资源路由
1. 资源路由,采用固定的常用方法来实现简化URL的功能;
Route::resource('ads', 'Address');
2. 系统提供了一个命令,方便开发者快速生成一个资源控制器;
php think make:controller Blog
3. 从生成的多个方法,包含了显示、增删改查等多个操作方法;
4. 在路由定义文件下创建一个资源路由,资源名称可自定义;
Route::resource('blog', 'Blog');
5. 这里的blog表示资源规则名,Blog表示路由的访问路径;
6. 资源路由注册成功后,会自动提供以下方法,无须手动注册;
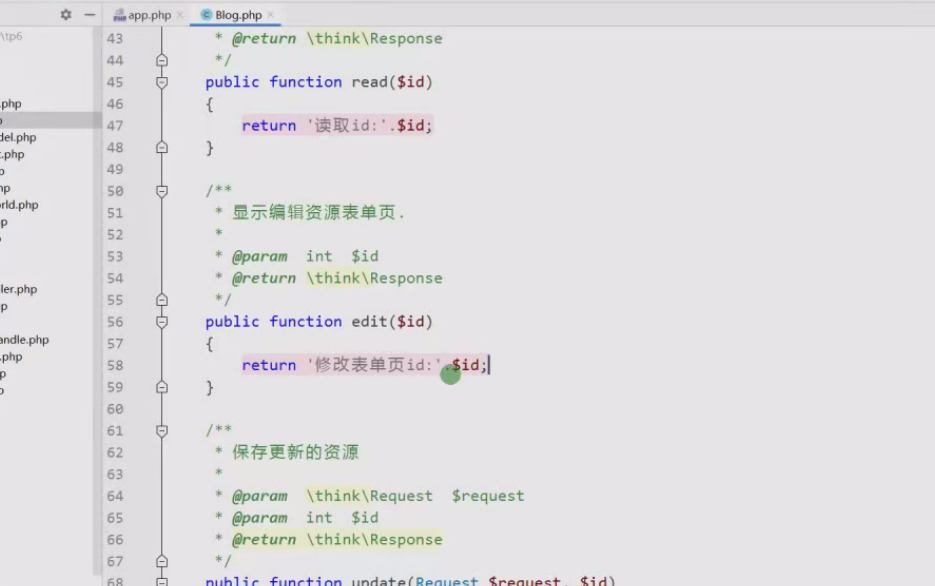
7. GET访问模式下:index(blog),create(blog/create),read(blog/:id) edit(blog/:id/edit)
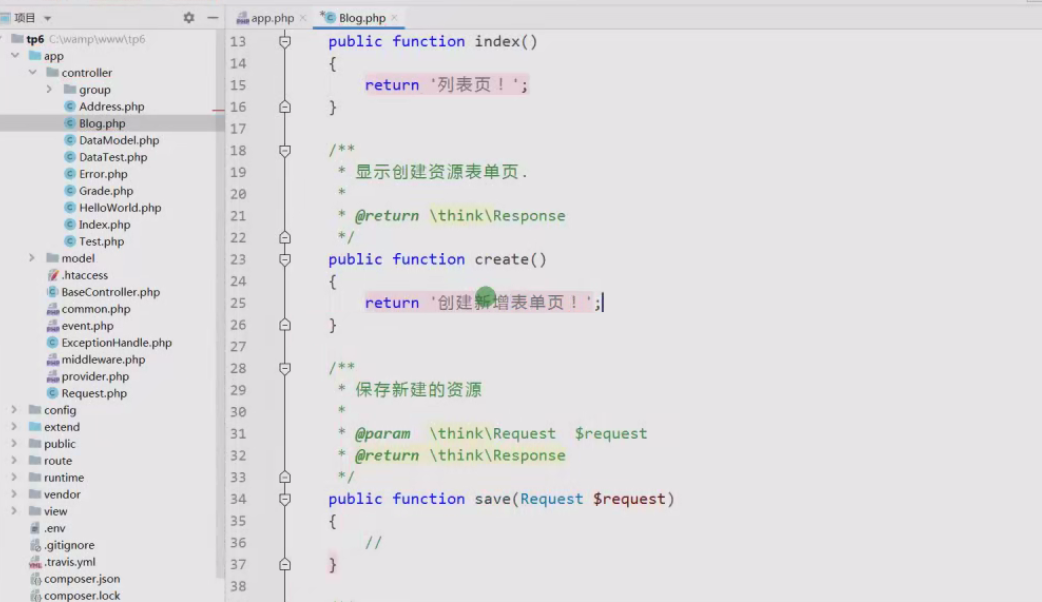
8. POST 访问模式下:save(blog);
9. PUT 方式模式下:update(blog/:id);
10. DELETE 方式模式下:delete(blog/:id);
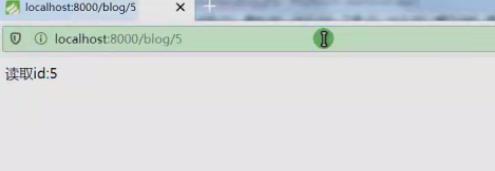
