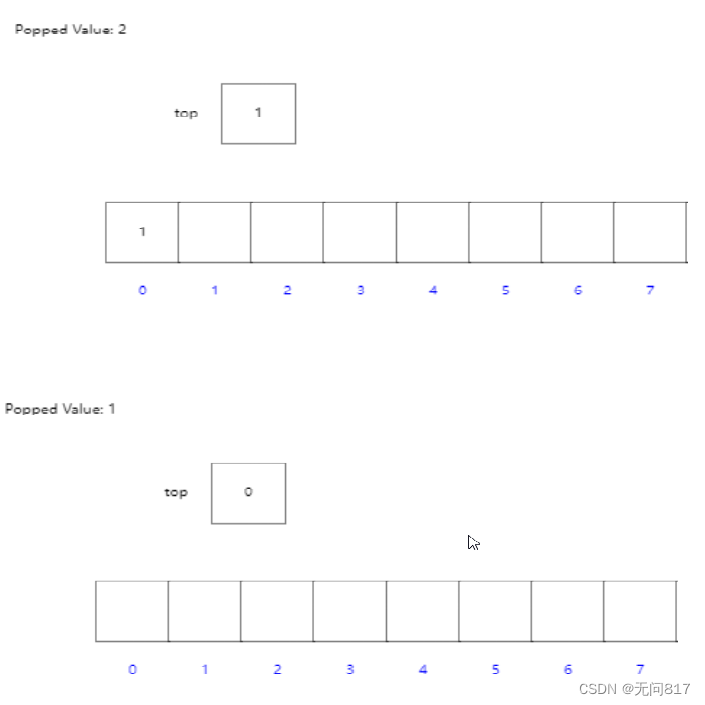
演示
把1和2压入栈,并依次压出栈

队列
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先
进先出
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
相当于你去排队,先去的总是先完成

优先选择链表实现,数组的话队头的数据要出的话需要的成本大

队列的实现
自定义结构体
要入的数据,结构体指针next,头尾指针,
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
struct QueueNode* head;
struct QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
初始化队列和销毁队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur =pq->head ;//保存下队头,直接free,会造成野指针的解引用
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;//让next成为新的头
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
判断是否为空队列
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;//逻辑判断
}
插入数据
如果队列为空,把新创建的节点作为头和尾节点
不为空就链到尾节点,让新节点成为新的尾
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
struct QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
删除数据,出队
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));//断言不为队列空
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
if (pq->head == NULL)//如果没有这步,在访问尾指针的数据时,会造成野指针访问
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
}
返回队头和队尾的元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
返回队列的元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
int n = 0;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
n++;
}
return n;
}
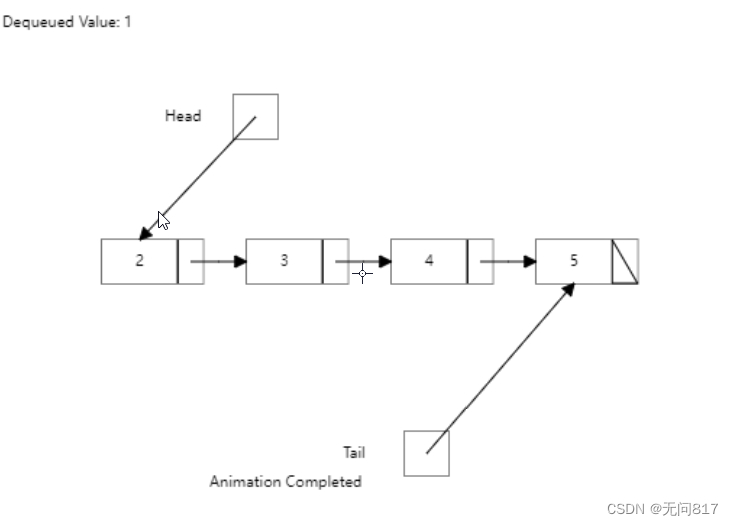
演示


源码
stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;//数组首元素地址
STDataType top;
STDataType capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps,STDataType x);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;//top=0是指向栈顶的下一个,先给值后++,top=-1,先加加后给值后++
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) //如果满了就要增容
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;//按倍数增容
STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);//数组的首元素
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail!");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//栈为空,就不要再删了
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//栈为空,防止越界
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//同理
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;//top是指向top的下一个,所以top就是size
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;//逻辑真假;如果栈顶为空就返回true,否则返回false
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Stack.h"
void test2()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
}
void test1()
{
ST st;//定义一个结构体指针变量
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
StackPush(&st, 5);
StackPush(&st, 6);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))//遍历
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));//栈的遍历要出栈了之后pop掉然后再出栈
StackPop(&st);
}
StackDestroy(&st);//pop后也要销毁
}
int main()
{
test1();
//test2();
return 0;
}
queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
struct QueueNode* head;
struct QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur =pq->head ;
while (cur != NULL)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;//逻辑判断
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
struct QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
if (pq->head == NULL)//如果没有这步,会造成野指针访问,在访问尾指针的数据时
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
int n = 0;
while (cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
n++;
}
return n;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"queue.h"
void QueueTest1()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePop(&q);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
QDataType Front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", Front);
QueuePop(&q);
}
//QueuePop(&q);
//QueuePop(&q);
//QueuePop(&q);
// printf("%d\n", QueueBack);
// printf("%d\n", QueueFront);
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
QueueTest1();
return 0;





















 1483
1483

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