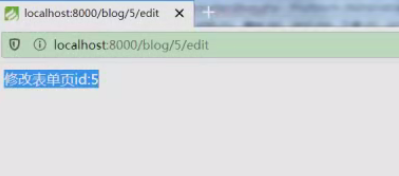
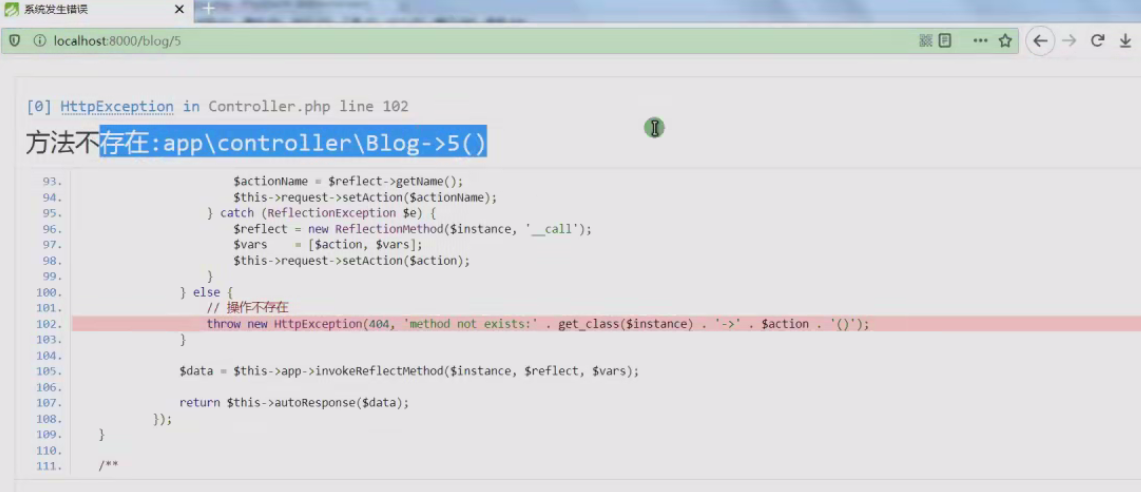
网址驶入/blog/5就会自动判断read方法。
http://localhost:8000/blog/ (index)
http://localhost:8000/blog/5 (read)
http://localhost:8000/blog/5/edit (edit)
11. 对于POST,是新增,一般是表单的POST提交,而PUT和DELETE用AJAX访问;
12. 将跨域提交那个例子修改成.ajax,其中type设置为DELETE即可访问到;
$.ajax({
type : "DELETE",
url : "http://localhost:8000/blog/10",
success : function (res) {
console.log(res);
}
});
13. 默认的参数采用id名称,如果你想别的,比如:blog_id,则:
->vars(['blog'=>'blog_id']); //相应的delete($blog_id)
14.也可以通过only()方法限定系统提供的资源方法,比如:
->only(['index','save','create'])
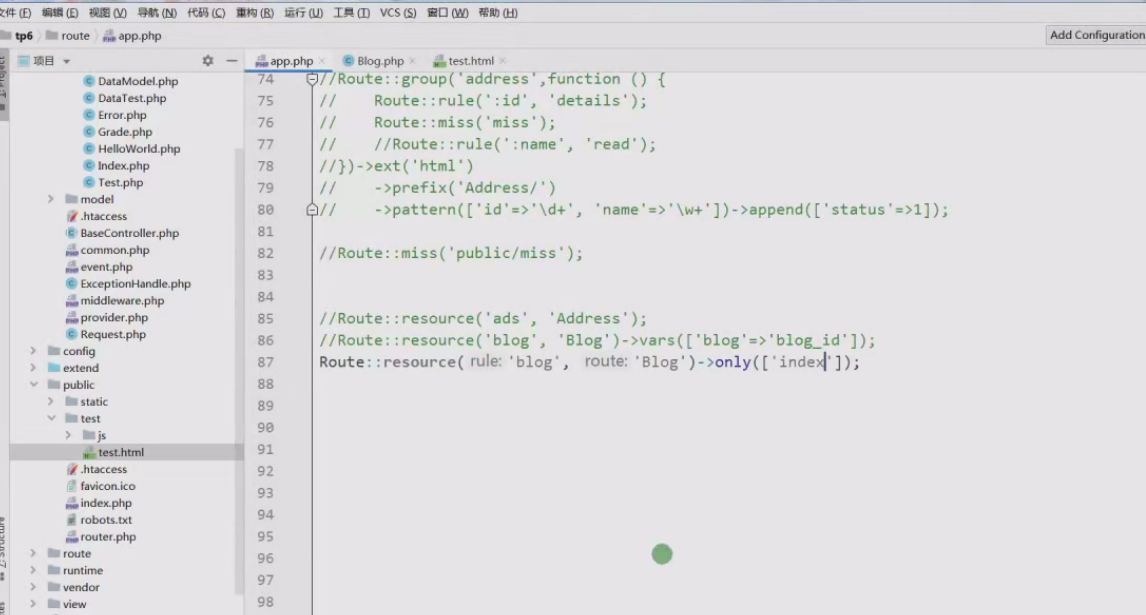
only()是指定方法,比如/blog/5的话就会报错,因为没有让read方法允许。
15.还可以通过except()方法排除系统提供的资源方法,比如:
->except(['read','delete','update'])
16.使用rest()方法,更改系统给予的默认方法,1.请求方式;2.地址;3.操作;
Route::rest('create',['GET','/:id/add', 'add']);
//批量
Route::rest([
'save' =>['POST', '', 'store'],
'update' => ['PUT', '/:id', 'save'],
'delete' => ['DELETE','/:id', 'destory'],
]);
这种必须得放在Route的最前面
然后'create'就是请求方法,'/:id:add'就是控制器,'add'就是方法。
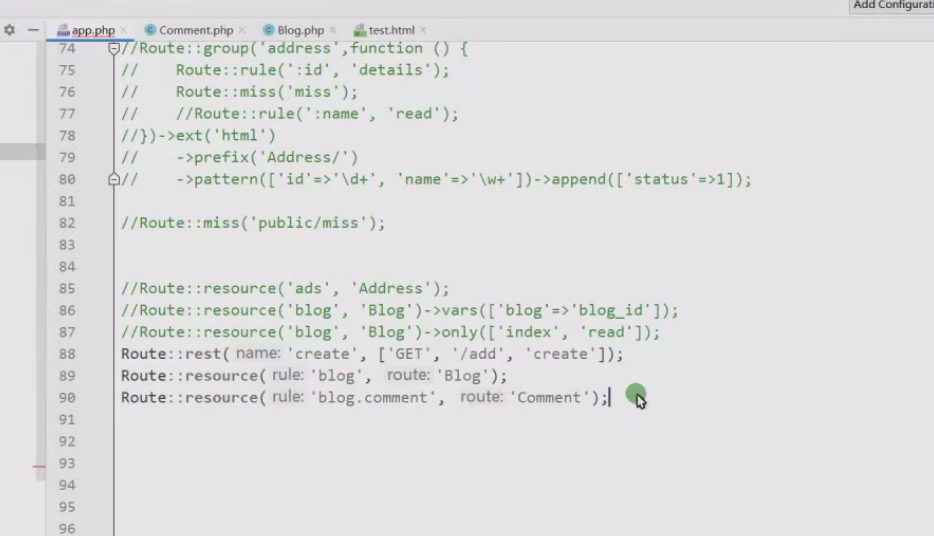
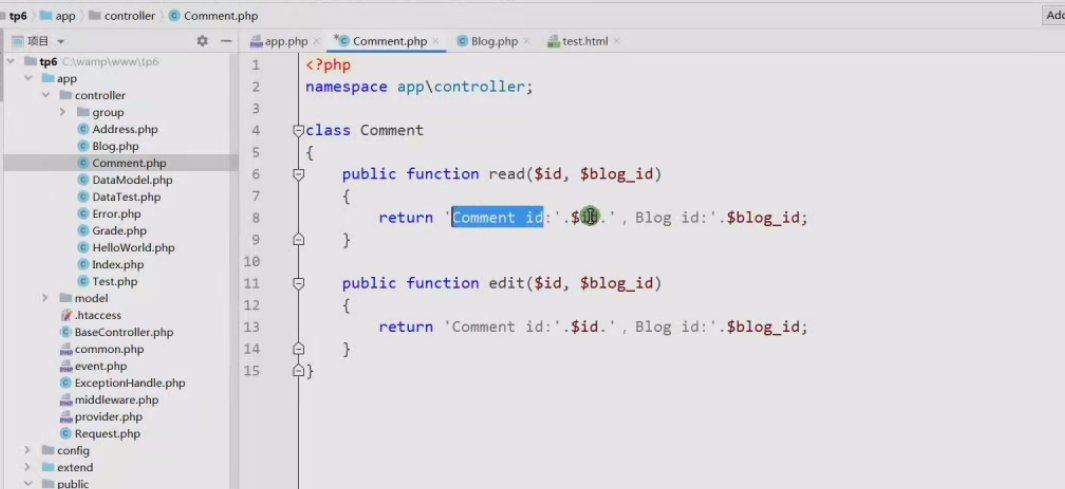
17.使用嵌套资源路由,可以让上级资源对下级资源进行操作,创建Comment资源;
class Comment
{
publicfunction read($id,$blog_id)
{
return'Comment id:'.$id.',Blog id:'.$blog_id;
}
publicfunction edit($id,$blog_id)
{
return'Comment id:'.$id.',Blog id:'.$blog_id;
}
}
18.使用嵌套资源路由,可以让上级资源对下级资源进行操作,创建Comment资源;
Route::resource('blog.comment','Comment');
19.资源嵌套生成的路由规则如下:
http://localhost:8000/blog/:blog_id/comment/:id http://localhost:8000/blog/:blog_id/comment/:id/edit
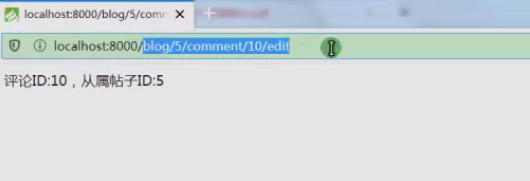
20.嵌套资源生成的上级资源默认id为:blog_id,可以通过vars更改;
Route::resource('blog.comment','Comment')->vars(['blog'=>'blogid']);




















 226
226

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








